Python之数据容器
- 2026-01-12 01:21:51
第四章 数据容器
数据容器:一种能存放
多个数据的数据类型。数据容器可以更高效的管理成批的数据,且便于存储,访问。
容器中的每一个数据,又称为:每一个
元素。Python中有很多种数据容器。
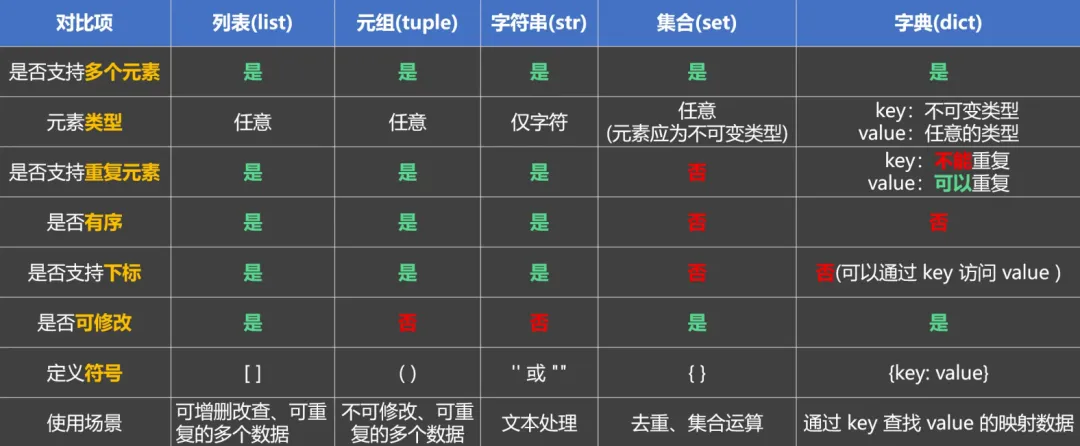
列表(list) 元组(tuple) 字符串(str) 集合(set) 字典(dict) 不同的数据容器,有不同的特点和不同的语法,但是都有一个共性,就是可以存储多个元素。
一. 列表(list)
1.1 定义列表
列表:⽤来存放⼀组有序的数据,并且可以对其中的数据进⾏:增删改查。
使⽤
⽅括号 []来定义⼀个列表,不同元素之间⽤ , 去分隔。
# 定义格式
[元素0, 元素1, 元素2, 元素3, ......]
# 列表示例,可以存储不同的数据类型
list1 = [34,56, 21, 56, 11]
list2 = ['北京', 'Hello', 'Python']
list3 = [23, 'Python', True, None]
list4 = [23,'Python',True, None, [16,288,300]]
# 定义空列表:列表中的数据,后期会通过特定写法填充
list5 = []
list6 = list()
# 定义有内容的列表
list1 = [34, 56, 21, 56, 11]
list2 = ['北京', 'Python', '你好啊']
list3 = [23, 'Python', True, None]
list4 = [23, 'Python', True, None, [100, 200, 300]] # list4 是⼀个嵌套列表
# 定义空列表(列表中的数据,后期会通过特定写法填充)
list5 = []
list6 = list()
print(list1, type(list1)) # [34, 56, 21, 56, 11] <class 'list'>
print(list2, type(list2)) # ['北京', 'Python', '你好啊'] <class 'list'>
print(list3, type(list3)) # [23, 'Python', True, None] <class 'list'>
print(list4, type(list4)) # [23, 'Python', True, None, [100, 200, 300]] <class 'list'>
print(list5, type(list5)) # [] <class 'list'>
print(list6, type(list6)) # [] <class 'list'>
1.2 列表的下标(索引值)
下标又叫
索引值,其实就是元素在列表中的位置编号,分为正索引,负索引。
# 正索引:从左往右,起始元素是0,随后是1,依次类推。
nums = [10,20,30,40,50]
0, 1 ,2, 3, 4
#负索引:从右往左,起始元素是-1,随后是-2,依次类推。
nums = [10,20,30,40,50]
-5,-4,-3,-2,-1
下标最直接的用途:就是从列表中读取元素。
注意:通过下标取值时,下标不要超出范围,否则会报索引下标越界的错误。
# 定义一个列表
nums = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]
# 测试正索引
print(nums[0])
print(nums[1])
print(nums[2])
print(nums[3])
# 测试负索引
print(nums[-1])
print(nums[-2])
print(nums[-3])
print(nums[-4])
print(nums[-5])
# 测试错误索引
# print(nums[5])
# 定义一个嵌套索引
# 定义一个嵌套列表
nums2 = [10, 20, ['Hello','Python'], 40, 50]
# 取出“尚硅谷”
print(nums2[2][1])
1.3 列表的增删改查
我们先认识下方法,如下:
列表.append()在上述写法中,如果只看 append(元素) ,这就是在调⽤ append 函数,但 append 前⾯还有 列表. 这种形式,所以也可以换⼀个说法,叫:调⽤列表的 append ⽅法。
那⽅法和函数之间是什么关系呢?从更正式的⻆度来说:当⼀个函数⾪属于某个对象时,这个函数就被称为该对象的⽅法。不过对于初学者来说,这句话可能⼀时还不好理解,因为我们尚未学习“类”和“对象”等相关内容。所以这⾥⼤家暂时不必纠结⽅法的严格定义,只要先理解下⾯这种
写法的含义即可:
b() :这叫调⽤ b 函数。
a.b() :这叫调⽤ a 的 b ⽅法。
列表的增删改查:
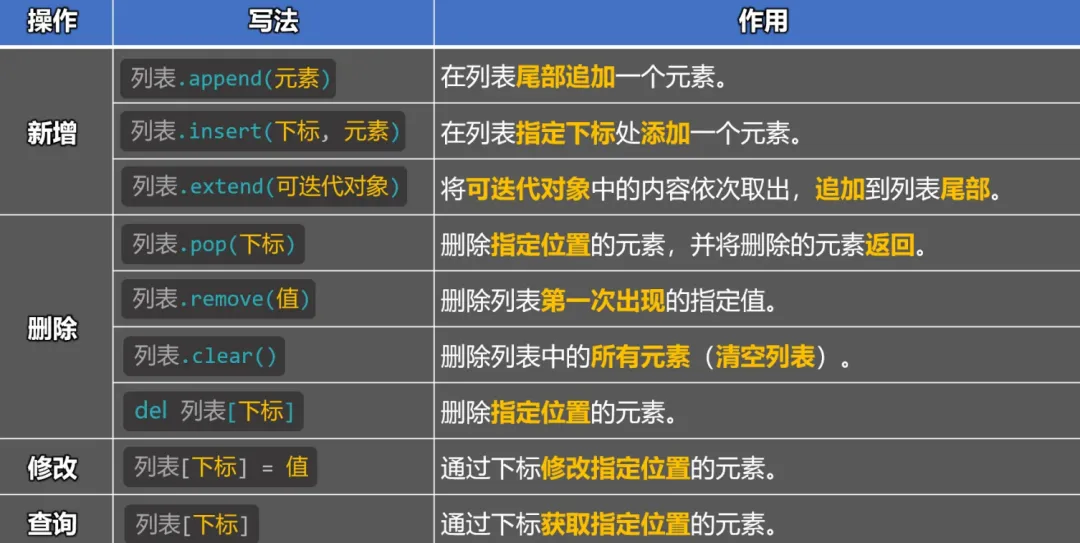
新增
# 新增操作
# 方式一:通过列表的append方法,在列表尾部追加一个元素
nums1 = [10, 20, 30, 40]
nums1.append(50)
print(nums1) # [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]
# 方式二:通过列表的insert方法,在列表的指定下标出添加一个元素
nums2 = [10, 20, 30, 40]
nums2.insert(2,66)
print(nums2) # [10, 20, 66, 30, 40]
# 方式三:通过列的extend方法,将可迭代对象中的内容依次取出,追加到列表尾部
nums3 = [10, 20, 30, 40]
nums3.extend('Python')
nums3.extend(range(1, 4))
nums3.extend([50, 60, 70])
print(nums3) # [10, 20, 30, 40, 'P', 'y', 't', 'h', 'o', 'n', 1, 2, 3, 50, 60, 70]
删除
# 删除
# 方式一:通过列表的pop方法,删除指定位置的元素,并返回元素
nums4 = [10, 20, 30, 40]
result = nums4.pop(1)
print(nums4) # [10, 30, 40]
print(result) # 20
# 方式二:通过列表的remove方法,删除列表中第一次出现的指定值
nums5 = [10, 20, 30, 40]
nums5.remove(10)
print(nums5) # [20, 30, 40]
# 方式三:通过列表的clear方法,删除列表中的所有元素(清空列表)
nums6 = [10, 20, 30, 40]
nums6.clear()
print(nums6) # []
# 方式四:通过del关键字,删除指定元素
nums7 = [10, 20, 30, 40]
del nums7[3]
print(nums7) # [10, 20, 30]
修改
