一、按年份 / 月份自动归档文件:告别手动建文件夹的苦差事1.1 办公场景:财务行政的文件整理噩梦
财务和行政经常面临几千个文件的整理任务,需要按 “2024 年 / 10 月” 这样的层级结构存放。手动建文件夹、拖文件,不仅费时费力,还容易出错。想想看,几千个文件,一个个手动创建文件夹,再把文件拖进去,这得花费多少时间和精力?而且,一旦出错,可能又得重新再来,简直是一场噩梦。
1.2 AI 指令与代码实现
给 AI 下达指令:“请写一个脚本:获取文件的‘最后修改时间’,提取年份和月份。在目标目录下自动创建‘年份 / 月份’的多级目录,并将文件移动进去。”
import shutilfrom datetime import datetimefrom pathlib import Pathsource = Path("D:/发票库")for file in source.iterdir(): if file.is_file(): # 获取修改时间戳 mtime = file.stat().st_mtime # 转为日期对象 date_obj = datetime.fromtimestamp(mtime) # 提取年、月 year_folder = str(date_obj.year) + "年" month_folder = str(date_obj.month) + "月" # 拼装目标路径:D:/发票库/2024年/10月 target_dir = source / year_folder / month_folder target_dir.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True) # 移动 shutil.move(str(file), str(target_dir / file.name)) print(f"📅 归档到:{year_folder}/{month_folder} -> {file.name}")
1.3 小李避坑提醒
parents=True 是关键!它能帮你一次性建好 “2024 年” 和 “10 月” 两层目录,不用分两步写。在处理文件前,最好先打印出文件的移动路径,确认无误后再执行移动操作,避免误操作导致文件丢失。
二、智能检索文件:按文件名和内容快速定位,让 “找不到” 成为过去
在日常办公中,文件检索是一项高频操作。你是否经常遇到这样的情况:只记得文件名里有个关键词,或者记得文件里的某段内容,但就是找不到文件在哪里?别担心,AI 和 Python 可以帮你解决这些问题。
2.1 按文件名查找:用 glob 像搜索引擎一样翻目录
2.1.1 办公场景:忘记文件位置的尴尬
只记得文件名里有个关键词,比如 “vft”,但忘了放在哪个子文件夹。手动打开一层层目录查找效率极低,而脚本可以一次性递归搜索,列出全部匹配路径。想象一下,你在一个巨大的文件库中寻找一个文件,只知道文件名里有 “vft”,但不知道它在哪个文件夹里。如果手动查找,你可能需要花费大量的时间和精力,一个文件夹一个文件夹地打开,一个文件一个文件地查看。而使用 Python 脚本,只需要几秒钟就能找到所有包含 “vft” 的文件。
2.1.2 AI 提问与代码实现
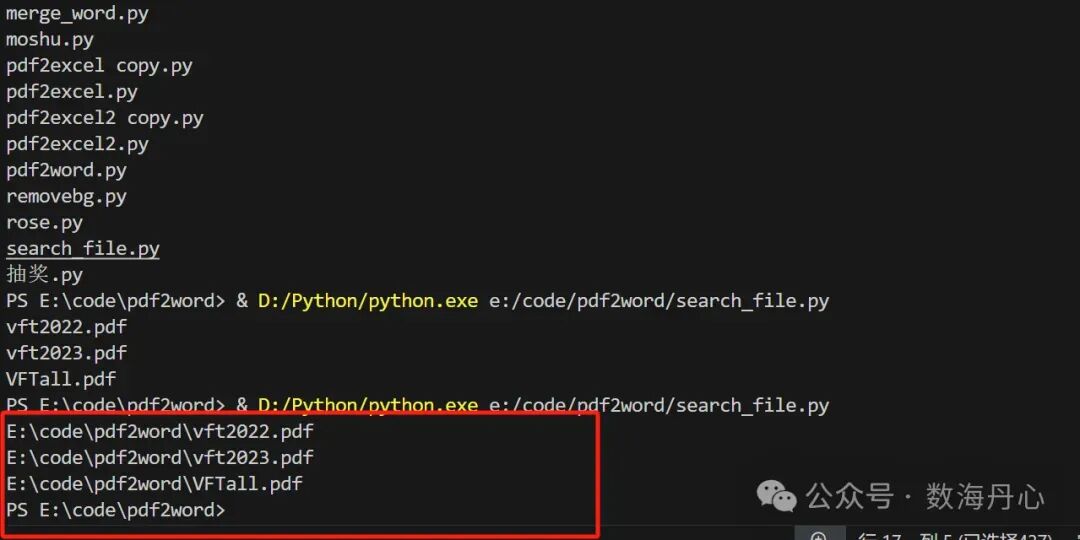
向 AI 提问:“请写一个 Python 函数,支持按文件名通配符模式在指定目录递归查找文件(支持 \\),返回匹配路径列表;并给我一个示例:在 E:\code\pdf2word 下查找文件名包含 vft 的 pdf(vft.pdf),打印数量和路径。”
import glob # 用于文件路径匹配(通配符搜索)def find_files_by_name(pattern, path='.'): """ 按照文件名模式查找文件 参数: pattern (str): 文件名匹配模式,支持通配符 例如: "*.pdf" (所有pdf文件), "*vft*.pdf" (包含vft的pdf文件) path (str): 查找的根目录路径,默认为当前目录 (.) 返回: list: 匹配到的文件路径列表 通配符说明: * : 匹配任意数量的字符(包括空字符) ? : 匹配单个字符 []: 匹配方括号内的任意一个字符 **: 递归匹配任意层级的子目录 """ # ====================== # 构建搜索路径模式 # ====================== # f'{path}/**/{pattern}': 构建完整的搜索模式 # - path: 指定的根目录 # - /**/: 递归搜索所有子目录(**表示任意层级) # - pattern: 文件名匹配模式 # 例如: 'E:\\code\\pdf2word\\/**/*vft*.pdf' search_pattern = f'{path}/**/{pattern}' # ====================== # 执行文件搜索 # ====================== # glob.glob(): 根据模式查找匹配的文件路径 # recursive=True: 启用递归搜索,支持 ** 通配符 # 返回值: 匹配文件的完整路径列表 matched_files = glob.glob(search_pattern, recursive=True) return matched_files# ======================# 使用示例# ======================# 调用函数查找文件# 参数1: "*vft*.pdf" - 查找文件名包含"vft"的所有pdf文件# 参数2: 'E:\\code\\pdf2word\\' - 指定搜索根目录file_list = find_files_by_name("*vft*.pdf", 'E:\\code\\pdf2word\\')# ======================# 输出搜索结果# ======================print(f"🔍 找到 {len(file_list)} 个匹配的文件:")print("-" * 50)for file_path in file_list: # 输出每个匹配文件的完整路径 print(file_path)print("-" * 50)print(f"✅ 搜索完成,共找到 {len(file_list)} 个文件")
