Python gc模块详细介绍
- 2026-02-10 21:26:27
1. 创始时间与作者
创始时间:Python的垃圾回收机制最早在 Python 1.5 版本中引入(约1998年),最初的引用计数机制更早存在于Python诞生之初(1991年)
核心开发者:
Guido van Rossum:Python创始人,设计了最初的引用计数机制
Neil Schemenauer:实现了Python的循环垃圾收集器(Python 2.0)
Martin von Löwis:改进和优化了GC系统
Antoine Pitrou:为Python 3.4重新设计了GC,引入了分代收集
Python核心团队:持续维护和优化
项目定位:Python内存管理核心组件,自动管理内存分配和回收,防止内存泄漏
2. 官方资源
Python文档地址:https://docs.python.org/3/library/gc.html
源代码位置:Python源码中的
Modules/gcmodule.c和Include/internal/pycore_gc.h相关PEP文档:
PEP 349:允许GC影响对象复活
PEP 442:安全的对象终结
PEP 523:GC性能改进
GitHub讨论区:https://github.com/python/cpython/issues?q=label%3Agc
3. 核心功能
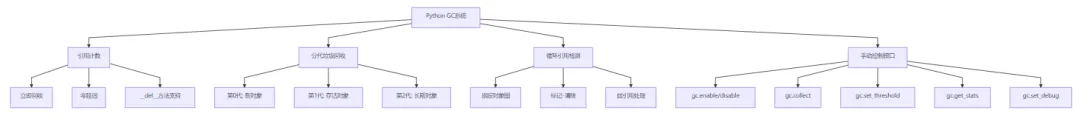
4. 应用场景
1. 内存泄漏检测
import gcimport tracemallocimport weakrefclass LeakyObject:def __init__(self, name):self.name = nameself.data = [i for i in range(10000)] # 占用内存def __del__(self):print(f"删除对象: {self.name}")def detect_memory_leak():"""检测内存泄漏"""# 启用内存跟踪tracemalloc.start()# 创建对象但保留引用objects = []for i in range(100):obj = LeakyObject(f"obj_{i}")objects.append(obj) # 保持引用# 检查GC统计print("GC统计:")print(f"第0代: {gc.get_count()[0]}")print(f"第1代: {gc.get_count()[1]}")print(f"第2代: {gc.get_count()[2]}")# 手动触发垃圾回收collected = gc.collect()print(f"回收的对象数: {collected}")# 获取内存快照snapshot = tracemalloc.take_snapshot()top_stats = snapshot.statistics('lineno')[:5]print("\n内存使用前5:")for stat in top_stats:print(stat)tracemalloc.stop()# 运行检测detect_memory_leak()
2. 循环引用处理
import gcimport sysclass Node:"""循环引用的节点类"""def __init__(self, value):self.value = valueself.parent = Noneself.children = []def add_child(self, child):self.children.append(child)child.parent = selfdef __del__(self):print(f"删除节点: {self.value}")def create_cycle():"""创建循环引用"""root = Node("根节点")child1 = Node("子节点1")child2 = Node("子节点2")root.add_child(child1)root.add_child(child2)# 创建循环引用child2.add_child(root) # 子节点引用父节点return rootdef manage_cycles():"""管理循环引用"""print("创建循环引用对象...")obj = create_cycle()# 查看引用计数print(f"根节点引用计数: {sys.getrefcount(obj)}")# 删除引用del obj# 检查垃圾回收print(f"GC阈值: {gc.get_threshold()}")print(f"GC计数: {gc.get_count()}")# 强制垃圾回收collected = gc.collect()print(f"回收的循环引用对象: {collected}")# 运行示例manage_cycles()
3. 性能敏感应用优化
import gcimport timeimport numpy as npclass HighPerformanceProcessor:"""高性能处理器,需要禁用GC"""def __init__(self):self.buffer = []self.gc_was_enabled = gc.isenabled()def process_data(self, data_size):"""处理大量数据"""# 在处理前禁用GCif self.gc_was_enabled:gc.disable()try:start_time = time.time()# 处理大量数据results = []for i in range(data_size):# 模拟数据处理data = np.random.randn(1000, 100)processed = data.mean(axis=0)results.append(processed)# 定期手动触发GCif i%1000 == 0 and i>0:gc.collect()end_time = time.time()print(f"处理 {data_size} 个数据点耗时: {end_time - start_time:.2f}秒")return resultsfinally:# 恢复GC状态if