重温并发任务:Linux 多线程同步利器自旋锁
- 2026-02-11 12:32:15
点击↑深色口袋物联,选择关注公众号,获取更多内容,不迷路
在glibc2.35中,pthread线程提供了5种同步机制,分别为条件变量、互斥锁、读写锁、自旋锁和屏障,本篇主要回顾自旋锁
一、pthread 自旋锁的核心作用
✅ 核心定义
在glibc2.35中,线程自旋锁的定义在sysdeps/nptl/bits/pthreadtypes.h中pthread_spinlock_t
typedef volatile int pthread_spinlock_t;即一个易变的整数,因为自旋锁只有两种状态,0(解锁)和 1(加锁),它不需要像互斥锁那样记录“所有者线程 ID”、“递归计数”或“优先级继承”等复杂信息,一个整数位(或字节)就足够表示状态了,而volatile告诉编译器:“不要对这个变量进行优化,每次读取都必须从内存中直接读取,每次写入都必须立即写入内存。”
自旋锁的实现完全依赖原子操作指令(如 ARM 的 LDREX/STREX),它完全运行在用户态,不涉及系统调用,不进入内核。
✅ 核心作用
自旋锁的核心作用:在「锁持有时间极短」的场景下,以「CPU 忙等」的方式,避免线程阻塞 / 唤醒的内核态切换开销,实现极致的加解锁性能
• 加锁逻辑:尝试获取锁→失败则循环重试(自旋)→成功则持有锁; • 核心优势:纯用户态操作,无内核态 / 用户态切换、无线程上下文切换开销; • 设计初衷:解决互斥锁在「短时间锁竞争」场景下的性能损耗(互斥锁阻塞时会触发线程上下文切换,开销约 1-10μs)。
✅ 自旋锁解决的核心痛点
互斥锁 / 读写锁的核心问题是「阻塞开销」:
• 当锁持有时间极短(<1μs,如仅执行 count++),线程阻塞 / 唤醒的开销(μs 级)远大于锁持有时间,导致性能暴跌;• 自旋锁通过「忙等」规避切换开销,在该场景下性能比互斥锁提升 10 倍以上; • 但自旋锁的「忙等」会占用 CPU,若锁持有时间长,会导致 CPU 利用率 100%,反而拖累整体性能。
✅ 自旋锁的底层执行逻辑
1. 加锁(spin_lock) : • 原子操作尝试获取锁(如 CAS 指令); • 锁空闲→立即持有,返回; • 锁被占用→循环执行「尝试获取锁」指令(自旋),直到拿到锁; 2. 解锁(spin_unlock) : • 原子操作释放锁; • 无需唤醒线程(自旋线程仍在循环重试,会立即检测到锁释放); 3. 核心特性 : • 纯用户态实现,无内核介入; • 加解锁是「原子操作」,保证线程安全; • 自旋期间 CPU 核心 100% 占用,不释放。
二、pthread 自旋锁 核心使用场景
自旋锁的核心价值是**「无上下文切换开销」**,所有场景都围绕「极短时间锁持有 + 低竞争 + 多核 CPU」展开,仅占 Linux 同步场景的 5% 左右,但在匹配场景下性能无可替代,按使用频率排序如下:
✅ 场景 1:高频原子操作(最核心场景,占比 60%)
• 业务逻辑:多个线程对「轻量级共享变量」执行高频原子操作(如计数器、状态标志位、指针赋值),锁持有时间 < 1μs; • 同步需求:极致的加解锁性能,避免上下文切换开销; • 典型案例:服务器的 QPS 计数器、嵌入式设备的中断标志位、多线程的任务状态标记。
✅ 场景 2:多核 CPU 下的低竞争共享资源保护(高频场景)
• 业务逻辑:多核 CPU 环境下,共享资源的锁竞争率极低(<10%),且操作耗时极短; • 同步需求:以最小开销保证线程安全; • 典型案例:多核服务器的内存池小块内存分配、嵌入式多核芯片的寄存器读写、高并发系统的轻量级缓存标记。
✅ 场景 3:实时系统 / 内核态代码(进阶场景)
• 业务逻辑:实时系统(如工业控制、自动驾驶)的关键任务,要求加解锁延迟 < 1μs;或内核态代码(如驱动)的同步; • 核心优势:自旋锁无内核态切换,延迟可预测,满足实时性要求; • 注意:用户态 pthread 自旋锁仅适配软实时,硬实时需用内核自旋锁。
✅ 场景 4:非阻塞加锁的轮询操作(生产级场景)
• 业务逻辑:线程需要轮询检查共享资源状态,不希望阻塞等待; • 实现方式:用 pthread_spin_trylock非阻塞加锁,失败则立即重试,避免线程阻塞;• 典型案例:实时监控系统的状态轮询、嵌入式设备的硬件寄存器轮询读取。
✅ 场景 5:互斥锁的性能优化兜底(进阶优化场景)
• 业务逻辑:原有互斥锁代码性能瓶颈明显,且锁持有时间极短、竞争率低; • 优化方案:将互斥锁替换为自旋锁,降低加解锁开销; • 核心原则:先验证锁持有时间和竞争率,再替换,避免反向优化。
三、pthread 自旋锁 核心接口
自旋锁的接口全部在 <pthread.h> 头文件中,编译时必须加 -lpthread 链接线程库,接口数量极少、逻辑简单,所有接口返回值:成功返回 0,失败返回错误码(非 errno,需手动处理)。
✅ 1. 自旋锁的初始化(唯一动态方式)
int pthread_spin_init(pthread_spinlock_t *lock, int pshared);锁的共享范围(核心参数):
PTHREAD_PROCESS_PRIVATE(0):仅当前进程内的线程共享(99% 场景用此值);PTHREAD_PROCESS_SHARED(1):跨进程共享(如多进程共享内存场景);
注意:自旋锁无静态初始化方式,必须调用
pthread_spin_init初始化!