2.1.3 避坑提醒
Windows 路径建议统一用 / 或原始字符串 r"E:\code\pdf2word",避免转义字符问题。
glob 在超大目录上递归会很慢;如果你只想查某种类型(比如.pdf),一定要把 pattern 写窄(.pdf 比.* 快很多)。
如果你后续要对结果做移动 / 重命名,建议返回 Path 对象(pathlib 版本更适合做自动化流水线)
。在使用 glob 模块时,还可以结合 os.path 或 pathlib 模块,对文件路径进行更灵活的操作。
2.2 按文件内容搜索:从 “全盘翻找” 到 “精准命中”
2.2.1 办公场景:记得内容却不知文件位置
记得某段内容,比如代码里出现了 import,或者合同里出现了 “违约金”,但不知道在哪个文件里。手动搜索基本不可控,脚本可以递归扫描并输出所有命中的文件路径。有时候,我们对文件的内容有印象,但就是想不起来文件名和文件位置。这时候,手动搜索就像大海捞针,而 Python 脚本可以帮助我们快速定位到目标文件。
2.2.2 AI 提问与代码实现
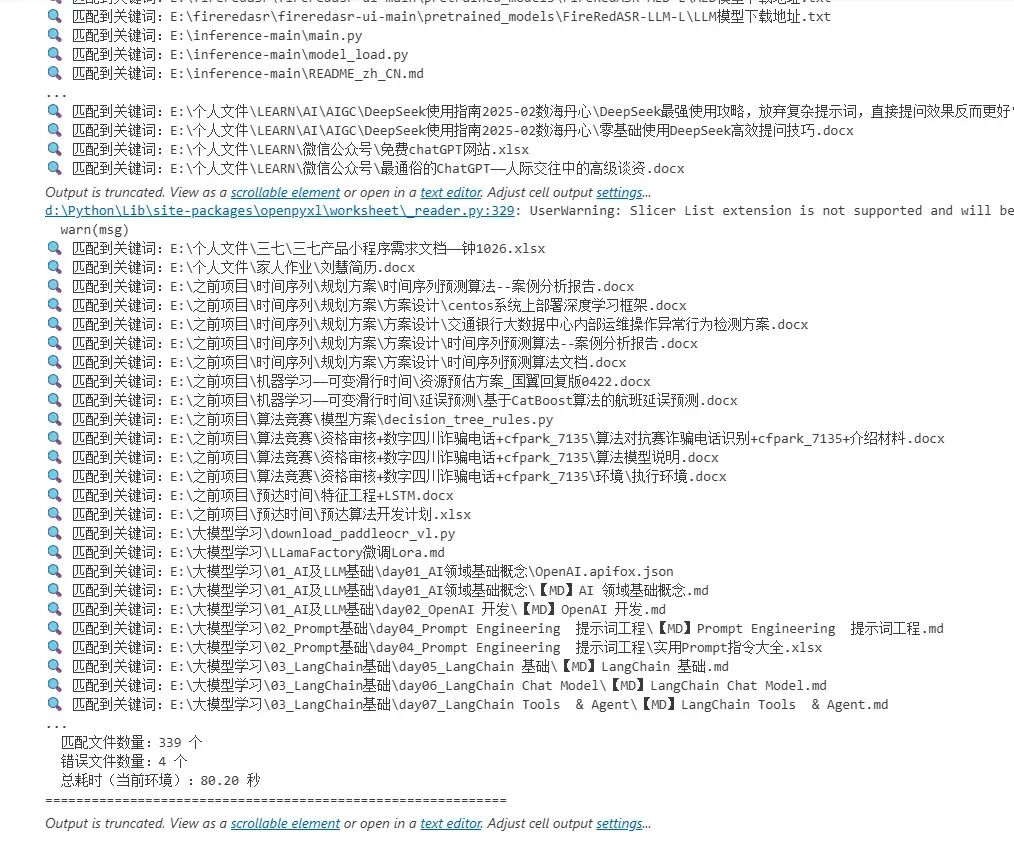
向 AI 提问:“请写一个 Python 脚本:递归遍历指定目录,针对指定后缀文件读取文本内容(忽略编码错误),用正则搜索关键词,命中则记录文件路径并打印;最后输出匹配数量与耗时统计。要求:遇到读取异常不中断。”
import osimport reimport timefrom typing import List, Dict# 第三方库导入(需提前安装)try: from docx import Document from openpyxl import load_workbookexcept ImportError as e: raise ImportError( f"缺少必要依赖库,请执行:pip install python-docx openpyxl\n错误详情:{e}")# ======================# 配置项(可按需修改)# ======================TARGET_KEYWORD = r'模型' # 要搜索的关键词(支持正则)ROOT_DIR = "E:\\" # 搜索根目录# 分类型定义支持的文件后缀SUPPORTED_FILES = { "text": (".txt", ".csv", ".py", ".md", ".json", ".log"), # 纯文本文件 "docx": (".docx",), # Word文档 "xlsx": (".xlsx",) # Excel文档}# ======================# 全局统计容器(避免函数内反复传参)# ======================stats: Dict[str, any] = { "matching_files": [], # 匹配关键词的文件路径 "error_files": [], # 读取/解析失败的文件(含错误原因) "start_time": 0.0, # 开始时间 "end_time": 0.0 # 结束时间}def read_text_file(file_path: str) -> str: """ 读取纯文本文件,优先UTF-8,失败则GBK,仍失败则ignore并记录 """ content = "" try: # 第一次尝试:UTF-8编码 with open(file_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f: content = f.read() except UnicodeDecodeError: try: # 第二次尝试:GBK编码(适配中文Windows文件) with open(file_path, 'r', encoding='gbk') as f: content = f.read() except UnicodeDecodeError: # 最后尝试:忽略编码错误,记录文件 with open(file_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8', errors='ignore') as f: content = f.read() stats["error_files"].append( (file_path, "编码错误(UTF-8/GBK均失败),已忽略错误读取")) except Exception as e: stats["error_files"].append((file_path, f"文本文件读取失败:{str(e)}")) return contentdef read_docx_file(file_path: str) -> str: """ 解析docx文件正文内容 """ content = "" try: doc = Document(file_path) # 提取所有段落文本 content = "\n".join([para.text for para in doc.paragraphs]) except Exception as e: stats["error_files"].append((file_path, f"docx解析失败:{str(e)}")) return contentdef read_xlsx_file(file_path: str) -> str: """ 解析xlsx文件所有单元格内容 """ content = "" try: wb = load_workbook(file_path, read_only=True, data_only=True) # 