self.gc_was_enabled:gc.enable()def benchmark_gc_impact():"""基准测试GC影响"""processor = HighPerformanceProcessor()print("禁用GC处理...")results1 = processor.process_data(10000)print("\n启用GC处理...")gc.enable()start_time = time.time()results2 = []for i in range(10000):data = np.random.randn(1000, 100)results2.append(data.mean(axis=0))end_time = time.time()print(f"启用GC处理耗时: {end_time - start_time:.2f}秒")# 运行基准测试benchmark_gc_impact()
4. 弱引用管理
import gcimport weakrefclass CacheManager:"""使用弱引用的缓存管理器"""def __init__(self):self._cache = weakref.WeakValueDictionary()self._callbacks = []def add_to_cache(self, key, obj):"""添加对象到缓存(弱引用)"""self._cache[key] = obj# 添加对象被回收时的回调def cleanup(ref):print(f"对象 {key} 已被垃圾回收")self._callbacks.append(weakref.ref(obj, cleanup))def get_from_cache(self, key):"""从缓存获取对象"""return self._cache.get(key)def cache_stats(self):"""获取缓存统计"""print(f"缓存大小: {len(self._cache)}")print(f"回调数量: {len(self._callbacks)}")def demonstrate_weak_refs():"""演示弱引用"""cache = CacheManager()# 创建大对象class LargeObject:def __init__(self, id):self.id = idself.data = [i for i in range(10000)]def __del__(self):print(f"LargeObject {self.id} 被销毁")# 添加到缓存obj1 = LargeObject("obj1")cache.add_to_cache("key1", obj1)print("添加对象后:")cache.cache_stats()# 删除强引用del obj1print("\n删除强引用后:")# 强制垃圾回收gc.collect()print("\n垃圾回收后:")cache.cache_stats()# 尝试获取(应该失败)retrieved = cache.get_from_cache("key1")print(f"从缓存获取: {retrieved}")# 运行演示demonstrate_weak_refs()
5. 底层逻辑与技术原理
Python GC系统架构
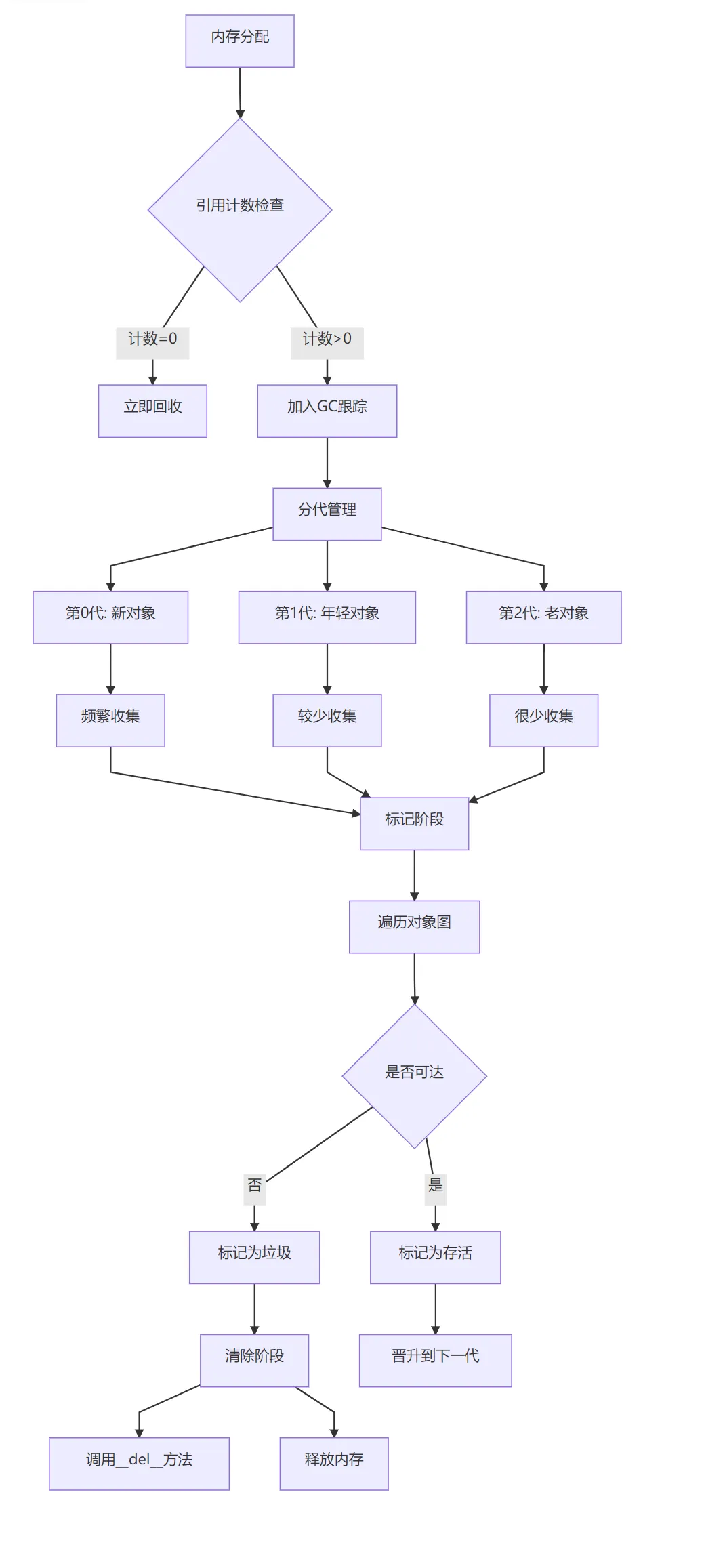
关键技术实现
引用计数机制:
// 简化版引用计数实现type def struct {PyObject_HEADlongob_refcnt; // 引用计数PyTypeObject*ob_type;} PyObject;// 增加引用#define Py_INCREF(op) ((op)->ob_refcnt++)// 减少引用#define Py_DECREF(op) \if (--(op)->ob_refcnt == 0) \_Py_Dealloc(op) // 立即回收
分代垃圾回收算法:
# Python中的分代阈值# 默认阈值 (700, 10, 10)# 第0代: 分配对象数 - 释放对象数 > 700 时触发GC# 第1代: 第0代GC执行10次后触发第1代GC# 第2代: 第1代GC执行10次后触发第2代GC# Python实现的核心逻辑def collect_generations():# 从最老的一代开始检查for generation in reversed(range(NUM_GENERATIONS)):if gc.should_collect(generation):n = gc.collect(generation)if generation<NUM_GENERATIONS-1:# 年轻一代存活的对象晋升gc.promote_young_objects(generation)break
循环引用检测算法:
标记-清除算法:
三色标记法:
# 三色标记状态WHITE = 0# 未访问GRAY = 1# 访问中BLACK = 2# 已访问def mark_from_root(root):# 将所有根对象标记为灰色gray_list = [root]while gray_list:obj = gray_list.pop()# 标记为黑色obj.color = BLACK# 遍历所有引用for ref in get_references(obj):if ref.color == WHITE:ref.color = GRAYgray_list.append(ref)
从根对象(全局变量、栈变量等)开始遍历
标记所有可达对象
清除所有未标记对象
弱引用处理:
弱引用不增加引用计数
GC时自动清理弱引用目标已被回收的弱引用
支持弱引用字典、弱引用集合等数据结构
6. 安装与配置
基础说明
gc是Python标准库的一部分,无需单独安装
# 验证gc模块python -c "import gc; print(f'GC已启用: {gc.isenabled()}')"
Python版本GC特性
| Python版本 | GC特性 | 重要改进 |
|---|---|---|
| Python 1.5 | 引入循环GC | 基本标记-清除算法 |
| Python 2.0 | 分代GC | 三色标记法 |
