Java编程技巧之样板代码
- 2026-01-22 05:14:53

庆历中,有布衣毕昇,又为活版。其法用胶泥刻字,薄如钱唇,每字为一印,火烧令坚……若止印三、二本,未为简易;若印数十百千本,则极为神速。
try (BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(fileName))) {String line;while (Objects.nonNull(line = reader.readLine())) {// 处理一行...}} catch (IOException e) {String message = String.format("读取文件(%s)异常", fileName);log.error(message, e);throw new ExampleException(message, e);}
提供一种标准样例:可以用于新人学习,能够快速上手并使用;
提供一种解决方案:遇到类似案例时,可以快速利用该方案进行解决;
有助于不断积累经验:当发现一种样例代码时,都会不断地进行优化,力求达到最佳样例;
有助于提高代码质量:样板代码必然通过了时间考验,存在BUG和出错的几率相对比较低;
有助于提高编码速度:利用样板代码编码,只是复制粘贴修改代码,编码速度大幅提高;
有助于统一代码样式:心中有了样板代码,就能保证每次都写出统一样式的代码。
复制粘贴生成代码:利用复制粘贴样板代码,用好了编码会事半功倍。
用文本替换生成代码:利用文本替换生成代码,可以很快生成一段新代码。
用Excel公式生成代码:把样板代码先公式化,传入不同的参数,生成不同的代码。
用工具或插件生成代码:很多开发工具或插件都提供一些工具生成代码,比如:生成构造方法、重载基类/接口方法、生成Getter/Setter方法、生成toString方法、生成数据库访问方法……能够避免很多手敲代码。
用代码生成代码:用代码生成代码,就是自己编写代码,按照自己的样板代码格式生成代码。
public class User {private Long id;...public Long getId() {return id;}public void setId(Long id) {this.id = id;}...}
@Getter@Setterpublic class User {private Long id;...}
/** 查询公司员工 */public List<EmployeeDO> queryEmployee(Long companyId) {try (Connection connection = tddlDataSource.getConnection();PreparedStatement statement = connection.prepareStatement(QUERY_EMPLOYEE_SQL)) {statement.setLong(1, companyId);try (ResultSet result = statement.executeQuery()) {List<EmployeeDO> employeeList = new ArrayList<>();while (result.next()) {EmployeeDO employee = new EmployeeDO();employee.setId(result.getLong(1));employee.setName(result.getString(2));...employeeList.add(employee);}return employeeList;}} catch (SQLException e) {String message = String.format("查询公司(%s)用户异常", companyId);log.error(message, e);throw new ExampleException(message, e);}}
@Mapperpublic interface UserDAO {List<EmployeeDO> queryEmployee(@Param("companyId") Long companyId);}
<mapper namespace="com.example.repository.UserDAO"><select id="queryEmployee" resultType="com.example.repository.UserDO">select id, name...from t_userwhere company_id = #{companyId}</select></mapper>
try (BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(fileName))) {String line;while (Objects.nonNull(line = reader.readLine())) {// 处理一行...}} catch (IOException e) {String message = String.format("读取文件(%s)异常", fileName);log.error(message, e);throw new ExampleException(message, e);}
/** 定义方法 */public static void readLine(String fileName, Consumer<String> lineConsumer) {try (BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(fileName))) {String line;while (Objects.nonNull(line = reader.readLine())) {lineConsumer.accept(line);}} catch (IOException e) {String message = String.format("读取文件(%s)异常", fileName);log.error(message, e);throw new ExampleException(message, e);}}// 使用代码readLine("example.txt", line -> {// 处理一行...});
/** 例子工具类 */public class ExampleHelper {/** 常量值 */public final static int CONST_VALUE = 123;/** 求和方法 */public static int sum(int a, int b) {return a + b;}}

public class MyExampleHelper extends ExampleHelper {/** 常量值 */public static final int CONST_VALUE = 321;/** 求和方法 */public static int sum(int a, int b) {return a * b;}}