只读模式提升效率 # 遍历所有工作表 for sheet_name in wb.sheetnames: ws = wb[sheet_name] # 遍历所有行和单元格 for row in ws.iter_rows(values_only=True): # 拼接非空单元格内容 row_content = " ".join([str(cell) for cell in row if cell is not None]) content += row_content + "\n" wb.close() except Exception as e: stats["error_files"].append((file_path, f"xlsx解析失败:{str(e)}")) return contentdef get_file_content(file_path: str) -> str: """ 统一入口:根据文件后缀调用对应解析函数 """ # 判断文件类型 if file_path.endswith(SUPPORTED_FILES["text"]): return read_text_file(file_path) elif file_path.endswith(SUPPORTED_FILES["docx"]): return read_docx_file(file_path) elif file_path.endswith(SUPPORTED_FILES["xlsx"]): return read_xlsx_file(file_path) return ""def recursive_search(keyword_pattern: re.Pattern): """ 递归遍历目录,解析文件并搜索关键词 """ # 遍历目录树 for root, _, files in os.walk(ROOT_DIR): for file in files: file_path = os.path.join(root, file) # 仅处理支持的文件类型 if any(file_path.endswith(suffix) for suffix in SUPPORTED_FILES["text"] + SUPPORTED_FILES["docx"] + SUPPORTED_FILES["xlsx"]): # 获取文件内容 content = get_file_content(file_path) # 搜索关键词 if content and keyword_pattern.search(content): stats["matching_files"].append(file_path) print(f"🔍 匹配到关键词:{file_path}")def print_stats(): """ 打印最终统计信息 """ stats["end_time"] = time.time() total_time = stats["end_time"] - stats["start_time"] print("\n" + "="*60) print("📋 搜索结果汇总") print("-"*60) # 输出匹配文件列表 if stats["matching_files"]: print("✅ 匹配到关键词的文件(共{}个):".format(len(stats["matching_files"]))) for idx, path in enumerate(stats["matching_files"], 1): print(f" {idx}. {path}") else: print("❌ 未找到任何包含关键词的文件") # 输出错误文件列表 if stats["error_files"]: print("\n⚠️ 读取/解析失败的文件(共{}个):".format(len(stats["error_files"]))) for idx, (path, reason) in enumerate(stats["error_files"], 1): print(f" {idx}. {path} - {reason}") # 输出核心统计 print("\n📊 性能与统计信息") print("-"*60) print(f" 遍历根目录:{ROOT_DIR}") print(f" 搜索关键词:{TARGET_KEYWORD}") print(f" 匹配文件数量:{len(stats['matching_files'])} 个") print(f" 错误文件数量:{len(stats['error_files'])} 个") print(f" 总耗时(当前环境):{total_time:.2f} 秒") print("="*60)if __name__ == "__main__": # 初始化开始时间 stats["start_time"] = time.time() # 编译正则表达式(提升匹配效率) try: keyword_pattern = re.compile(TARGET_KEYWORD) except re.error as e: print(f"❌ 正则表达式格式错误:{e}") exit(1) # 执行递归搜索 print(f"🚀 开始搜索(目录:{ROOT_DIR},关键词:{TARGET_KEYWORD})...") recursive_search(keyword_pattern) # 打印统计结果 print_stats()
三、重复文件清理:安全高效去重,守护你的硬盘空间
在日常办公中,文件的重复问题常常让人头疼不已。随着工作的推进,文件在微信、邮件、网盘等平台来回传输,不知不觉就堆积成了 “重复文件地狱”,不仅占用大量磁盘空间,还会给文件管理带来极大的困扰。
3.1 办公场景:重复文件堆积成 “地狱”
微信、邮件和网盘,这些我们日常工作中频繁使用的文件传输工具,在给我们带来便利的同时,也容易引发重复文件的问题。就拿合同文件来说,可能会出现 “合同.pdf”“合同 (1).pdf”“合同最终版.pdf” 等多个看似不同版本的文件,但实际上它们的内容可能一模一样。这种内容重复的文件才是真正占用硬盘空间的 “元凶”,而不仅仅是名字相似的文件。想象一下,你的硬盘里有大量这样的重复文件,不仅会导致硬盘空间被浪费,还会让你在查找文件时感到困惑和烦躁。