修改操作⽐较简单,主要是通过下标进⾏修改,语法为: 列表[下标] = 值
# 修改操作
nums8 = [10, 20, 10, 40, 50]
nums8[2] = 66
print(nums8) # [10, 20, 66, 40, 50]
查询
# 查询操作
nums9 = [10, 20, 10, 40, 50]
print(nums9[3]) # 40
1.4 列表的常用方法

# 1.使用index方法,查找指定元素在列表中第一次出现的下标,返回值是:元素下标。
fruits = ['香蕉', '苹果', '橙子', '香蕉']
result = fruits.index('香蕉')
print(result) # 0
# 2.使用count方法,统计某个元素在列表中出现的次数,返回值是:元素出现的次数。
nums = [10, 20, 10, 30, 10, 40, [10, 10, 10]]
result = nums.count(10)
print(result) # 3
# 3.使用revers方法,对列表进行反转(会改变原列表)
nums = [23, 11, 32, 30, 17, [6, 7, 8, 9]]
nums.reverse()
print(nums) # [[6, 7, 8, 9], 17, 30, 32, 11, 23]
# 4.使用sort方法,对列表排序(默认从小到大),若想从大到小,可以将reverse参数设置为True
# 4.1 若列表中的元素:都是数字,则按照数字的大小顺序进行排序。
nums = [23, 11, 32, 30, 17]
nums.sort(reverse=True) # [32, 30, 23, 17, 11]
print(nums)
# 4.2 若列表中的元素:既有数字,又有字符串,那就会报错。
# nums = [23, 11, 32, 30, 17, '尚硅谷']
# nums.sort()
# print(nums)
# 4.3 若列表中的元素:都是字符串,则按照字符串的 Unicode 编码大小进行排序
msg_list = ['北京', 'Python', '北好']
msg_list.sort()
print(msg_list)
print(ord('京'), ord('好'), ord('北'))
# 备注:所有的列表方法,都只作用于“当前层”的元素(浅层操作),不会自动进入嵌套的“里层”结构中。
1.5 列表的内置函数
以下内置函数,不仅适⽤于列表,⽽是适⽤于:
所有的数据容器。
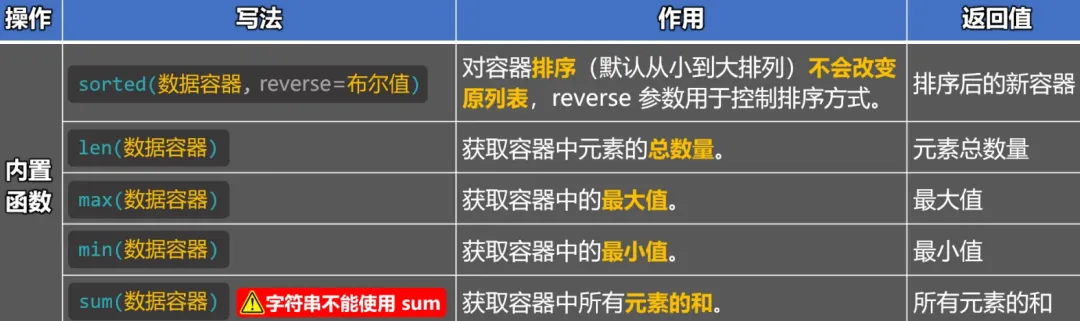
# 1.使用内置的sorted函数,返回一个排序后的新容器(不改变原容器,默认顺序,从小到大)
# 1.1 若列容器中的元素都是数字,则按照数字的大小顺序进行排序。
nums1 = [23, 11, 32, 30, 17]
result = sorted(nums1, reverse=True)
print(result) # [32, 30, 23, 17, 11]
# 1.2 若列容器中的元素,既有数字,又有字符串,那就会报错。
# nums2 = [23, 11, 32, 30, 17, 'Python']
# sorted(nums2)
# 1.3 若列容器中的元素,都是字符串,则按照字符串的Unicode编码大小进行排序。
msg_list = ['北京', 'Python', '你好']
result = sorted(msg_list)
print(msg_list) # ['北京', 'Python', '你好']
print(result) # ['Python', '你好', '北京']
# 2.使用内置的len函数,获取容器中元素的总数量,返回值是:元素总数量。
nums2 = [10, 20, 10, 30, 10, 40, [50, 60, 70]]
result = len(nums2)
print(result) # 7
# 3.使用内置的 max 函数,获取容器中的最大值,返回值是:最大值。
# 3.1 如果容器中的元素:都是数字,那 max 返回的是最大的数。
nums3 = [23, 11, 32, 30, 17]
result = max(nums3)
print(nums3) # [23, 11, 32, 30, 17]
print(result) # 32
# 3.2 如果容器中的元素:既有数字又有字符串,那 max 会报错。
# nums4 = [23, 11, 32, 30, 17, 'Python']
# max(nums4)
# 3.3 如果容器中的元素:都是字符串,那 max 会返回:Unicode 编码最大的字符。
msg_list = ['北京', 'Python', '你好']
result = max(msg_list)
print(msg_list) # ['北京', 'Python', '你好']
print(result) # 北京
# 3.4 max 函数也可以接收多个值,并筛选出最大值
result = max(33, 45, 12, 78, 99)
print(result) # 99
# 4.使用内置的 min 函数,获取容器中的最小值,返回值是:最小值。
# 备注:min 函数的使用方式与注意点与 max 函数一样,只不过 min 函数返回的是最小值
nums4 = [23, 11, 32, 30, 17]
result = min(nums4)
print(result) # 11
# 5.使用内置的 sum 函数,对容器中的数据进行求和(元素只能是数值)。
nums = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]
result = sum(nums)
print(result) # 150
1.6 列表的循环
# 定义一个成绩列表
score_list = [62, 50, 60, 48, 80, 20, 95]
# 使用while循环遍历列表
index = 0
while index < len(score_list):
print(score_list[index])
index += 1
# 使用for循环遍历列表
for item in score_list:
print(item)
# 使用for循环遍历列表(通过range函数 和 len函数按照索引遍历)
for index in range(len(score_list)):
print(score_list[index])
# 使用for循环遍历列表(通过enumerate函数,同时获取下标(索引值)和元素)
# enumerate 的 start 参数,可以让计数从指定值开始(改变的是循环时的“编号”,不是真正的索引值)
for index, item in enumerate(score_list, start=5):
print(index, item, score_list[0])
print('最后的打印', score_list[0])
1.7 列表综合小案例
print('请输入学生成绩,输入“结束”停止录入')