int value = ExampleHelper.CONST_VALUE;int sum = ExampleHelper.sum(1, 2);
ExampleHelper exampleHelper = new ExampleHelper();int value = exampleHelper.CONST_VALUE;int sum = exampleHelper.sum(1, 2);
/** 例子工具类 */public final class ExampleHelper {/** 常量值 */public static final int CONST_VALUE = 123;/** 构造方法 */private ExampleHelper() {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}/** 求和方法 */public static int sum(int a, int b) {return a + b;}}
/** 例子枚举类 */public enum ExampleEnum {/** 枚举相关 */ONE(1, "one(1)"),TWO(2, "two(2)"),THREE(3, "two(3)");/** 属性相关 */private Integer value;private String desc;/** 构造方法 */private ExampleEnum(Integer value, String desc) {this.value = value;this.desc = desc;}/** 获取取值 */public Integer getValue() {return value;}/** 获取描述 */public String getDesc() {return desc;}}

/** 修改取值 */public static void modifyValue() {for (ExampleEnum value : values()) {value.value++;}}
/** 例子枚举类 */public enum ExampleEnum {/** 枚举相关 */ONE(1, "one(1)"),TWO(2, "two(2)"),THREE(3, "two(3)");/** 字段相关 */private final int value;private final String desc;/** 构造方法 */ExampleEnum(int value, String desc) {this.value = value;this.desc = desc;}/** 获取取值 */public int getValue() {return value;}/** 获取描述 */public String getDesc() {return desc;}}
必须具有一个无参的构造方法;
所有属性字段必须是私有的;
所有属性字段必须通过遵循一种命名规范的Getter/Setter方法开放出来。
/** 用户类 */public class User {private Long id;private String name;private Integer age;private String desc;public Long getId() {return id;}public void setId(Long id) {this.id = id;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public Integer getAge() {return age;}public vid setAge(Integer age) {this.age = age;}public String getDesc() {return desc;}public void setDesc(String desc) {this.desc = desc;}}
注意:也可以通过Lombok的@Getter/@Setter注解生成对应个Getter/Setter方法。
User user = new User();user.setId(1L);user.setName("alibaba");user.setAge(102);user.setDesc("test");verifyUser(user);
代码非常简单,只有私有属性字段及其公有Getter/Setter方法;
赋值对象代码可读性较强,明确地知道哪个属性字段对应哪个值;
非常简单实用,被广泛地用于HSF、Dubbo、MyBatis等中间件。
由于可以通过Setter方法设置属性字段,所以不能定义为不可变类;
由于每个字段分别设置,所以不能保证字段必填,必须设置完毕后进行统一验证。
/** 用户类 */public final class User {private Long id;private String name;private Integer age;private String desc;public User(Long id, String name) {this(id, name, null);}public User(Long id, String name, Integer age) {this(id, name, age, null);}public User(Long id, String name, Integer age, String desc) {Assert.notNull(id, "标识不能为空");Assert.notNull(name, "名称不能为空");this.id = id;this.name = name;this.age = age;this.desc = desc;}public Long getId() {return id;}public String getName() {return name;}public Integer getAge() {return age;}public String getDesc() {return desc;}}
User user1 = new User(1L, "alibaba");User user2 = new User(1L, "alibaba", 102, "test");
初始化对象代码简洁,只有简单的一行代码;
可以定义为不可变类,初始化后属性字段值不可变更;
可以在构造方法内进行不可空验证。
重载构造方法数量过多,无法覆盖必填字段和非必填字段的所有组合;
初始化对象代码可读性差,无法看出哪个属性字段对应哪个值;
如果删除某个字段,初始化对象代码可能不会报错,导致出现赋值错误问题。