| Python 2.1 | 弱引用支持 | weakref模块 |
| Python 3.0 | 引用计数优化 | 消除部分引用计数 |
| Python 3.4 | 改进的分代GC | PEP 442安全终结 |
| Python 3.7 | GC性能优化 | 减少停顿时间 |
| Python 3.11 | 更快的GC | 专用GC分配器 |
环境变量配置
# 设置GC环境变量export PYTHONGC=enable # 启用GC(默认)export PYTHONGC=disable # 禁用GCexport PYTHONGC=debug # 调试模式# 设置GC阈值export PYTHONGCENABLE=700,10,10 # 第0,1,2代阈值# 设置GC调试标志export PYTHONGCDEBUG=leak # 只报告泄漏export PYTHONGCDEBUG=collect # 报告所有收集export PYTHONGCDEBUG=stats # 显示统计信息
运行时配置
import gcimport osdef configure_gc():"""运行时配置GC"""# 1. 检查当前配置print(f"GC已启用: {gc.isenabled()}")print(f"当前阈值: {gc.get_threshold()}")print(f"当前计数: {gc.get_count()}")# 2. 设置自定义阈值# 格式: (第0代阈值, 第1代阈值, 第2代阈值)gc.set_threshold(1000, 15, 15) # 更频繁的GCprint(f"新阈值: {gc.get_threshold()}")# 3. 启用调试gc.set_debug(gc.DEBUG_STATS|gc.DEBUG_COLLECTABLE)# 4. 禁用自动GC(手动控制)# gc.disable()# 5. 设置GC触发回调def gc_callback(phase, info):if phase == "start":print(f"GC开始: {info}")elif phase == "stop":print(f"GC结束: {info}")# Python 3.10+ 支持if hasattr(gc, 'callbacks'):gc.callbacks.append(gc_callback)# 应用配置configure_gc()
7. 性能优化与调优
GC性能基准测试
import gcimport timeimport psutilimport osclass GCBenchmark:"""GC性能基准测试类"""@staticmethoddef memory_usage():"""获取当前内存使用"""process = psutil.Process(os.getpid())return process.memory_info().rss/1024/1024# MB@staticmethoddef benchmark_allocation(num_objects=100000):"""测试对象分配性能"""print(f"分配 {num_objects} 个对象...")# 禁用GCgc_was_enabled = gc.isenabled()if gc_was_enabled:gc.disable()start_mem = GCBenchmark.memory_usage()start_time = time.time()# 创建大量对象objects = []for i in range(num_objects):obj = {'id': i,'data': 'x'*100, # 100字节数据'nested': [j for j in range(10)] }objects.append(obj)end_time = time.time()end_mem = GCBenchmark.memory_usage()# 恢复GC状态if gc_was_enabled:gc.enable()print(f"分配时间: {end_time - start_time:.4f}秒")print(f"内存增加: {end_mem - start_mem:.2f}MB")return objects@staticmethoddef benchmark_collection():"""测试垃圾回收性能"""print("\n测试垃圾回收性能...")# 创建一些对象objects = GCBenchmark.benchmark_allocation(50000)# 测量GC时间start_time = time.time()collected = gc.collect()end_time = time.time()print(f"GC回收对象: {collected}")print(f"GC耗时: {end_time - start_time:.4f}秒")# 获取GC统计stats = gc.get_stats()print("\nGC统计:")for gen, stat in enumerate(stats):print(f"第{gen}代: {stat}")# 运行基准测试if __name__ == "__main__":benchmark = GCBenchmark()benchmark.benchmark_collection()
最佳实践优化