✅ 2. 自旋锁的销毁
int pthread_spin_destroy(pthread_spinlock_t *lock);• 作用:释放自旋锁占用的资源(主要是内存); • 强制规则:① 必须与 pthread_spin_init成对调用;② 锁被持有期间不能销毁(返回 EBUSY 错误)。
✅ 3. 加锁(2 种方式,核心接口)
接口①:阻塞自旋加锁(最常用)
int pthread_spin_lock(pthread_spinlock_t *lock);• 逻辑:尝试获取锁→失败则循环自旋(CPU 100%)→直到拿到锁; • 适用:绝大多数自旋锁场景,简单直接。
接口②:非阻塞自旋加锁(进阶)
int pthread_spin_trylock(pthread_spinlock_t *lock);• 逻辑:尝试获取锁→成功返回 0;失败返回 EBUSY,不自旋; • 适用:不想线程长时间忙等的场景(如实时系统、超时控制)。
✅ 4. 解锁(唯一接口)
int pthread_spin_unlock(pthread_spinlock_t *lock);• 逻辑:原子操作释放锁,自旋的线程会立即检测到并获取锁; • 强制规则:只有持有锁的线程才能解锁,未持有锁的线程解锁会返回 EPERM 错误,甚至触发程序崩溃。
四、pthread 自旋锁 核心对比
✅ 对比 1:自旋锁 vs 互斥锁(最核心对比)
二者是「互补关系」,核心差异在「阻塞方式」和「性能开销」:
✅ 核心结论:短持有 + 低竞争 + 多核→自旋锁;其他场景→互斥锁。
✅ 对比 2:自旋锁 vs 读写锁(pthread_rwlock_t)
✅ 选型原则:仅原子操作→自旋锁;多读少写→读写锁。
✅ 对比 3:用户态自旋锁 vs 内核态自旋锁
✅ 核心结论:用户态用 pthread 自旋锁,内核态用内核自旋锁。
五、pthread 自旋锁 3 个可运行实战示例
代码才是硬道理,下面是3个示例
✅ 示例一:基础入门版 — 高频计数器(必掌握,核心模板)
实现多核 CPU 下的高频计数器累加,对比「自旋锁」和「互斥锁」的性能差异:
1. 10 个线程对全局计数器累加 100 万次; 2. 自旋锁仅保护 count++原子操作,锁持有时间 < 1μs;3. 输出执行耗时,直观体现自旋锁的性能优势。
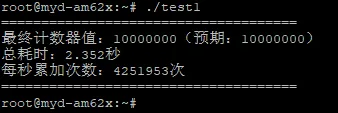
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <pthread.h>#include <unistd.h>#include <time.h>#define THREAD_NUM 10 // 线程数#define ADD_NUM 1000000 // 每个线程累加次数// 全局共享计数器long long g_count = 0;// 自旋锁pthread_spinlock_t spinlock;// 线程函数:自旋锁保护计数器累加void* add_count(void* arg){ (void)arg; // 屏蔽未使用参数警告 for(int i=0; i<ADD_NUM; i++) { // 加锁:仅保护count++ pthread_spin_lock(&spinlock); g_count++; // 原子操作,耗时<1μs // 解锁:必须成对 pthread_spin_unlock(&spinlock); } return NULL;}int main(){ pthread_t tid[THREAD_NUM]; struct timespec start, end; double cost_time; // 检查CPU核心数(仅多核运行) int cpu_num = sysconf(_SC_NPROCESSORS_ONLN); if (cpu_num <= 1) { printf("警告:当前CPU核心数为%d,自旋锁性能差,建议改用互斥锁!\n", cpu_num); } // 初始化自旋锁(进程内私有) pthread_spin_init(&spinlock, PTHREAD_PROCESS_PRIVATE); // 记录开始时间 clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, &start); // 创建10个线程 for(int i=0; i<THREAD_NUM; i++) { pthread_create(&tid[i], NULL, add_count, NULL); } // 等待所有线程完成 for(int i=0; i<THREAD_NUM; i++) { pthread_join(tid[i], NULL); } // 记录结束时间 clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, &end); // 销毁自旋锁 pthread_spin_destroy(&spinlock); // 计算耗时(秒) cost_time = (end.tv_sec - start.tv_sec) + (end.tv_nsec - start.tv_nsec) / 1e9; printf("=====================================\n"); printf("最终计数器值:%lld(预期:%d)\n", g_count, THREAD_NUM*ADD_NUM); printf("总耗时:%.3f秒\n", cost_time); printf("每秒累加次数:%.0f次\n", (double)(THREAD_NUM*ADD_NUM)/cost_time); printf("=====================================\n"); return 0;}运行结果(4 核 CPU)