3.2 用 MD5 哈希识别内容重复并删除
面对重复文件的困扰,我们可以利用 MD5 哈希算法来识别和删除重复文件,让硬盘空间得到释放。
3.2.1 AI 提问与代码实现
向 AI 提问:“请写一个 Python 去重脚本:递归遍历目录,对每个文件计算 MD5 哈希,哈希相同视为重复。保留首次出现的文件,删除后续重复文件。要求:输出删除日志,并提示用户这是永久删除操作。”
import os # 用于文件系统操作(路径处理、文件删除)import hashlib # 用于计算文件哈希值def file_hash(filepath): """ 计算文件的MD5哈希值 参数: filepath (str): 文件路径 返回: str: 文件的MD5哈希值(32位十六进制字符串) """ # ====================== # 1. 创建MD5哈希对象 # ====================== # hashlib.md5(): 创建MD5哈希计算对象 hash_md5 = hashlib.md5() # ====================== # 2. 以二进制模式打开文件 # ====================== # "rb": 以二进制读取模式打开文件(避免编码问题) with open(filepath, "rb") as f: # ====================== # 3. 分块读取文件内容 # ====================== # iter(lambda: f.read(4096), b""): 创建迭代器,每次读取4096字节 # 当读取到空字节(b"")时停止迭代 # 这样可以处理大文件而不占用过多内存 for chunk in iter(lambda: f.read(4096), b""): # ====================== # 4. 更新哈希值 # ====================== # hash_md5.update(): 将数据块添加到哈希计算中 hash_md5.update(chunk) # ====================== # 5. 返回十六进制格式的哈希值 # ====================== # hexdigest(): 返回32位十六进制字符串格式的MD5值 return hash_md5.hexdigest()def remove_duplicates(directory): """ 删除指定目录下的重复文件 参数: directory (str): 要处理的目录路径 """ # ====================== # 1. 初始化哈希字典 # ====================== # 用于存储文件哈希值和对应文件路径的映射 # 格式: {哈希值: 文件路径} hashes = {} # ====================== # 2. 递归遍历目录 # ====================== # os.walk(): 递归遍历目录树,返回 (子目录路径, 子目录列表, 文件列表) for subdir, dirs, files in os.walk(directory): # 遍历当前目录下的所有文件 for filename in files: # ====================== # 3. 构建文件完整路径 # ====================== # os.path.join(): 将目录路径和文件名组合成完整路径 filepath = os.path.join(subdir, filename) # ====================== # 4. 计算文件哈希值 # ====================== filehash = file_hash(filepath) # ====================== # 5. 检查是否为重复文件 # ====================== if filehash not in hashes: # ====================== # 6. 首次出现的文件 # ====================== # 将哈希值和文件路径添加到字典中 hashes[filehash] = filepath print(f"📝 记录文件: {filepath}") else: # ====================== # 7. 重复文件处理 # ====================== # 哈希值已存在,说明找到了重复文件 print(f"🗑️ 发现重复文件: {filepath}") print(f" 原始文件: {hashes[filehash]}") # ====================== # 8. 删除重复文件 # ====================== # os.remove(): 删除指定路径的文件 os.remove(filepath) print(f"✅ 已删除重复文件: {filepath}")# 1. 定义要处理的目录路径# ======================# 注意:请将 '/path/to/folder' 替换为实际的目录路径directory = '/path/to/folder'# ======================# 2. 执行去重操作# ======================print(f"🚀 开始处理目录: {directory}")print("💡 注意:此操作会永久删除重复文件,请确保已备份重要数据")print("-" * 50)remove_duplicates(directory)print("-" * 50)print("🎉 文件去重任务完成!")