import gcimport numpy as npfrom collections import defaultdictclass OptimizedMemoryManager:"""优化内存管理的实用类"""@staticmethoddef reduce_memory_fragmentation():"""减少内存碎片"""# 1. 使用对象池object_pool = defaultdict(list)def get_object(cls, *args):"""从对象池获取或创建对象"""if object_pool[cls]:obj = object_pool[cls].pop()obj.__init__(*args) # 重新初始化return objreturn cls(*args)def return_object(obj):"""返回对象到池中"""object_pool[type(obj)].append(obj)# 2. 预分配内存def preallocate_list(size):"""预分配列表减少重新分配"""return [None] *size# 3. 使用数组代替列表(对于数值数据)def use_array_for_numbers(data):"""使用数组减少内存使用"""return np.array(data, dtype=np.float32)return {'get_object': get_object,'return_object': return_object,'preallocate_list': preallocate_list,'use_array_for_numbers': use_array_for_numbers }@staticmethoddef optimize_gc_settings(application_type):"""根据应用类型优化GC设置"""presets = {'web_server': {'threshold': (1000, 10, 10), # 频繁小规模GC'auto_enable': True,'debug': 0 },'batch_processing': {'threshold': (10000, 100, 100), # 减少GC频率'auto_enable': False, # 手动控制'debug': 0 },'data_science': {'threshold': (5000, 50, 50),'auto_enable': True,'debug': gc.DEBUG_STATS },'game_development': {'threshold': (700, 10, 10), # 默认值'auto_enable': True,'debug': gc.DEBUG_SAVEALL } }preset = presets.get(application_type, presets['web_server'])# 应用设置gc.set_threshold(*preset['threshold'])if not preset['auto_enable']:gc.disable()gc.set_debug(preset['debug'])print(f"应用 {application_type} 的GC设置已配置")return preset# 使用优化器optimizer = OptimizedMemoryManager()# 配置为Web服务器optimizer.optimize_gc_settings('web_server')# 获取内存管理工具tools = optimizer.reduce_memory_fragmentation()# 使用对象池class DatabaseConnection:def __init__(self, db_name):self.db_name = db_nameself.connection = Nonedef connect(self):print(f"连接到 {self.db_name}")# 使用对象池获取对象conn = tools['get_object'](DatabaseConnection, 'my_database')conn.connect()# 使用后返回对象池tools['return_object'](conn)
8. 调试与问题排查
内存泄漏检测
import gcimport objgraphimport tracemallocimport sysclass MemoryLeakDetector:"""内存泄漏检测器"""def __init__(self):self.snapshots = []self.object_types = {}tracemalloc.start()def take_snapshot(self, label=""):"""获取内存快照"""snapshot = tracemalloc.take_snapshot()self.snapshots.append((label, snapshot))# 分析对象类型gc.collect()self.object_types[label] = objgraph.most_common_types(limit=10)print(f"\n=== 快照: {label} ===")print(f"活跃对象数: {len(gc.get_objects())}")# 显示前5个对象类型for obj_type, count in self.object_types[label][:5]:print(f" {obj_type}: {count}")def compare_snapshots(self, snapshot1, snapshot2):"""比较两个快照"""print(f"\n=== 比较 {snapshot1[0]} 和 {snapshot2[0]} ===")stats = snapshot2[1].compare_to(snapshot1[1], 'lineno')print("内存增加前5:")for stat in stats[:5]:print(f" {stat}")print("\n对象类型变化:")old_types = dict(self.object_types[snapshot1[0]][:10])new_types = dict(self.object_types[snapshot2[0]][:10])for obj_type in set(old_types) | set(new_types):old_count = old_types.get(obj_type, 0)new_count = new_types.get(obj_type, 0)if new_count>old_count:print(f" {obj_type}: +{new_count - old_count}")def detect_circular_references(self):"""检测循环引用"""print("\n=== 检测循环引用 ===")# 获取可能包含循环引用的对象garbage = gc.garbageprint(f"未回收的垃圾对象数: {len(garbage)}")if garbage:print("未回收的对象类型:")for obj in garbage[:5]: # 显示前5个print(f" {type(obj).