/** 用户类 */public final class User {private Long id;private String name;private Integer age;private String desc;private User(Builder builder) {this.id = builder.id;this.name = builder.name;this.age = builder.age;this.desc = builder.desc;}public static Builder newBuilder(Long id, String name) {return new Builder(id, name);}public Long getId() {return id;}public String getName() {return name;}public Integer getAge() {return age;}public String getDesc() {return desc;}public static class Builder {private Long id;private String name;private Integer age;private String desc;private Builder(Long id, String name) {Assert.notNull(id, "标识不能为空");Assert.notNull(name, "名称不能为空");this.id = id;this.name = name;}public Builder age(Integer age) {this.age = age;return this;}public Builder desc(String desc) {this.desc = desc;return this;}public User build() {return new User(this);}}}
注意:可以采用Lombok的@Builder注解简化代码。
User user = User.newBuilder(1L, "alibaba").age(102).desc("test").build();明确了必填参数和可选参数,在构造方法中进行验证;
可以定义为不可变类,初始化后属性字段值不可变更;
赋值代码可读性较好,明确知道哪个属性字段对应哪个值;
支持链式方法调用,相比于调用Setter方法,代码更简洁。
代码量较大,多定义了一个Builder类,多定义了一套属性字段,多实现了一套赋值方法;
运行效率低,需要先创建Builder实例,再赋值属性字段,再创建目标实例,最后拷贝属性字段。
/** 例子工具类 */public final class ExampleHelper {/** 常量值列表 */public static final List<Integer> CONST_VALUE_LIST = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3);/** 常量值集合 */public static final Set<Integer> CONST_VALUE_SET = new HashSet<>(Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3));/** 常量值映射 */public static final Map<Integer, String> CONST_VALUE_MAP;static {CONST_VALUE_MAP = new HashMap<>(MapHelper.DEFAULT);CONST_VALUE_MAP.put(1, "value1");CONST_VALUE_MAP.put(2, "value2");CONST_VALUE_MAP.put(3, "value3");}...}
// 使用常量值集合List<Integer> constValueList = ExampleHelper.CONST_VALUE_LIST;Set<Integer> constValueSet = ExampleHelper.CONST_VALUE_SET;Map<Integer, String> constValueMap = ExampleHelper.CONST_VALUE_MAP

// 操作常量列表ExampleHelper.CONST_VALUE_LIST.remove(3); // UnsupportedOperationExceptionExampleHelper.CONST_VALUE_LIST.add(4); // UnsupportedOperationExceptionExampleHelper.CONST_VALUE_LIST.set(1, 20); // [1,20,3]ExampleHelper.CONST_VALUE_LIST.clear(); // UnsupportedOperationException// 操作常量集合ExampleHelper.CONST_VALUE_SET.remove(3); // [1,2]ExampleHelper.CONST_VALUE_SET.add(3); // [1,2,3]ExampleHelper.CONST_VALUE_SET.clear(); // []// 操作常量映射ExampleHelper.CONST_VALUE_MAP.remove(3); // {1:"value1",2:"value2"}ExampleHelper.CONST_VALUE_MAP.put(3, "value3"); // {1:"value1",2:"value2",3:"value3"}ExampleHelper.CONST_VALUE_MAP.clear(); // []
/** 例子工具类 */public final class ExampleHelper {/** 常量值列表 */public static final List<Integer> CONST_VALUE_LIST = Collections.unmodifiableList(Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3));/** 常量值集合 */public static final Set<Integer> CONST_VALUE_SET = Collections.unmodifiableSet(new HashSet<>(Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3)));/** 常量值映射 */public static final Map<Integer, String> CONST_VALUE_MAP;static {Map<Integer, String> valueMap = new HashMap<>(MapHelper.DEFAULT);valueMap.put(1, "value1");valueMap.put(2, "value2");valueMap.put(3, "value3");CONST_VALUE_MAP = Collections.unmodifiableMap(valueMap);}...}