score_list = []
# 持续循环,让用户输入学生成绩
whileTrue:
data = input('📝请输入成绩:')
if data == '结束':
break
else:
score_list.append(int(data))
# 如果score_list中有数据,则开始统计
if score_list:
# 统计平均分
avg = sum(score_list) / len(score_list)
# 合格人数
pass_count = 0
# 优秀人数
excellent_count = 0
# 遍历列表,开始统计
for item in score_list:
if item >= 60:
pass_count += 1
if item >= 90:
excellent_count += 1
# 合格率
pass_rate = pass_count / len(score_list) * 100
# 优秀率
excellent_rate = excellent_count / len(score_list) * 100
# 打印信息
print('********⬇️统计信息如下⬇️********')
print(f'🧑🎓总人数为:{len(score_list)}')
print(f'🔺最高分为:{max(score_list)}')
print(f'🔻最低分为:{min(score_list)}')
print(f'✅合格人数:{pass_count}人')
print(f'📈合格率为:{pass_rate:.1f}%')
print(f'🏆优秀人数:{excellent_count}人')
print(f'📈优秀率为:{excellent_rate:.1f}%')
print(f'📊平均分数:{avg:.1f}')
else:
print('您没有输入任何成绩!')
1.8 列表的总结
可存放不同类型的元素。
元素是有序存储的(正索引、负索引)。
列表中的元素允许重复。
元素是允许修改的(增、删、改、查、其他操作)。
⻓度不固定,可以随着操作⾃动调整⼤⼩。
⼀句话总结:列表是最常⽤的数据容器,当遇到要“存储⼀批数据”的场景时,⾸选列表。
二. 元组(tuple)
元组:⽤来存放⼀组有序的数据,但其中的内容⼀旦创建就
不可修改(不能增、删、改,只能查)。由于元组不可变,所以元组不能使⽤ append() 、 insert() 这些⽅法,它⾥⾯的元素也不能被重新赋值。
2.1 元组的定义
# 使⽤⽅括号 () 来定义⼀个列表,⽤ , 去分隔不同的元素:
(元素0, 元素1, 元素2, 元素3,......)
# 定义元组
t1 = (28, 67, 21, 67, 11)
t2 = ('北京', 'Hello', 'Python')
t3 = (100, True, '你好', None)
t4 = (100, True, '你好', None, (50, 60, 70))
print(type(t1), t1) # <class 'tuple'> (28, 67, 21, 67, 11)
print(type(t2), t2) # <class 'tuple'> ('北京', 'Hello', 'Python')
print(type(t3), t3) # <class 'tuple'> (100, True, '你好', None)
print(type(t4), t4) # <class 'tuple'> (100, True, '你好', None, (50, 60, 70))
# 定义空元组
# t1 = ()
# t2 = tuple()
# print(type(t1), t1)
# print(type(t2), t2)
当元组中只有一个元素时,末尾必须写上
,
# 定义只有一个元素的元组
t1 = ('你好',)
t2 = (18,)
print(type(t1), t1) # <class 'tuple'> ('你好',)
print(type(t2), t2) # <class 'tuple'> (18,)
实际开发中元组,不一定使我们自己定义的,比如函数的可变产生
*args就是一个元组。
# 实际开发中的元组,不一定是我们自己定义的,比如函数的可变参数*args就是一个元组
defdemo(*args):
return sum(args)
result = demo(100, 200, 300)
print(result) # 600
读取数据
元组也支持下标,所以使用
元组名[索引值]的方式来读取值。
# 元组的下标
t1 = (28, 67, 21, 67, 11)
print(t1[3]) # 67
print(t1[-1]) # 11
元组不可修改
元组中的元素,不可修改,但元组中如果存放了可变类型(如:列表),那可变类型中的内容仍可修改。
# 元组中的元素,不可修改
t1 = (28, 67, 21, 67, 11)
t1[0] = 100
# 元组中的元素,不可修改,但元组中如果存放了可变类型(列表),那可变类型中的内容仍可修改
t2 = (28, 67, 21, 67, 11, [100, 200, 300, ('你好', 'Python')])
t2[5] = 400
t2[5][2] = 400
t2[5][3][0] = 'hello'
print(t2)
元组的常用方法
由于元组不可修改,所以它的常用方法只有两个:
使用 元组.index(元素),获取指定元素在元组中第一次出现的下标。使用 元组.count(元组),统计指定元素在元组中出现的次数。
# index 方法:获取指定元素在元组中第一次出现的下标。
t1 = (28, 67, 21, 67, 11)
result = t1.index(67)
print(result) # 1
# count 方法:统计指定元素在元组中出现的次数。
t1 = (28, 67, 21, 67, 11)
result = t1.count(67)
print(result) # 2
元组的常用内置函数
元组的常用内置函数和列表一样,依然是这几个:
max,min,len,sorted,sum。
# 常用内置函数
# max 函数,返回元组中的最大值
t1 = (23, 11, 32, 30, 17)
result = max(t1)
print(result) # 32
# min 函数,返回元组中的最小值
t1 = (23, 11, 32, 30, 17)
result = min(t1)
print(result) # 11
# len 函数,返回元组中元素的个数(元组长度)
t1 = (23, 11, 32, 30, 17)
result = len(t1)
print(result) # 5
# sorted 函数,对元组进行排序(不修改原元组,返回一个新的列表)
t1 = (23, 11, 32, 30, 17)
result = sorted(t1, reverse=True)
print(tuple(result)) # (32, 30, 23, 17, 11)