__name__}")# 显示循环引用图objgraph.show_backrefs(garbage[:3], max_depth=5,filename='circular_refs.png' )print("循环引用图已保存到 circular_refs.png")def monitor_memory_growth(self, iterations=10):"""监控内存增长"""print(f"=== 监控内存增长 ({iterations}次迭代) ===")baseline = tracemalloc.take_snapshot()for i in range(iterations):# 创建一些对象data = [{'id': j, 'value': j*2} for j in range(1000)]# 获取快照current = tracemalloc.take_snapshot()stats = current.compare_to(baseline, 'lineno')if stats:print(f"\n迭代 {i+1}:")print(f" 总内存增长: {stats[0].size / 1024:.2f} KB")# 更新基线baseline = current# 使用内存泄漏检测器def example_leaky_function():"""有内存泄漏的函数"""cache = []def process_data():# 模拟数据处理,但会泄漏内存data = [i for i in range(10000)]processed = [x*2 for x in data]# 错误:将数据添加到缓存但从不清理cache.append(processed)return len(processed)return process_data# 运行检测detector = MemoryLeakDetector()# 初始快照detector.take_snapshot("初始状态")# 运行可能有泄漏的函数leaky_func = example_leaky_function()for _ in range(5):result = leaky_func()# 再次快照detector.take_snapshot("运行后")# 比较快照detector.compare_snapshots(detector.snapshots[0],detector.snapshots[1])# 检测循环引用detector.detect_circular_references()# 监控内存增长detector.monitor_memory_growth(3)# 清理tracemalloc.stop()
GC调试标志
import gcdef demonstrate_gc_debug_flags():"""演示GC调试标志"""debug_flags = {'DEBUG_STATS': gc.DEBUG_STATS,'DEBUG_COLLECTABLE': gc.DEBUG_COLLECTABLE,'DEBUG_UNCOLLECTABLE': gc.DEBUG_UNCOLLECTABLE,'DEBUG_SAVEALL': gc.DEBUG_SAVEALL,'DEBUG_LEAK': gc.DEBUG_LEAK,'DEBUG_INSTANCES': gc.DEBUG_INSTANCES,'DEBUG_OBJECTS': gc.DEBUG_OBJECTS, }print("GC调试标志:")print("="*50)for name, flag in debug_flags.items():print(f"{name:20} = {flag:08b} ({flag})")print("\n组合使用示例:")print("-"*50)# 常用组合combinations = {'基本调试': gc.DEBUG_STATS|gc.DEBUG_COLLECTABLE,'内存泄漏检测': gc.DEBUG_LEAK|gc.DEBUG_UNCOLLECTABLE,'完整调试': gc.DEBUG_STATS|gc.DEBUG_COLLECTABLE|gc.DEBUG_UNCOLLECTABLE|gc.DEBUG_INSTANCES, }for name, combo in combinations.items():print(f"{name:20} = {combo:08b} ({combo})")# 设置并测试gc.set_debug(combo)# 创建一些垃圾class TestObject:def __init__(self, value):self.value = value# 创建循环引用a = TestObject(1)b = TestObject(2)a.ref = bb.ref = a# 删除引用del a, b# 触发GCprint(f" GC收集: {gc.collect()}")print()# 运行演示demonstrate_gc_debug_flags()
9. 高级主题与扩展
自定义GC策略
import gcimport threadingimport timeclass AdaptiveGCManager:"""自适应GC管理器"""def __init__(self, min_threshold=100, max_threshold=10000):self.min_threshold = min_thresholdself.max_threshold = max_thresholdself.current_threshold = 1000self.memory_history = []self.gc_times = []self.adaptive_mode = True# 启动监控线程self.monitor_thread = threading.Thread(target=self._monitor_memory,daemon=True )self.monitor_thread.start()def _monitor_memory(self):"""监控内存使用并调整GC策略"""import