上述代码中,file_hash函数用于计算文件的 MD5 哈希值,remove_duplicates函数则递归遍历指定目录,对每个文件计算 MD5 哈希,并将哈希值存储在字典中。如果发现哈希值已经存在,说明该文件是重复文件,将其删除。
3.2.2 避坑提醒
这是 “真删除”(os.remove),一旦执行,文件将不可恢复。因此,在办公落地时,建议至少做两层保护:
1)先 dry - run 生成清单(只打印不删除),这样可以让你提前了解哪些文件会被删除,避免误删重要文件;
2)优先移动到回收站 / 隔离目录,而不是直接删除,以便在发现误删时能够及时恢复文件。
MD5 冲突概率极低但不是 0;对极端严谨场景可改用sha256,它的安全性更高,冲突概率更低。
大目录去重很耗时:因为必须读完整文件内容计算哈希。在处理大目录时,要有耐心,或者可以考虑在空闲时间进行去重操作。
如果你担心误删 “同内容但不同用途” 的文件(例如同一模板在不同项目中留档),建议按目录分批执行,或先输出报告给人工确认,确保不会误删重要文件。
3.3 去重增强版安全加固
为了让重复文件清理更加安全可靠,我们可以对去重脚本进行增强,增加一些安全机制。
3.3.1 办公场景:先看报告再删,更安全的去重
在实际办公中,我们可能希望在删除重复文件之前先查看报告,了解哪些文件是重复的,以及删除这些文件后能够节省多少空间。或者,我们希望把重复文件移动到隔离区,在确认无误后再清空隔离区,这样可以避免误删重要文件。
3.3.2 AI 提问与代码实现
向 AI 提问:“在现有 MD5 去重脚本基础上,请帮我做一个更安全的版本:增加 dry_ run 模式、把重复文件移动到 quarantine 文件夹而不是直接删除、输出重复文件报告 csv,并统计节省空间估算。”
import osimport hashlibimport shutilfrom pathlib import Pathimport csvdef file_hash_md5(filepath: str, chunk_size: int = 1024 * 1024) -> str: h = hashlib.md5() with open(filepath, "rb") as f: for chunk in iter(lambda: f.read(chunk_size), b""): h.update(chunk) return h.hexdigest()def remove_duplicates_safe(directory: str, dry_run: bool = True) -> Path: root = Path(directory) if not root.exists(): raise FileNotFoundError(root) quarantine = root / "_quarantine_duplicates" report = root / "duplicate_report.csv" hashes: dict[str, str] = {} quarantine.mkdir(exist_ok=True) saved_bytes = 0 with report.open("w", newline="", encoding="utf-8") as f: writer = csv.DictWriter(f, fieldnames=["重复文件", "保留文件", "大小(bytes)", "md5"]) writer.writeheader() for subdir, _, files in os.walk(root): # 跳过隔离区,避免二次处理 if Path(subdir).resolve() == quarantine.resolve(): continue for filename in files: fp = str(Path(subdir) / filename) md5 = file_hash_md5(fp) size = os.path.getsize(fp) if md5 not in hashes: hashes[md5] = fp else: keep = hashes[md5] writer.writerow({"重复文件": fp, "保留文件": keep, "大小(bytes)": size, "md5": md5}) saved_bytes += size print(f"🧾 重复: {fp}") print(f" 保留: {keep}") if not dry_run: # 移动到隔离区(保留原文件名,若冲突自动加序号) target = quarantine / Path(fp).name i = 1 while target.exists(): target = quarantine / f"{Path(fp).stem}_{i:03d}{Path(fp).suffix}" i += 1 shutil.move(fp, target) print(f"✅ 报告已生成:{report}") print(f"📦 预计可释放空间:{saved_bytes / (1024**3):.2f} GB(估算)") if dry_run: print("ℹ️ 当前为 dry_run:未移动/未删除任何文件") else: print(f"🧯 重复文件已移动到隔离区:{quarantine}") return report# 示例:# remove_duplicates_safe("D:/日常办公/附件堆积", dry_run=True)