# sum 函数,统计元组中所有元素的和(元素必须是纯数字)
t1 = (23, 11, 32, 30, 17)
result = sum(t1)
print(result) # 113
2.2 元组的循环遍历
元组的遍历和列表一样,可以使用
while循环遍历,或者for循环遍历。
# 元组的循环遍历
t1 = (23, 11, 32, 30, 17)
# while循环遍历
index = 0
while index < len(t1):
print(t1[index])
index += 1
# for循环遍历
for item in t1:
print(item)
2.3 解包列表或元组传参
解包列表,解包元组传参,就是把其中的元素依次取出,作为多个毒理的参数传入函数。
# 定义函数时,使用*args(变量不一定非要用args,比如写:*data也可以),将收到的多个参数,打包成一个元组
deftest(*args):
print(f'我是test函数,我收到的参数是:{args},参数类型是:{type(args)}')
list1 = [100, 200, 300, 400]
tuple1 = ('你好', 'Hello', 'Python')
# 函数调用时,正常传递:列表 或 元组
# test(list1)
# test(tuple1)
# 函数调用时,使用*对:列表 或 元组进行解包后,再传递参数
test(*list1) # 此种写法相当于:test(100, 200, 300, 400)
test(*tuple1) # 此种写法相当于:test('你好', 'Hello', 'Python')
# 我是test函数,我收到的参数是:(100, 200, 300, 400),参数类型是:<class 'tuple'>
# 我是test函数,我收到的参数是:('你好', 'Hello', 'Python'),参数类型是:<class 'tuple'>
2.4 元组总结
可存放不同类型的元素。
元素是有序存储的(正索引、负索引)。
元组中的元素允许重复。
元素不允许修改⽂(不能:增、删、改、只能:查)。
⻓度固定定(⼀旦创建,元素个数不能增减)。
⼀句话总结:元组是⼀种“只读”的数据容器,想保存⼀批“不会变的数据”时,⾸选元组。
元组和列表对比
注意:元组不是⽤来替代列表的,⽽是⽤来在数据不需要修改的情况下,作为列表的补充选择。
三. 字符串
字符串(str):⽤来存放⼀组有序的字符数据,但其中的内容不可修改(只能查,不能增删改), 我们之前讲解了⼀部分字符串的相关知识,如:字符串的定义⽅式、字符串的格式化输出等,这些内容就不在本⼩节重复讲解了。
字符串的特点
字符串和列表,元组一样,也支下标。
# 字符串的下标
msg = 'Hello Python'
print(msg[3]) # l
print(msg[-1]) # n
字符串不可以修改,不可嵌套。
# 字符串中的字符,不可修改
msg = 'Hello Python'
# msg[0] = 'a' # 报错
# 字符串不能嵌套
# msg = 'Hello 'world' Python'
msg = 'Hello \'world\' Python'
print(msg) # Hello 'world' Python
字符串常用方法
使用
字符串.index(字符),获取指定字符在字符串中第一次出现的下标,返回值:下标。
# 常用方法
# index方法:获取指定字符,在字符串中第一次出现的下标
msg = 'Hello world Python'
result = msg.index('l')
print(result) # 2
使用
字符串.split(字符),将字符串按照指定字符进行分隔,返回值:列表。
# split方法:将字符串按照指定字符串进行分隔,并将分隔后的内容存入一个列表.
msg = 'Hello $world$ Python'
result = msg.split('$')
print(result) # ['Hello ', 'world', ' Python']
使用
字符串.replace(字符串片段),将字符串中的某个字符串片段,替换成目标字符串,不会修改原字符串,返回新字符串。
# replace方法:将字符串中的某个字符串片段,替换成目标字符串(不修改原字符串,返回新字符串)
msg = 'Hello world Python'
result = msg.replace("Python", "Java")
print(result) # Hello world Java
print(msg) # Hello world Python
使⽤
字符串.count(字符),统计指定字符在字符串中出现的次数,返回值:下标。
# count 方法:统计指定字符,在字符串中出现的次数
msg = 'Hello world Python'
result = msg.count('l')
print(result) # 3
使⽤
字符串.strip(),从某个字符串中删除指定字符串中的任意字符,不会修改原字符串,返回值:新字符串。
# strip 方法:从某个字符串中删除:指定字符串中的任意字符
# 规则:从字符串两端开始删除,直到遇到第一个不在字符串中的字符就停下
msg = '666Py6th6on666'
result = msg.strip('6')
print(msg) # 666Py6th6on666
print(result) # Py6th6on
msg = '1234P12yth34on4321'
result = msg.strip('1324')
print(msg) # 1234P12yth34on4321
print(result) # P12yth34on
msg = '34215P12yth34on4132'
result = msg.strip('5432')
print(msg) # 34215P12yth34on4132
print(result) # 15P12yth34on41
msg = ' Python '
result = msg.strip()
print(msg) # Python
print(result) # Python
字符串重用内置函数
字符串也可以使⽤:
max、min、len、sorted、sum函数,但实际开发中len函数最常⽤。
# 常用内置函数
# len 函数:统计字符串中字符的个数(字符串长度)
msg = 'Hello Python'
result = len(msg)
print(result) # 12
遍历字符串
字符串的遍历,与列表⼀样,可以使⽤ while 循环遍历,或 for 循环遍历。
# 字符串的循环遍历
msg = 'Hello Python'
# while循环遍历
index = 0
while index < len(msg):
print(msg[index])
index += 1
# for循环遍历
for item in msg:
print(item)
四. 序列
什么是序列?
能连续存放元素的数据容器,而且元素有 先后顺序,而且可以通过下标访问,所以我们学过的:列表,元组,字符串,都是序列。什么是切片?