psutilimport osprocess = psutil.Process(os.getpid())while self.adaptive_mode:# 获取内存使用memory_mb = process.memory_info().rss/1024/1024self.memory_history.append(memory_mb)# 保持最近100个记录if len(self.memory_history) >100:self.memory_history.pop(0)# 分析内存趋势if len(self.memory_history) >= 20:recent = self.memory_history[-10:]older = self.memory_history[-20:-10]recent_avg = sum(recent) /len(recent)older_avg = sum(older) /len(older)# 计算内存增长速率growth_rate = (recent_avg-older_avg) /older_avg# 根据增长速率调整GC阈值if growth_rate>0.1: # 内存快速增长# 降低阈值,更频繁GCself.current_threshold = max(self.min_threshold,int(self.current_threshold*0.8) )elif growth_rate<-0.05: # 内存减少# 提高阈值,减少GC频率self.current_threshold = min(self.max_threshold,int(self.current_threshold*1.2) )# 应用新阈值gc.set_threshold(self.current_threshold,self.current_threshold//100,self.current_threshold//1000 )time.sleep(1) # 每秒检查一次def profile_gc(self, operation, *args, **kwargs):"""分析操作的GC性能"""gc.collect() # 清理现有垃圾# 记录初始状态initial_count = gc.get_count()initial_stats = gc.get_stats()# 记录时间start_time = time.time()# 执行操作result = operation(*args, **kwargs)# 记录结束时间end_time = time.time()# 手动触发GC以测量清理时间gc_start = time.time()collected = gc.collect()gc_end = time.time()# 收集统计final_count = gc.get_count()final_stats = gc.get_stats()# 计算指标operation_time = end_time-start_timegc_time = gc_end-gc_startprint(f"\n=== GC性能分析 ===")print(f"操作时间: {operation_time:.4f}秒")print(f"GC时间: {gc_time:.4f}秒")print(f"回收对象: {collected}")print(f"GC占比: {gc_time/operation_time*100:.2f}%")print(f"当前阈值: {self.current_threshold}")# 更新GC时间历史self.gc_times.append(gc_time)if len(self.gc_times) >100:self.gc_times.pop(0)return resultdef optimize_for_workload(self, workload_type, duration_seconds=10):"""为特定工作负载优化GC"""print(f"\n为 {workload_type} 工作负载优化GC...")# 保存原始设置original_threshold = gc.get_threshold()original_debug = gc.get_debug()try:if workload_type == 'bursty':# 突发性工作负载:降低阈值gc.set_threshold(500, 10, 10)gc.set_debug(0)print("配置:频繁小规模GC")elif workload_type == 'steady':# 稳定工作负载:提高阈值gc.set_threshold(5000, 50, 50)gc.set_debug(0)print("配置:较少大规模GC")elif workload_type == 'memory_intensive':# 内存密集型:手动控制gc.disable()print("配置:禁用自动GC")elif workload_type == 'latency_sensitive':# 延迟敏感:最小化GC停顿gc.set_threshold(10000, 100, 100)gc.set_debug(gc.DEBUG_STATS)print("配置:最小化GC频率,监控统计")# 模拟工作负载self._simulate_workload(workload_type, duration_seconds)finally:# 恢复原始设置gc.set_threshold(*original_threshold)gc.set_debug(original_debug)print("恢复原始GC设置")def _simulate_workload(self, workload_type, duration):"""模拟工作负载"""import randomend_time = time.time() +durationif workload_type == 'bursty':# 突发性:短时间内创建大量对象while time.time() <end_time:# 突发for _ in range(10000):data = [random.random() for _ in range(100)]time.sleep(0.1)elif