在这段代码中,remove_duplicates_safe函数增加了 dry_run 模式,默认情况下只生成报告而不进行实际的文件移动操作。如果 dry_run 为 False,则会将重复文件移动到隔离区_quarantine_duplicates,并生成 CSV 报告,统计每个重复文件的相关信息以及预计节省的空间。
3.3.3 避坑提醒
安全版本会额外生成隔离区与报告文件,适合办公环境 “可审计、可回滚”。通过查看报告,我们可以清楚地了解重复文件的情况,并且在需要时可以从隔离区恢复文件。真要删除时,建议先隔离 1 - 2 天,确认无误再清空隔离区。这样可以给我们足够的时间来检查隔离区的文件,确保没有误删重要文件。在处理重复文件时,一定要谨慎操作,避免因为误删而给工作带来不必要的麻烦。
四、跨目录同步:备份、镜像、增量复制的 “办公版 DevOps”
4.1 办公场景:高效备份文件的需求
在日常办公中,数据备份是一项至关重要的任务。我们经常需要定期把 “工作盘” 里的重要资料备份到 “移动硬盘” 或 “公司服务器”,以防止数据丢失。然而,直接全选复制粘贴的方式存在诸多问题。一方面,这种方式速度太慢,当数据量达到几百 G 时,每次全量复制都需要等待很长时间,这无疑会浪费大量的工作时间。另一方面,这种方式容易出错,一不小心就可能覆盖了最新修改的版本,导致数据丢失或不一致。
为了更高效地备份文件,我们希望实现新文件能够自动复制到备份目录,源文件有更新时能够及时覆盖备份,同时还可以选择是否开启镜像模式,即源文件删除时备份也相应删除。这样的备份方式可以确保我们的数据始终保持最新和完整,同时也能节省大量的时间和精力。
4.2 AI 提问与代码实现
为了实现上述需求,我们向 AI 提问:“请写一个 Python 单向同步脚本:把源目录增量复制到目标目录,保留文件修改时间(用 copy2)。只复制比目标更新的文件。输出同步日志。目标目录不存在自动创建。”
from pathlib import Pathimport shutildef sync_one_way(src: str | Path, dst: str | Path): src_path = Path(src) dst_path = Path(dst) if not src_path.exists(): raise FileNotFoundError(src_path) dst_path.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True) copied = 0 skipped = 0 for p in src_path.rglob("*"): if p.is_dir(): continue rel = p.relative_to(src_path) target = dst_path / rel target.parent.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True) if not target.exists(): shutil.copy2(p, target) copied += 1 print(f"✅ 新增: {rel}") else: if p.stat().st_mtime > target.stat().st_mtime: shutil.copy2(p, target) copied += 1 print(f"🔄 更新: {rel}") else: skipped += 1 print(f"🎉 同步完成:复制/更新 {copied} 个,跳过 {skipped} 个")# 示例:sync_one_way("D:/工作资料", "E:/备份/工作资料")
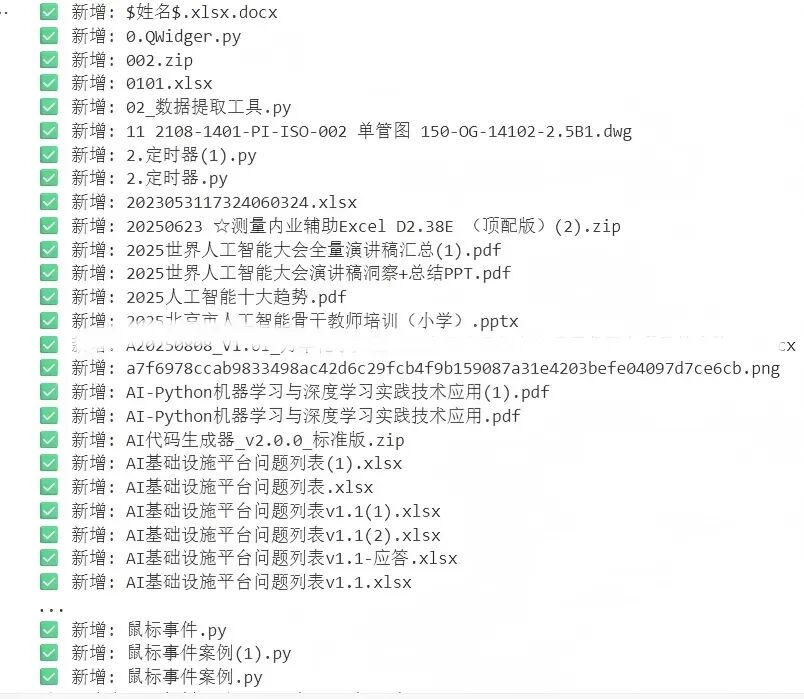
在这段代码中,sync_one_way函数实现了单向同步的功能。它首先检查源目录是否存在,如果不存在则抛出异常。然后,它会创建目标目录(如果不存在)。接下来,通过rglob递归遍历源目录下的所有文件,对于每个文件,检查其是否为目录,如果是则跳过。接着,构建目标文件的路径,如果目标文件不存在,则直接复制文件,并记录复制的文件数量。如果目标文件已存在,则比较源文件和目标文件的修改时间,如果源文件的修改时间更新,则覆盖目标文件,并记录更新的文件数量;否则跳过该文件,并记录跳过的文件数量。最后,输出同步完成的日志信息。