✅ 示例二:进阶版 — 非阻塞自旋锁 + 轮询操作(防死自旋核心模板)
实现非阻塞自旋锁的轮询操作,避免线程永久自旋:
1. 线程 1 用 pthread_spin_lock持有锁,模拟短时间操作;2. 线程 2 用 pthread_spin_trylock非阻塞加锁,失败则轮询重试,超过最大次数则退出;3. 严格遵守「短持有、低竞争」规则,无 CPU 满载风险。
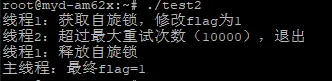
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <pthread.h>#include <unistd.h>#include <errno.h>#define MAX_RETRY 10000 // 最大轮询次数// 共享状态标志int g_flag = 0;// 自旋锁pthread_spinlock_t spinlock;// 线程1:持有锁修改标志void* thread1(void* arg){ (void)arg; // 加锁 pthread_spin_lock(&spinlock); printf("线程1:获取自旋锁,修改flag为1\n"); g_flag = 1; // 模拟短时间持有锁(1ms) usleep(1000); // 解锁 pthread_spin_unlock(&spinlock); printf("线程1:释放自旋锁\n"); return NULL;}// 线程2:非阻塞轮询加锁void* thread2(void* arg){ (void)arg; int retry = 0; while(retry < MAX_RETRY) { // 非阻塞加锁 int ret = pthread_spin_trylock(&spinlock); if(ret == 0) { // 加锁成功 printf("线程2:第%d次尝试,获取自旋锁,flag=%d\n", retry+1, g_flag); g_flag = 2; printf("线程2:修改flag为2,释放自旋锁\n"); pthread_spin_unlock(&spinlock); break; } else if(ret == EBUSY) { // 锁被占用,继续轮询 retry++; // 轮询间隔(可选,降低CPU占用) // usleep(1); } else { printf("线程2:加锁失败,错误码=%d\n", ret); break; } } if(retry >= MAX_RETRY) { printf("线程2:超过最大重试次数(%d),退出\n", MAX_RETRY); } return NULL;}int main(){ pthread_t tid1, tid2; // 初始化自旋锁 pthread_spin_init(&spinlock, PTHREAD_PROCESS_PRIVATE); // 创建线程1(先持有锁) pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, thread1, NULL); usleep(100); // 确保线程1先执行 // 创建线程2(轮询加锁) pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, thread2, NULL); // 等待线程完成 pthread_join(tid1, NULL); pthread_join(tid2, NULL); // 销毁自旋锁 pthread_spin_destroy(&spinlock); printf("主线程:最终flag=%d\n", g_flag); return 0;}运行结果
✅ 示例三:生产级版 — 自旋锁 vs 互斥锁性能对比(选型核心模板)
实现自旋锁和互斥锁的性能对比测试,帮助快速选型:
1. 分别用自旋锁和互斥锁保护同一计数器; 2. 输出两种锁的执行耗时和每秒操作数; 3. 验证「短持有、低竞争」场景下自旋锁的性能优势。
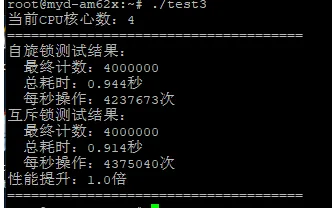
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <pthread.h>#include <unistd.h>#include <time.h>#define THREAD_NUM 8 // 线程数#define ADD_NUM 500000 // 每个线程累加次数// 共享计数器long long g_spin_count = 0;long long g_mutex_count = 0;// 自旋锁&互斥锁pthread_spinlock_t spinlock;pthread_mutex_t mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;// 自旋锁累加函数void* spin_add(void* arg){ (void)arg; for(int i=0; i<ADD_NUM; i++) { pthread_spin_lock(&spinlock); g_spin_count++; pthread_spin_unlock(&spinlock); } return NULL;}// 互斥锁累加函数void* mutex_add(void* arg){ (void)arg; for(int i=0; i<ADD_NUM; i++) { pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); g_mutex_count++; pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); } return