从序列中按照指定范围,取出一部分元素,形成一个新的序列的操作。
基本语法:
语法格式为: 序列[起始索引:结束索引:步长]注意点如下:
切片操作的区间是 左闭右开,即:截取时包含起始位置,但不包含结束位置。步长是指取出元素的间隔,例如:
步长为1,就是一个一个的去处。 步长为2,就是每次越过1个元素取出。 步长为3,就是每次越过2个元素取出。 步长为n,就是每次越过n-1个元素取出。 起始索引 默认值为0,结束索引默认截取到末尾,步长默认值为1。当起始索引大于结束索引时,步长必须为 负数,否则结果是空列表。
序列的切片操作
# 对列表的切片
list1 = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, 100]
list2 = list1[0:5:1]
print(list2) # [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]
list3 = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, 100]
list4 = list3[1:8:2]
print(list4) # [20, 40, 60, 80]
list5 = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, 100]
list6 = list5[1:8:3]
print(list6) # [20, 50, 80]
list7 = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, 100]
list8 = list7[:999:]
print(list8) # [10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, 100]
list9 = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, 100]
list10 = list9[3::]
print(list10) # [40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, 100]
list11 = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, 100]
list12 = list11[:5:]
print(list12) # [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]
list13 = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, 100]
list14 = list13[::4]
print(list14) # [10, 50, 90]
list15 = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, 100]
list16 = list15[7:2:-1]
print(list16) # [80, 70, 60, 50, 40]
# 一个特殊情况,当同时省略起始索引和结束索引时,如果步长为负数,那Python会自动对调:起始位置和结束位置(相当于列表反转)
list17 = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, 100]
list18 = list17[::-1]
print(list18) # [100, 90, 80, 70, 60, 50, 40, 30, 20, 10]
# 对元组进行切片
tuple1 = (10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, 100)
tuple2 = tuple1[0:5:1]
print(tuple2) # (10, 20, 30, 40, 50)
# 对字符串进行切片
msg1 = 'Hello Python'
msg2 = msg1[2:9:2]
print(msg2) # loPt
切片的其他操作
序列相加:把两个序列拼接在一起。
注意:只有同类型的序列才能相加(字符串+字符串,列表+列表,元组+元组)
# 序列相加
list1 = [10, 20, 30, 40]
list2 = [50, 60, 70, 80]
list3 = list1 + list2
print(list3) # [10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80]
tuple1 = (10, 20, 30, 40)
tuple2 = (50, 60, 70, 80)
tuple3 = tuple1 + tuple2
print(tuple3) # (10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80)
str1 = 'Hello'
str2 = 'Python'
str3 = str1 + str2
print(str3) # HelloPython
# 错误示例
# list4 = [10, 20, 30, 40]
# str5 = 'Hello'
# print(list4 + str5) # 不同的类型不能相加
序列相乘(重复):把序列重复指定的次数。
# 序列相乘(重复)
list6 = [10, 20, 30, 40]
list7 = list6 * 3
print(list7) # [10, 20, 30, 40, 10, 20, 30, 40, 10, 20, 30, 40]
tuple3 = (10, 20, 30, 40)
tuple4 = tuple3 * 3
print(tuple4) # (10, 20, 30, 40, 10, 20, 30, 40, 10, 20, 30, 40)
str7 = 'hello'
str8 = str7 * 6
print(str8) # hellohellohellohellohellohello
五. 集合
5.1 集合的概述
概述:
集合是一种:
无序,元素唯一的容器类型。
备注:无序是指从集合中取出元素的顺序,与定义集合时存入的顺序不一定一致。集合分为两种,分别是:
==可变集合(set):==内部的元素无序(不保证顺序),不能通过下标访问元素,会自动去除重复元素。 ==不可变集合(forzenset):==特点和可变集合一样,唯一的区别就是:其中的元素不可修改。
5.2 定义集合
可变集合的定义方式:使用花括号
{}包裹,不同的数据项之间,用,做分隔。
# 定义有内容的【可变集合
s1 = {10, 20, 20, 30, 40, 40, 50, 60, 60, 70, 80, 90, 100}
s2 = {'你好', 'hello', '你好', 'Python', '北京'}
s3 = {10, '你好', True, 1, 12.4}
print(type(s1), s1) # <class 'set'> {100, 70, 40, 10, 80, 50, 20, 90, 60, 30}
print(type(s2), s2) # <class 'set'> {'北京', 'hello', '你好', 'Python'}
print(type(s3), s3) # <class 'set'> {True, 10, 12.4, '你好'}
# 定义空集合(可变集合)
s4 = set()
print(type(s4), s4) # <class 'set'> set()
# 直接写{},定义的是空字典
s5 = {}
print(type(s5), s5) # <class 'dict'> {}
注意:不能直接写{}来定义空集合,因为直接写{}定义的是:空字典。
不可变集合的定义方式:借助内置的
forzenset函数。
# 定义有内容【不可变集合】
s6 = {10, 20, 20, 30, 40, 40, 50, 60, 60, 70, 80, 90, 100}
s7 = {'你好', 'hello', '你好', 'Python', '北京'}
s8 = {10, '你好', True, 1, 12.4}
print(type(s6), s6) # <class 'set'> {100, 70, 40, 10, 80, 50, 20, 90, 60, 30}
print(type(s7), s7) # <class 'set'> {'北京', 'Python', '你好', 'hello'}
print(type(s8), s8) # <class 'set'> {True, 10, 12.4, '你好'}
# frozenset接收的参数,可以是任意可迭代的对象,但最终返回的一定是【不可变集合
s9 = frozenset([10, 20, 30, 40, 50])
s10 = frozenset((10, 20, 30, 40, 50))
s11 = frozenset('hello')
print(type(s9), s9) # <class 'frozenset'> frozenset({40, 10, 50, 20, 30})
print(type(s10), s10) # <class 'frozenset'> frozenset({40, 10, 50, 20, 30})
print(type(s11), s11) # <class 'frozenset'> frozenset({'h', 'o', 'l', 'e'})
# 定义空集合(不可变集合)
s12 = frozenset()
print(type(s12), s12) # <class 'frozenset'> frozenset()
集合中不能嵌套【可变集合】,但可以嵌套【不可变集合】。只有
不可变的东西,才能安全的放进集合中。
# 集合中不能嵌套【可变集合】,但可以嵌套【不可变集合】
# 通俗理解:只有“不可变”的东西,才能安全的放进集合里
s13 = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50}