4.3 避坑提醒
需要注意的是,这是 “增量备份”,它只会复制新增或更新的文件,不会删除目标目录多出来的文件。如果希望做 “镜像同步”,即源文件删除时目标文件也相应删除,要谨慎设计删除逻辑,建议先做 dry_run 并输出待删除清单。因为一旦误删文件,可能会造成数据丢失,给工作带来严重影响。在实际应用中,还可以考虑定期进行全量备份,以确保数据的完整性。同时,对于重要的数据,最好进行异地备份,以防止因本地灾难导致数据丢失。
五、生成索引清单:把文件夹变成 “可点击的目录册”
在日常办公中,文件管理是一项重要的任务。当我们面对大量的文件时,如何快速找到自己需要的文件成为了一个难题。这时候,生成索引清单就显得尤为重要。它可以把杂乱无章的文件夹变成一个 “可点击的目录册”,让我们能够轻松地找到所需文件。下面,我们将介绍如何使用 AI 和 Python 生成 HTML 超链接索引和 Excel 索引清单。
5.1 生成 HTML 超链接索引:发给同事一眼可找
5.1.1 办公场景:交付文件时的便利需求
在工作中,我们经常需要整理交付包,里面可能包含几十上百个文件。对于接收方来说,最怕的就是在这些文件中找不到自己需要的内容。而生成一个index.html文件,就可以像网站目录一样,通过点击链接直接跳转到对应的文件,大大提高了文件查找的效率。比如,在一个项目交付中,我们需要将大量的文档、图片、代码等文件交给客户或团队成员。如果没有一个清晰的索引,对方可能需要花费大量的时间在众多文件中寻找所需内容,这不仅浪费时间,还可能影响工作进度。而有了 HTML 超链接索引,对方只需打开index.html文件,就可以一目了然地看到所有文件的列表,通过点击链接即可快速打开文件,方便快捷。
5.1.2 AI 提问与代码实现
向 AI 提问:“请写一个 Python 脚本:遍历目录生成 HTML 索引,包含文件名、相对路径、大小,点击可打开文件。要求:递归、排序、输出到根目录 index.html。”
from pathlib import Pathimport htmldef generate_html_index(folder: str | Path, output_name: str = "index.html"): root = Path(folder) if not root.exists(): raise FileNotFoundError(root) rows = [] for p in sorted(root.rglob("*")): if p.is_dir(): continue rel = p.relative_to(root).as_posix() size = p.stat().st_size rows.append((rel, size)) html_lines = [ "<html><head><meta charset='utf-8'><title>文件索引</title></head><body>", f"<h2>文件索引:{html.escape(str(root))}</h2>", "<ul>", ] for rel, size in rows: html_lines.append( f"<li><a href='{html.escape(rel)}'>{html.escape(rel)}</a> ({size} bytes)</li>") html_lines += ["</ul>", "</body></html>"] out = root / output_name out.write_text("\n".join(html_lines), encoding="utf-8") print(f"✅ 已生成索引:{out}")# 示例:generate_html_index("D:/code")
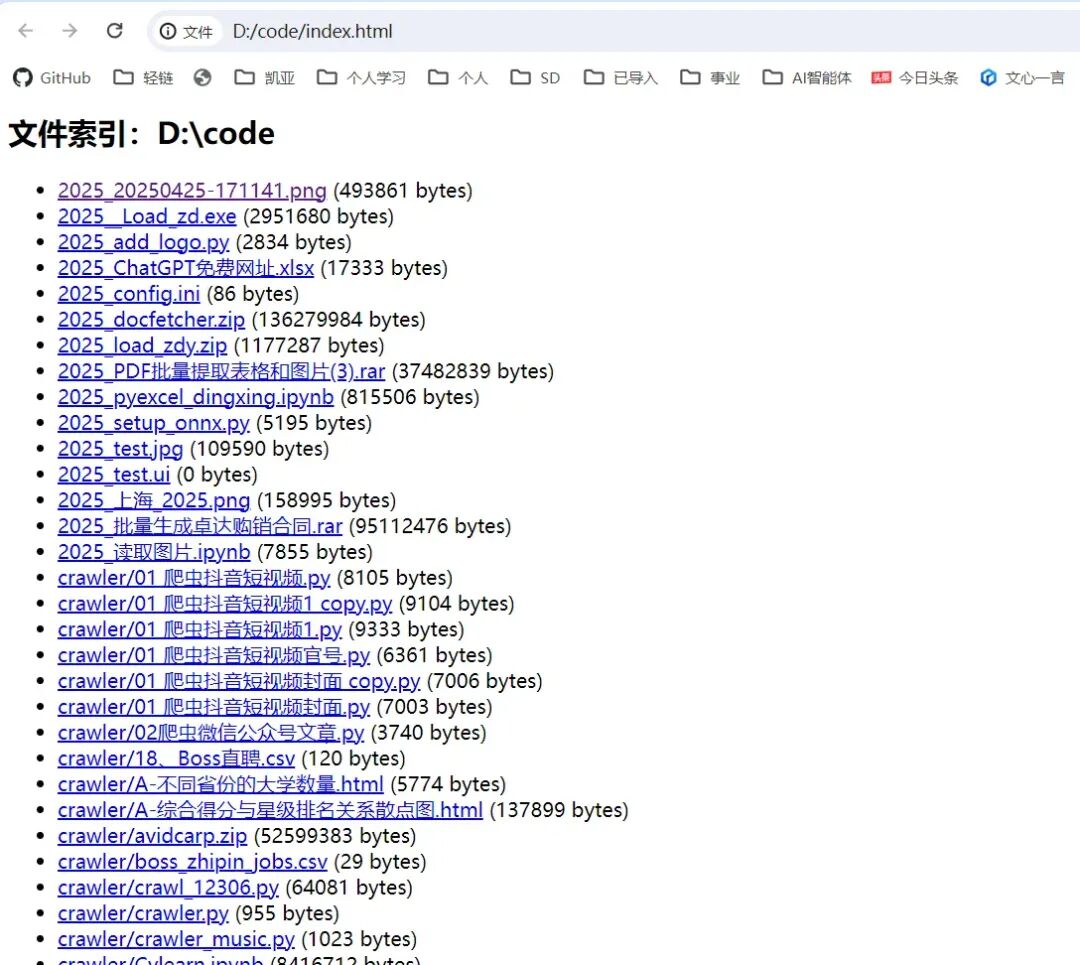
上述代码中,generate_html_index函数首先检查指定的目录是否存在,如果不存在则抛出FileNotFoundError异常。然后,通过rglob递归遍历目录下的所有文件,并将文件的相对路径和大小存储在rows列表中。接着,生成 HTML 格式的文件索引内容,将文件名、相对路径和大小以列表项的形式展示,并添加超链接,点击即可打开文件。最后,将生成的 HTML 内容写入到index.html文件中。
5.1.3 避坑提醒