workload_type == 'steady':# 稳定性:持续创建对象while time.time() <end_time:data = [random.random() for _ in range(100)]time.sleep(0.01)print(f"模拟 {workload_type} 工作负载完成")# 使用自适应GC管理器manager = AdaptiveGCManager()# 定义一个测试操作def create_lots_of_objects(count):"""创建大量对象"""objects = []for i in range(count):obj = {'id': i,'data': 'x'*100,'nested': [j for j in range(10)] }objects.append(obj)return objects# 分析操作manager.profile_gc(create_lots_of_objects, 10000)# 为特定工作负载优化manager.optimize_for_workload('bursty', 5)# 停止自适应管理manager.adaptive_mode = False
10. 替代方案与扩展
第三方内存管理工具
| 工具 | 用途 | 特点 | 与GC的关系 |
|---|---|---|---|
| pympler | 内存分析 | 对象大小跟踪,泄漏检测 | 补充GC,提供更详细分析 |
| objgraph | 对象引用图 | 可视化对象引用关系 | 基于GC数据生成图表 |
| guppy3 | 堆分析 | 内存使用分析,对象统计 | 与GC配合使用 |
| memory_profiler | 内存分析 | 逐行内存使用分析 | 监控GC效果 |
| tracemalloc | 内存分配跟踪 | Python内置内存跟踪 | 提供GC之外的分配信息 |
替代GC策略
# 1. 手动内存管理(特定场景)import ctypesclass ManualMemoryBuffer:"""手动内存管理缓冲区"""def __init__(self, size):# 使用ctypes直接分配内存self.buffer = (ctypes.c_char*size)()self.size = sizedef __del__(self):# 手动释放内存(实际上Python会处理)print(f"释放 {self.size} 字节缓冲区")# 在实际C扩展中需要手动释放# 2. 对象池模式class ObjectPool:"""对象池减少GC压力"""def __init__(self, factory, max_size=100):self.factory = factoryself.max_size = max_sizeself.pool = []def acquire(self):"""获取对象"""if self.pool:return self.pool.pop()return self.factory()def release(self, obj):"""释放对象回池"""if len(self.pool) <self.max_size:self.pool.append(obj)# 3. 使用__slots__减少内存class OptimizedObject:"""使用__slots__优化内存"""__slots__ = ['x', 'y', 'z'] # 固定属性,减少内存使用def __init__(self, x, y, z):self.x = xself.y = yself.z = z# 比较内存使用import sysclass RegularObject:def __init__(self, x, y, z):self.x = xself.y = yself.z = z# 创建对象并比较大小regular = RegularObject(1, 2, 3)optimized = OptimizedObject(1, 2, 3)print(f"常规对象大小: {sys.getsizeof(regular)} 字节")print(f"优化对象大小: {sys.getsizeof(optimized)} 字节")
11. 企业级最佳实践
生产环境GC配置
import gcimport jsonimport loggingclass ProductionGCConfig:"""生产环境GC配置管理器"""def __init__(self, app_name):self.app_name = app_nameself.logger = self._setup_logger()self.config = self._load_config()def_setup_logger(self):"""设置GC日志"""logger = logging.getLogger(f'{self.app_name}.gc')logger.setLevel(logging.INFO)handler = logging.FileHandler(f'{self.app_name}_gc.log')formatter = logging.Formatter('%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s' )handler.setFormatter(formatter)logger.addHandler(handler)return loggerdef _load_config(self):"""加载GC配置"""default_config = {'enabled': True,'threshold': [1000, 10, 10],'debug_flags': 0,'monitoring': {'enabled': True,'interval': 60, # 秒'metrics': ['collections', 'collected', 'uncollectable'] },'optimizations': {'disable_for_batches': True,'object_pooling': True,'use_slots': True } }try:with