s14 = frozenset({100, 200, 300, 400, 500})
l1 = [666, 777, 888]
t1 = ('hello', 'atguigu', '北京')
# s15 = {11, 22, 33, s1} # 报错
# s15 = {11, 22, 33, s2} # 没问题
# s15 = {11, 22, 33, l1} # 报错
s15 = {11, 22, 33, t1} # 没问题
print(s15) #{('hello', 'atguigu', '北京'), 33, 11, 22}
5.3 集合的增删改查
新增:
方式一:使用
集合.add(元素),向集合中添加元素,无返回值。方式二:使用
集合.update(元素),向集合中批量添加元素(接收可迭代对象),无返回值。
# 增
# add方法,向集合中添加元素。
s1 = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50}
s1.add(60)
print(s1) # {50, 20, 40, 10, 60, 30}
# update方法,向集合中添加元素(必须传递可迭代对象,例如:列表,元组,集合等)
s2 = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50}
s2.update([60, 70])
s2.update((80, 90))
s2.update({100, 200})
s2.update(range(300, 302))
print(s2) # {70, 200, 10, 80, 20, 90, 30, 100, 40, 300, 301, 50, 60}
删除:
方式一:使用 集合.remove(元素),从集合中移除指定元(若元素不存在,会报错),无返回值。方式二:使用 集合.discard(元素),从集合中移除指定元素(若元素不存在,不会报错),无返回值。方式三:使用 集合.pop(),从集合中移除一个任意元素,返回值:移除的那个元素。方式四:使用 集合.clear(),清空集合,无返回值。
# 删
# remove方法:从集合中移除元素(移除不存在的元素,会报错)
s3 = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]
s3.remove(20)
print(s3) # [10, 30, 40, 50]
# discard方法:从集合中移除元素(移除不存在的元素,不会报错)
s4 = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50}
s4.discard(80)
print(s4) # {50, 20, 40, 10, 30}
# pop方法:从集合中移除一个任意元素,返回值是移除的那个元素
s5 = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50}
result = s5.pop()
print(s5) # {50, 20, 40, 10, 30}
print(result) # 50
# clear方法:清空集合
s6 = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50}
s6.clear()
print(s6) # set()
修改:
注意:集合没有下标,也不支持replace方法,所以集合没有专门用于修改的方法,但可以使用:remove + add的组合,来达到修改的效果。
# 改
# 使用 add + remove 的组合,来实现修改的效果
s7 = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50}
s7.remove(20)
s7.add(66)
print(s7) # {50, 66, 40, 10, 30}
查询:
注意:由于集合没有下标,也不⽀持切⽚操作,所以集合不具备按位置访问的能⼒。虽然不能通过下标读取元素,但可以使⽤【成员运算符】来判断:某个元素是否在集合中,成员运算符我们会放在后⾯讲,不过⼤家可以提前感受⼀下:
# 查:集合不能通过下标去读取元素,但能通过 【成员运算符】去查看集合中是否包含指定元素
# 由于成员运算符适用于所有数据容器,所以我们会等所有数据容器都讲完以后,再说成员运算符
s8 = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50}
# s1[0] # 此行报错,因为集合不能通过下标访问元素
# 先提前感受一下成员运算符
result = 20notin s8
print(result) # False
5.4 集合的常用方法
使用
集合A.difference(集合B),找出集合A中,不同于集合B的元素。
# 集合A.difference(集合B)
# 作用:找出集合A中,不同与集合B的元素(集合A与集合B都不变,返回一个新的集合)
s1 = {10, 20, 30, 40 ,50}
s2 = {30, 40, 50, 60, 70}
result = s1.difference(s2)
print(s1) # {50, 20, 40, 10, 30}
print(s2) # {50, 20, 40, 10, 30}
print(result) # {10, 20}
使⽤
集合A.difference_update(集合B),从集合A中,删除集合B中存在的元素。
# 集合A.difference_update(集合B):
# 作用:从集合A中,删除集合B中存在的元素(集合A会被修改,集合B不会)
s3 = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50}
s4 = {30, 40, 50, 60, 70}
s3.difference_update(s4)
print(s3) # {20, 10}
print(s4) # {50, 70, 40, 60, 30}
使⽤
集合A.union(集合B),合并两个集合,集合A 和 集合B 都不变,返回的是⼀个新的集合。
# 集合A.union(集合B):
# 作用:合并两个集合,集合A 和 集合B 都不变,返回的是一个新的集合
s5 = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50}
s6 = {30, 40, 50, 60, 70}
result = s6.union(s5)
print(s5) # {50, 20, 40, 10, 30}
print(s6) # {50, 70, 40, 60, 30}
print(result) # {70, 40, 10, 50, 20, 60, 30}
使⽤
集合A.issubset(集合B),判断集合A是否为集合B的⼦集,返回值为布尔值。
# 集合A.issubset(集合B):
# 作用:判断集合A是否为集合B的子集
# 如果 集合A的所有元素都在集合B中,那就返回True,否则返回False
s7 = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50}
s8 = {30, 40, 50, 60, 70}
s9 = {30, 40, 50}
result = s9.issubset(s7)
print(result) # True
使⽤
集合A.issuperset(集合B),判断集合A是否是集合B的超集,返回值为布尔值。
# 集合A.issuperset(集合B):
# 作用:判断集合A是否是集合B的超集
# 如果集合A中,包含了集合B中的所有元素,那就返回True,否则返回False
s10 = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50}
s11 = {30, 40, 50, 60, 70}
s13 = {30, 40, 50}
result = s10.issuperset(s13)
print(result) # True
使⽤
集合A.isdisjoint(集合B),判断集合A和集合B是否没有交集,返回值为布尔值。
# 集合A.isdisjoint(集合B):
# 作用:判断集合A和集合B是否没有交集
# 如果没有交集,返回True;只要有一个公共元素,就返回False
s14 = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50}
s15 = {30, 40, 50, 60, 70}
s16 = {80, 90}
result = s14.isdisjoint(s15)
print(result) # False
5.5 集合的数字运算
s1 = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60}
s2 = {40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90}
# 并集
result1 = s1 | s2
print(result1) # {70, 40, 10, 80, 50, 20, 90, 60, 30}
# 交集
result2 = s1 & s2
print(result2) # {40, 50, 60}
# 差集
result3 = s1 - s2
print(result3) # {10, 20, 30}
# 对称差集
result4 = s1 ^ s2
print(result4) # {70, 10, 80, 20, 90, 30}
5.6 集合的循环遍历
由于集合不支持下标,所有集合不能使用
while循环遍历。
s1 = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60}
# 集合不能使用while循环遍历(以下是错误示例)
# index = 0
# while index < len(s1):
# print(s1[index])
# index += 1
# 集合可以使用for循环遍历
for item in s1:
print(item)
5.7 集合特点总计
无序:集合中的元素没有固定顺序,无法通过下标访问。 不重复:集合会自动去重,同一个元素只会保留一份。 分为两种:可变集合(set)和不可变集合(forzenset)。 集合中的元素必须是不可变类型(如:数字,字符串,元组)。 集合支持:并集,交集,差集,对称差集等数字操作。
总结:集合时可以去重的数字容器,当只关心元素是否存在,而不在乎顺序的时候,首选集合。
六. 字典
6.1 字典概述
字典:用来存放一组
键值对数据,可通过键key对值value进行增删改查操作。字典就像一个带标签的收纳盒,你贴上标签
键,然后放进东西值。
6.2 定义字典
用大括号
{}包裹,每个元素之间用逗号,分隔,每个元素的格式为:key:value。
# 定义有内容的字典
d1 = {'张三丰': 99, '李大发': 98, '王重阳': 85}
print(type(d1), d1) # <class 'dict'> {'张三丰': 99, '李大发': 98, '王重阳': 85}
字典中的
key不能重复,若出现重复,则后写的会覆盖之前写的。
# 字典中的key不能重复,若出现重复,则后写的会覆盖之前写的
d2 = {'张三丰': 99, '李大发': 98, '王重阳': 85, '张三丰': 100}
print(d2) # {'张三丰': 100, '李大发': 98, '王重阳': 85}
定义空字典
# 定义空字典
d3 = {}
d4= dict()
print(type(d3), d3) # <class 'dict'> {}
print(type(d4), d4) # <class 'dict'> {}
字典中的key必须是不可变类型,但
value可以是任意类型。
# 字典中的key必须是不可变类型,但value可以是任意类型
# 通俗理解:只有不可变的东西,才能作为key
d5 = {250: 72, '李四': 60, '王五': 85}
d6 = {('抽烟', '喝酒'): 72, '李四': 60, '王五': 85}
print(d1) # {'张三丰': 99, '李大发': 98, '王重阳': 85}
print(d2) # {'张三丰': 100, '李大发': 98, '王重阳': 85}
# 错误示例:将列表作为key,是不行的
# d2 = {['抽烟', '喝酒']: 72, '李四': 60, '王五': 85}
字典是可以嵌套使用的
# 字典可以嵌套
student_dict = {
2025001: {
'姓名': '张三',
'年龄': 18,
'成绩': 72,
'爱好': ['抽烟', '喝酒', '烫头']
},
2025002: {
'姓名': '李四',
'年龄': 19,
'成绩': 60,
'爱好': ['唱歌', '跳舞', '打台球']
},
2025003: {
'姓名': '王五',
'年龄': 20,
'成绩': 85,
'爱好': ['学习', '看书', '打太极']
}
}
print(student_dict)
6.3 字典的增删改查
新增:
新增的语法: 字典[key] = 值。
# 新增
d1 = {'张三': 72, '李四': 60, '王五': 85}
d1['赵六'] = 100
print(d1) # {'张三': 72, '李四': 60, '王五': 85, '赵六': 100}
删除:
# 删除
d1 = {'张三': 72, '李四': 60, '王五': 85}
# 删除指定key所对应的那组键值对,并返回这个key所对应的值。
del d1['张三']
print(d1) # {'李四': 60, '王五': 85}
# 删除指定key所对应的那组键值对,并返回这个key所对应的值。
result = d1.pop('张三')
print(d1) # {'李四': 60, '王五': 85}
print(result) # 72
# pop方法可以设置默认值
# 默认值可以保证:当要删除的key不存在的情况下,程序不会报错,并且返回这个默认值
result = d1.pop('奥特曼', '删除失败!')
print(d1) # {'张三': 72, '李四': 60, '王五': 85}
print(result) # 删除失败!
# 清空字典
d1.clear()
print(d1) # {}
修改:
# 修改
d1 = {'张三': 72, '李四': 60, '王五': 85}
# 修改的写法,与新增的写法一样,若字典中有对应的key,就是修改;若没有,就是新增
d1['张三'] = 97
print(d1) # {'张三': 97, '李四': 60, '王五': 85}
# 批量修改
d1.update({'李四': 40, '王五': 67})
print(d1) # {'张三': 97, '李四': 40, '王五': 67}
查询:
# 查询
d1 = {'张三': 72, '李四': 60, '王五': 85}
# 直接取值,若键(key)不存在,会报错
result = d1['张三']
# 安全取值,若键(key)不存在,会返回默认值(若没有设置默认值,则会返回None)
result = d1.get('奥特曼', '抱歉,key不存在!')
print(result) # 抱歉,key不存在!
6.4 字典的常用方法
使用
keys方法,获取字典中所有的键。
# keys方法,用于获取字典中所有的键。
d1 = {'张三': 72, '李四': 60, '王五': 85}
# keys方法的返回值不是list,而是一种叫dict_keys的类型。
result = d1.keys()
print(result) # dict_keys(['张三', '李四', '王五'])
print(type(result)) # <class 'dict_keys'>
# dict_keys和列表类似,可以被遍历,但是注意的是:它不能通过下标访问元素。
# for item in d1:
# print(item)
# print(type(result[0]))
# 借助内置的list函数,可以将dict_keys转换成list
l1 = list(result)
print(l1) # ['张三', '李四', '王五']
print(type(l1)) # <class 'list'>
使用
values方法,获取字典中所有的值。
# values方法:获取字典中所有的值
d1 = {'张三': 72, '李四': 60, '王五': 85}
# values方法的返回值类型是:dict_values,它的特点和dict_keys一样
result = d1.values()
print(result) # dict_values([72, 60, 85])
print(type(result)) # <class 'dict_values'>
使用
items方法,获取字典中所有的键值对(每组键值对一元组的形式呈现)
# items方法:获取字典中所有的键值对(每组键值对以元组的形式呈现)
d1 = {'张三': 72, '李四': 60, '王五': 85}
result = d1.items()
print(result) # dict_items([('张三', 72), ('李四', 60), ('王五', 85)])
print(type(result)) # <class 'dict_items'>
6.5 字典的循环遍历
字典不能使用
while循环遍历,但是可以使用for循环遍历。
# 字典不能使用while循环遍历,但可以使用for循环遍历
d1 = {'张三': 72, '李四': 60, '王五': 85}
for key in d1:
print(f'{key}的成绩是{d1[key]}')
for key in d1.keys():
print(f'{key}的成绩是{d1[key]}')
6.6 字典总结
键值对结构:字典中的数据以
key:value的形式存在,每个键都对应⼀个值。键唯⼀:字典中的键(key)不能重复,若重复则后写的会覆盖前写的。
键不可变::键必须是不可变类型(如数字、字符串、元组等),⽽值可以是任意类型。
不⽀持下标:字典中的元素不能通过下标取值。
⽀持增删改查,⽀持for循环遍历。
⼀句话总结:字典是⼀种以“键”找“值”的映射型容器,当需要 唯⼀标识 → 对应信息 的结构时,⾸选字典。
七. 数据容器通用操作
我们之前在讲解【列表常用函数】时,给大家总结过如下函数,这些函数通用也适用于其他数据容器。
sorted(数据容器, reverse=布尔值) | |||
len(数据容器) | |||
max(数据容器) | |||
min(数据容器) | |||
sum(数据容器) |
除了上述这些内置函数以外,数据容器都可以进⾏如下通⽤操作
list 函数: 1.定义空列表;2.将【可迭代对象】转换为列表。
tuple 函数:1.定义空元组;2.将【可迭代对象】转换为元组。
set 函数: 1.定义空集合;2.将【可迭代对象】转换为集合。
str 函数: 1.定义空字符串;2.将【任意类型】转换为字符串。
dict 函数: 1.定义空字典;2.将【可迭代对象】转换为字典。所有的数据容器,都⽀持【成员运算符】
in / not in作⽤:判断某个元素是否在于容器中。
# 以下这五个函数:既能定义对应的【空容器】,又能将【其他类型】转换为对应的数据类型
# 1.list函数:
# (1).定义空列表。(2).将【可迭代对象】转换为列表
res1 = list(range(8))
res2 = list('Hello Python')
res3 = list({10, 20, 30, 40, 50})
res4 = list({'张三': 75, '李四': 60, '王五':85}.items())
print(type(res1), res1) # <class 'list'> [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