/** 例子工具类 */public final class ExampleHelper {/** 常量值数组 */public static final int[] CONST_VALUES = new int[] {1, 2, 3};...}
// 使用常量值数组int[] constValues = ExampleHelper.CONST_VALUES;
// 修改常量值数组ExampleHelper.CONST_VALUES[1] = 20; // [1, 20, 3]
/** 例子工具类 */public final class ExampleHelper {/** 常量值列表 */public static final List<Integer> CONST_VALUE_LIST =Collections.unmodifiableList(Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3));...}
// 使用常量值列表int[] constValues = ExampleHelper.CONST_VALUE_LIST.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).toArray();
/** 例子工具类 */public final class ExampleHelper {/** 常量值数组 */private static final int[] CONST_VALUES = new int[] {1, 2, 3};/** 获取常量值数组方法 */public static int[] getConstValues() {return CONST_VALUES.clone();}...}
// 使用常量值方法int[] constValues = ExampleHelper.getConstValues(); // [1, 2, 3]constValues[1] = 20; // [1, 20, 3]constValues = ExampleHelper.getConstValues(); // [1, 2, 3]
/** 获取审核结果方法 */private static Integer getAuditResult(AuditDataVO data) {if (isPassed(data.getAuditItem1())&& isPassed(data.getAuditItem2())...&& isPassed(data.getAuditItem11())) {return AuditResult.PASSED;}return AuditResult.REJECTED;}

麦凯布最早提出一种称为“基础路径测试”(Basis Path Testing)的软件测试方式,测试程序中的每一线性独立路径,所需的测试用例个数即为程序的圈复杂度。
/** 获取审核结果方法 */private static AuditResult getAuditResult(AuditDataVO data) {boolean isPassed = isPassed(data.getAuditItem1());isPassed = isPassed && isPassed(data.getAuditItem2());...isPassed = isPassed && isPassed(data.getAuditItem11());if (isPassed) {return AuditResult.PASSED;}return AuditResult.REJECTED;}
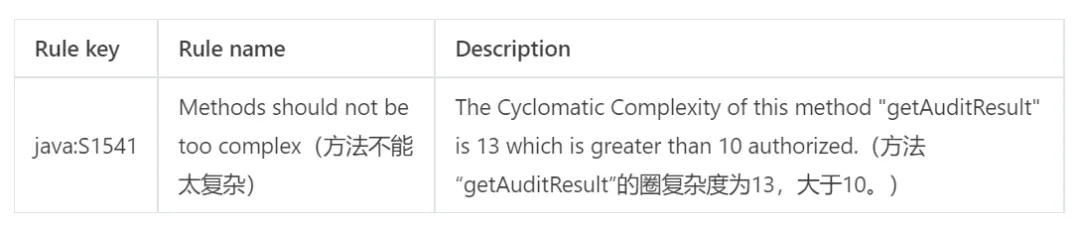
/** 获取审核结果方法 */private static AuditResult getAuditResult(AuditDataVO data) {List<BooleanSupplier> supplierList = new ArrayList<>();supplierList.add(() -> isPassed(data.getAuditItem1()));supplierList.add(() -> isPassed(data.getAuditItem2()));...supplierList.add(() -> isPassed(data.getAuditItem11()));for (BooleanSupplier supplier : supplierList) {if (!supplier.getAsBoolean()) {return AuditResult.REJECTED;}}return AuditResult.PASSED;}
/** 审核结果断言列表 */private static final List<Predicate<AuditDataVO>> AUDIT_RESULT_PREDICATE_LIST =Collections.unmodifiableList(Arrays.asList(data -> isPassed(data.getAuditItem1()),data -> isPassed(data.getAuditItem2()),...data -> isPassed(data.getAuditItem11())));/** 获取审核结果方法 */private static AuditResult getAuditResult(AuditDataVO data) {for (Predicate<AuditDataVO> predicate : AUDIT_RESULT_PREDICATE_LIST) {if (!predicate.test(data)) {return AuditResult.REJECTED;}}return AuditResult.PASSED;}
适合于&&(或||)连接大量条件表达式的情况;
适合于每个条件表达式都需要传入相同参数的情况,如果每个条件表达式传入参数不同,只能使用动态无参数Lambda表达式列表方法;
如果需要传入两个参数,可以使用BiPredicate类型来接收Lambda表达式;如果需要传入多个参数,则需要自定义方法接口。
初种根时,只管栽培灌溉,勿作枝想,勿作叶想,勿作花想,勿作实想。悬想何益?但不忘栽培之功,怕没有枝叶花实?
免费领取电子书
《高德技术2020年刊合辑》
高德技术重磅发布《高德技术2020年刊合辑》电子书,覆盖了大前端、算法、架构、汽车工程、质量等多个领域,以及数篇高德入选顶会论文的解读,分享高德在智慧出行上的最佳技术实践和总结。