open(f'{self.app_name}_gc_config.json', 'r') as f:config = json.load(f)return {**default_config, **config}except FileNotFoundError:return default_configdef apply_config(self):"""应用GC配置"""# 启用/禁用GCif self.config['enabled']:gc.enable()else:gc.disable()# 设置阈值thresholds = self.config['threshold']gc.set_threshold(*thresholds)# 设置调试标志gc.set_debug(self.config['debug_flags'])# 设置回调用于监控if self.config['monitoring']['enabled']:self._setup_monitoring()self.logger.info(f"GC配置已应用: {self.config}")def _setup_monitoring(self):"""设置GC监控"""import threadingdef monitor_gc():"""监控GC状态"""import timeinterval = self.config['monitoring']['interval']while True:try:# 收集GC统计stats = gc.get_stats()counts = gc.get_count()# 记录到日志self.logger.info(f"GC统计 - 计数: {counts}, "f"第0代: {stats[0]}, "f"第1代: {stats[1]}, "f"第2代: {stats[2]}" )# 检查内存泄漏if len(gc.garbage) >0:self.logger.warning(f"检测到未回收垃圾: {len(gc.garbage)} 个对象" )time.sleep(interval)except Exception as e:self.logger.error(f"GC监控错误: {e}")time.sleep(interval)# 启动监控线程monitor_thread = threading.Thread(target=monitor_gc, daemon=True)monitor_thread.start()def optimize_application(self):"""优化应用程序内存使用"""optimizations = self.config['optimizations']if optimizations['disable_for_batches']:self.logger.info("启用批处理GC优化")class GCOptimizer:"""批处理GC优化器"""def __enter__(self):self.gc_was_enabled = gc.isenabled()if self.gc_was_enabled:gc.disable()return selfdef __exit__(self, exc_type, exc_val, exc_tb):if self.gc_was_enabled:gc.enable()# 清理垃圾gc.collect()return GCOptimizer()return None# 生产环境使用示例def main():"""生产环境主函数"""# 初始化GC配置gc_config = ProductionGCConfig('my_web_app')gc_config.apply_config()# 使用GC优化器处理批处理with gc_config.optimize_application():# 执行批处理操作process_large_dataset()# 正常处理请求(GC自动管理)handle_requests()def process_large_dataset():"""处理大数据集"""# 模拟数据处理data = [i for i in range(1000000)]result = sum(data)print(f"处理结果: {result}")def handle_requests():"""处理请求"""# 模拟请求处理for i in range(100):response = {'request_id': i, 'status': 'ok'}print(f"处理请求 {i}")if __name__ == "__main__":main()
总结
Python的垃圾回收系统是一个成熟、高效的内存管理机制,核心价值在于:
自动化内存管理:开发者无需手动分配和释放内存
防止内存泄漏:自动检测和回收不可达对象
高性能:引用计数提供即时回收,分代GC优化性能
可配置性:提供丰富的API进行调优和监控
技术特色:
引用计数与分代GC的混合策略
三色标记法检测循环引用
弱引用机制避免循环引用
可配置的分代阈值和调试选项
安全警告:
__del__方法可能导致对象复活和复杂情况循环引用中的
__del__方法可能阻止对象回收永远避免在
__del__方法中创建新引用
最佳实践:
理解应用特点:根据应用类型调整GC策略
监控GC性能:使用
gc.get_stats()和gc.get_count()优化内存使用:使用
__slots__、对象池等减少GC压力避免常见陷阱:小心使用
__del__方法,管理循环引用
调优建议:
Web服务:使用较频繁的GC(阈值700-1000)
批处理:在批处理前后手动控制GC
实时系统:考虑禁用GC或使用极大阈值
内存敏感:使用对象池和内存视图
学习资源:
官方文档:https://docs.python.org/3/library/gc.html
Python源码:
Modules/gcmodule.c(深入理解实现)《Python高级编程》:内存管理和优化章节
Python内存管理PEP文档
GC作为Python核心组件,其设计和实现经过了数十年的优化。虽然大多数情况下无需手动干预,但理解其工作原理对于编写高性能、可靠的Python应用程序至关重要。正确的GC调优可以使应用程序性能提升数倍,特别是在内存敏感的应用场景中。