HTML 链接在本地打开通常没问题;若发给别人,要保证相对路径结构不变(不要只发 index.html)。因为如果只发送index.html文件,接收方在打开时可能会因为相对路径不正确而无法找到对应的文件。若要 “按文件类型分组” 或 “加入更新时间”,可以在rows里加字段扩展。比如,在rows列表中添加文件类型和更新时间的字段,然后在生成 HTML 内容时,根据这些字段进行分组展示或添加到文件信息中,这样可以让索引更加清晰和实用。
5.2 生成 Excel 索引清单:交付可读 + 可筛选
5.2.1 办公场景:团队习惯用 Excel 的需求
有些团队在处理文件时更习惯使用 Excel,因为它具有强大的数据处理和筛选功能。我们可以输出一个索引.xlsx文件,其中包含文件名、路径、大小、修改时间等信息,并且还能在表格里添加超链接,点击文件名即可打开本地文件。这对于需要对文件进行详细管理和筛选的团队来说非常方便。例如,在一个大型项目中,团队成员需要对大量的文件进行分类、筛选和查看。通过 Excel 索引清单,他们可以根据文件名、文件大小、修改时间等字段进行筛选,快速找到自己需要的文件。而且,点击文件名即可直接打开文件,无需在文件夹中逐个查找,大大提高了工作效率。
5.2.2 AI 提问与代码实现
向 AI 提问:“请结合 pathlib 和 pandas,遍历 'D:/code'。提取文件名、文件大小(MB)、修改日期。生成一个 Excel 表格,并在表格里添加超链接,点击文件名即可打开本地文件。”
import pandas as pdfrom pathlib import Pathfrom datetime import datetimefolder = Path("D:/code")data_list = []for file in folder.rglob("*"): if file.is_file(): # 提取信息 stats = file.stat() size_mb = round(stats.st_size / 1024 / 1024, 2) # 转 MB mtime = datetime.fromtimestamp(stats.st_mtime).strftime('%Y-%m-%d') # 构造 Excel 超链接公式 # HYPERLINK("路径", "显示名称") link = f'=HYPERLINK("{file}", "{file.name}")' data_list.append({ "文件名": link, # 写入公式 "大小(MB)": size_mb, "修改日期": mtime, "完整路径": str(file) })# 转 DataFrame 并导出# df = pd.read_excel(data_list) # 这里原逻辑有误,应是 pd.DataFramedf = pd.DataFrame(data_list) # 修正为 DataFramedf.to_excel("合同索引表.xlsx", index=False)print("✅ 索引表已生成!打开 Excel 点击文件名即可跳转。")
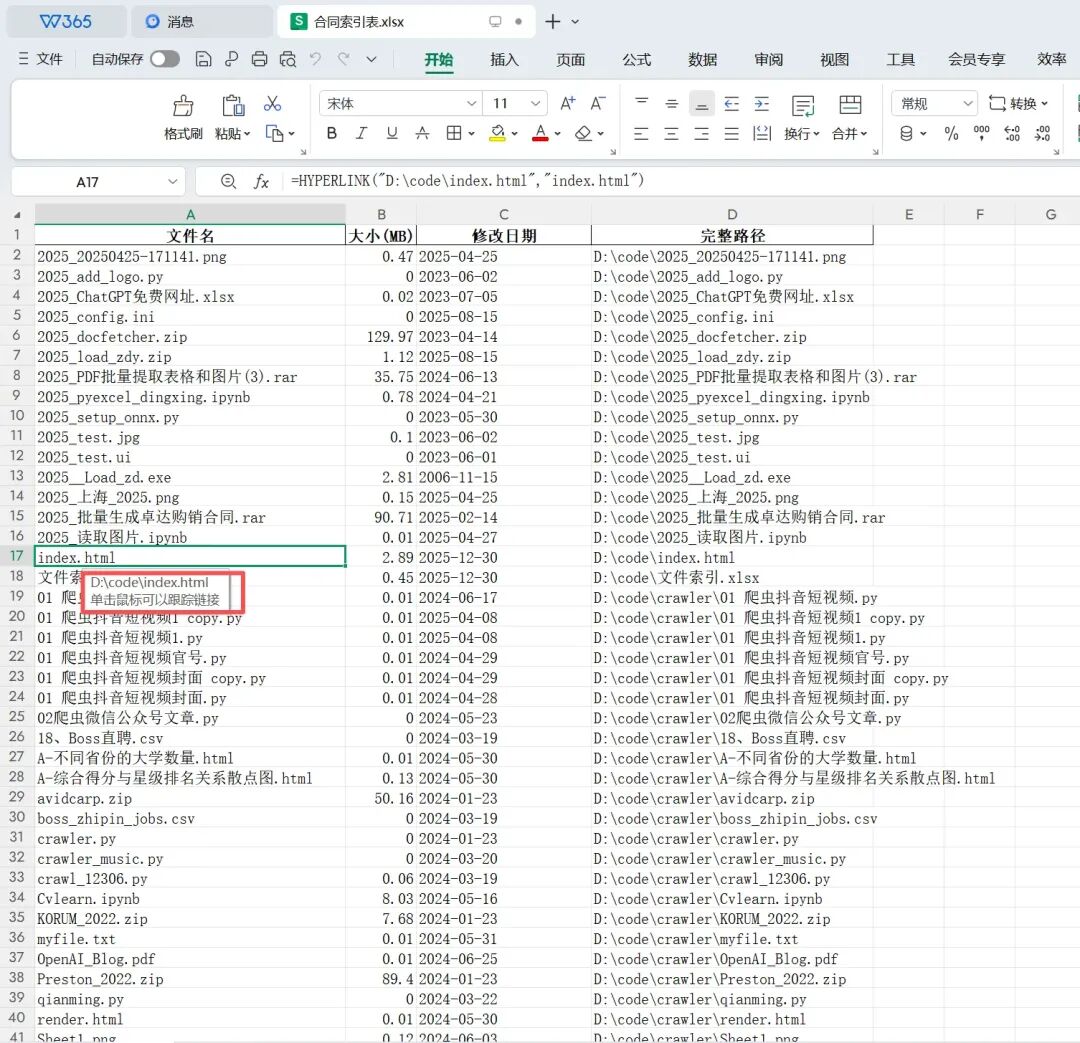
在这段代码中,首先使用pathlib模块的rglob方法递归遍历指定目录下的所有文件。对于每个文件,提取其文件名、文件大小(转换为 MB)、修改日期等信息,并构造 Excel 超链接公式。然后,将这些信息存储在data_list列表中。接着,使用pandas模块将data_list转换为DataFrame格式,并将其导出为 Excel 文件合同索引表.xlsx。最后,提示用户索引表已生成,打开 Excel 点击文件名即可跳转至对应的本地文件。
5.2.3 小李避坑提醒
Excel 的超链接公式HYPERLINK有长度限制(255 字符)。如果路径特别长,点击可能会失效。这是因为 Excel 对超链接公式的长度有限制,如果路径超过了这个限制,超链接可能无法正常工作。在实际应用中,我们可以尽量缩短文件路径,或者使用相对路径来避免这个问题。导出的 Excel 如果只显示公式不显示链接效果,双击一下单元格回车即可激活(或用 openpyxl 库设置格式)。这是因为 Excel 在某些情况下可能不会自动识别超链接公式,需要手动激活。使用openpyxl库可以更加灵活地设置 Excel 表格的格式,包括超链接的样式和显示效果。
六、核心口诀:一页纸掌控文件流
文件操作千变万化,但只要掌握了核心逻辑,就能轻松应对各种场景。下面是一套 Python 文件操作的口诀,涵盖了路径处理、文件查找、重命名、移动复制等常见操作,朗朗上口,方便记忆。
路径要用 pathlib,斜杠拼接不迷路; 查找文件用 glob,递归搜索全覆盖; os.listdir 太简陋,iterdir 对象信息足; 重命名用 rename,加前加后正则撸; 移动复制 shutil,备份归档超高速; 操作之前先 print,确认无误再输出!
记住:文件操作不可逆,下手之前先备份。现在,你已经掌握了指挥千军万马(文件)的令牌,去清理你的桌面吧!