print(type(res2), res2) # <class 'list'> ['H', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o', ' ', 'P', 'y', 't', 'h', 'o', 'n']
print(type(res3), res3) # <class 'list'> [50, 20, 40, 10, 30]
print(type(res4), res4) # <class 'list'> [('张三', 75), ('李四', 60), ('王五', 85)]
# 2.tuple 函数:1.定义空元组。2.将【可迭代对象】转换为元组
res1 = tuple(range(8))
res2 = tuple('Hello Python')
res3 = tuple({10, 20, 30, 40, 50})
res4 = tuple({'张三': 75, '李四': 60, '王五':85})
print(type(res1), res1) # <class 'tuple'> (0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7)
print(type(res2), res2) # <class 'tuple'> ('H', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o', ' ', 'P', 'y', 't', 'h', 'o', 'n')
print(type(res3), res3) # <class 'tuple'> (50, 20, 40, 10, 30)
print(type(res4), res4) # <class 'tuple'> ('张三', '李四', '王五')
# 3.set 函数:1.定义空集合。2.将【可迭代对象】转换为集合
res1 = set(range(8))
res2 = set('Hello Python')
res3 = set({10, 20, 30, 40, 50})
res4 = set({'张三': 75, '李四': 60, '王五':85})
print(type(res1), res1) # <class 'set'> {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7}
print(type(res2), res2) # <class 'set'> {'H', 't', 'e', 'o', 'y', 'n', 'P', 'h', 'l', ' '}
print(type(res3), res3) # <class 'set'> {50, 20, 40, 10, 30}
print(type(res4), res4) # <class 'set'> {'李四', '王五', '张三'}
# 4.str 函数:1.定义空字符串。2.将【任意类型】转换为字符串
res1 = str(range(8))
res2 = str('Hello Python')
res3 = str({10, 20, 30, 40, 50})
res4 = str({'张三': 75, '李四': 60, '王五':85})
res5 = str(False)
res6 = str(None)
res7 = str(100)
print(type(res1), res1) # <class 'str'> range(0, 8)
print(type(res2), res2) # <class 'str'> Hello Python
print(type(res3), res3) # <class 'str'> {50, 20, 40, 10, 30}
print(type(res4), res4) # <class 'str'> {'张三': 75, '李四': 60, '王五': 85}
print(type(res5), res5) # <class 'str'> False
print(type(res6), res6) # <class 'str'> None
print(type(res6), res6) # <class 'str'> None
print(type(res7), res7) # <class 'str'> 100
# 5.dict 函数:1.定义空字典。2.将【可迭代对象】转换为字典
# 备注:交给dict函数的内容必须是键值对才可以,否则就会报错
res1 = dict({'张三': 75, '李四': 60, '王五':85})
res2 = dict([('张三', 75), ('李四', 60), ('王五', 85)])
res3 = dict((('张三', 75), ('李四', 60), ('王五', 85)))
res4 = dict({('张三', 75), ('李四', 60), ('王五', 85)})
print(type(res1), res1) # <class 'dict'> {'张三': 75, '李四': 60, '王五': 85}
print(type(res2), res2) # <class 'dict'> {'张三': 75, '李四': 60, '王五': 85}
print(type(res3), res3) # <class 'dict'> {'张三': 75, '李四': 60, '王五': 85}
print(type(res4), res4) # <class 'dict'> {'张三': 75, '李四': 60, '王五': 85}
# 所有的数据容器,都支持【成员运算符】: in / not in 作用:判断某个“元素”是否在于容器中。
hobby = ['抽烟', '喝酒', '烫头']
nums = (10, 20, 30, 40, 50)
message = 'hello,atgiugu'
citys = {'北京', '天津', '上海', '重庆'}
score = {'张三': 75, '李四': 60, '王五':85}
print('喝酒'notin hobby) # False
print(20notin nums) # False
print('hel'notin message) # False
print('上海'notin citys) # False
print('李华'notin score) # True
##八. 数据容器练习
# 练习一:水果清单
fruits = {
'苹果': 4.5,
'香蕉': 3.2,
'橙子': 5.8,
'草莓': 12.0,
'哈密瓜': 8.8
}
# 需求1:打印所有的水果
for key in fruits:
print(f'{key}:{fruits[key]} 元/斤')
# 需求2:找到最贵水果
key = max(fruits, key=fruits.get)
print(f'最贵的水果是{key},价格是{fruits[key]} 元/斤')
# --------------------------------------------------------------------
# 练习二:学生成绩表
students = [
{
'name': '张三',
'scores': {'语文': 88, '数学': 92, '英语': 95}
},
{
'name': '李四',
'scores': {'语文': 75, '数学': 83, '英语': 80}
},
{
'name': '王五',
'scores': {'语文': 92, '数学': 95, '英语': 88}
}
]
# 需求1:计算每位学生的平均分
for stu in students:
# 获取当前学生的成绩列表
score_list = stu['scores'].values()
# 计算平均值
avg = sum(score_list) / len(score_list)
print(f'{stu["name"]}的平均成绩是:{avg:.1f}')
# 需求2:找到总分最高的学生
deffind_best():
# 记录分数最高的学生
best_students = []
# 记录最高分
best_score = 0
# 循环遍历
for stu in students:
# 获取当前学生的总成绩
total = sum(stu['scores'].values())
# 当前学生的成绩,如果大于best_score,就会更新数据
if total > best_score:
best_students = [stu['name']]
best_score = total
# 当前学生的成绩与最高分相同,就加入列表
elif total == best_score:
best_students.append(stu['name'])
print(f'最高分为{best_score},取得最高分的学生有:{best_students}')
find_best()
# --------------------------------------------------------------------
# 练习三:评论内容
comment = '这家奶茶真好喝,环境也不错,就是价格有点贵,好喝好喝好喝!强烈推荐!'
# 需求1:统计“好喝”出现次数
print(comment.count('好喝'))
# 需求2:将字符串中的“贵”替换为“略高”
comment2 = comment.replace('贵', '略高')
print(comment2)
# 需求3:是否包含“推荐”两个字
print('推荐'in comment)
九.数据容器总结
有序与⽆序:
有序:
列表(list)、元组(tuple)、字符串(str)—— 元素有顺序,可通过下标访问元素。⽆序:
集合(set)、字典(dict)—— 元素没有固定位置,不能⽤下标访问。可修改:
可变:
列表(list)、集合(set)、字典(dict)—— 可以对内容进⾏增、删、改操作。不可变:
元组(tuple) 、字符串(str)—— 内容固定,创建后⽆法修改。可重复:
允许重复:
列表(list) 、元组(tuple) 、字符串(str)。不允许重复:
集合(set) 、字典(dict)。备注:字典的 key 是唯⼀的,但 value 可重复