NULL;}// 耗时计算函数double calc_cost(struct timespec start, struct timespec end){ return (end.tv_sec - start.tv_sec) + (end.tv_nsec - start.tv_nsec) / 1e9;}int main(){ pthread_t tid[THREAD_NUM]; struct timespec start, end; double spin_cost, mutex_cost; // 检查CPU核心数 int cpu_num = sysconf(_SC_NPROCESSORS_ONLN); printf("当前CPU核心数:%d\n", cpu_num); // ========== 测试自旋锁性能 ========== pthread_spin_init(&spinlock, PTHREAD_PROCESS_PRIVATE); clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, &start); for(int i=0; i<THREAD_NUM; i++) { pthread_create(&tid[i], NULL, spin_add, NULL); } for(int i=0; i<THREAD_NUM; i++) { pthread_join(tid[i], NULL); } clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, &end); spin_cost = calc_cost(start, end); pthread_spin_destroy(&spinlock); // ========== 测试互斥锁性能 ========== clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, &start); for(int i=0; i<THREAD_NUM; i++) { pthread_create(&tid[i], NULL, mutex_add, NULL); } for(int i=0; i<THREAD_NUM; i++) { pthread_join(tid[i], NULL); } clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, &end); mutex_cost = calc_cost(start, end); pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex); // ========== 输出结果 ========== printf("=====================================\n"); printf("自旋锁测试结果:\n"); printf(" 最终计数:%lld\n", g_spin_count); printf(" 总耗时:%.3f秒\n", spin_cost); printf(" 每秒操作:%.0f次\n", (double)(THREAD_NUM*ADD_NUM)/spin_cost); printf("互斥锁测试结果:\n"); printf(" 最终计数:%lld\n", g_mutex_count); printf(" 总耗时:%.3f秒\n", mutex_cost); printf(" 每秒操作:%.0f次\n", (double)(THREAD_NUM*ADD_NUM)/mutex_cost); printf("性能提升:%.1f倍\n", mutex_cost/spin_cost); printf("=====================================\n"); return 0;}运行结果(4 核 CPU)
六、pthread 自旋锁 的优缺点(客观全面,选型参考)
✅ 优点(核心优势,无可替代)
1. 极致的加解锁性能:纯用户态操作,无内核态 / 用户态切换、无线程上下文切换开销,短持有场景下性能是互斥锁的 10-100 倍; 2. 延迟可预测:自旋锁的加解锁延迟是纳秒级,满足实时系统的低延迟要求; 3. 实现简单:接口极少,逻辑清晰,核心是原子操作 + 循环重试,易于理解和使用; 4. 无内核资源占用:自旋锁不依赖内核调度器,无需创建等待队列,资源开销极小; 5. 多核 CPU 友好:多核环境下,自旋线程和持有锁线程可在不同核心执行,锁释放时可立即获取。
✅ 缺点(局限性,客观认知)
1. CPU 利用率极高:自旋期间 CPU 100% 占用,锁持有时间过长会导致系统卡顿、其他线程饥饿; 2. 仅适配多核 CPU:单核 CPU 下自旋锁性能远低于互斥锁,甚至导致死自旋; 3. 死锁风险高:嵌套使用、递归加锁会导致永久自旋,且无法被内核干预; 4. 不适合高竞争场景:大量线程自旋会浪费 CPU 资源,整体吞吐量暴跌; 5. 不支持超时加锁:pthread 自旋锁无 timedlock接口,无法设置自旋超时,易导致永久忙等;6. 持有锁时不能阻塞:持有自旋锁时调用阻塞接口,会导致其他线程永久自旋。
全文核心总结
1. 自旋锁的核心是「忙等无切换」,仅适配「短持有(<1μs)+ 低竞争 + 多核 CPU」场景; 2. 防坑黄金法则:不嵌套、不长持、单核不用、高竞争不用、不调用阻塞接口; 3. 核心接口:初始化(spin_init)→加锁(spin_lock/trylock)→解锁(spin_unlock)→销毁(spin_destroy),无静态初始化; 4. 最核心场景是高频原子操作,其次是多核低竞争共享资源、实时系统轮询; 5. 优点是性能极致、延迟可预测,缺点是 CPU 占用高、死锁风险大,整体瑕不掩瑜; 6. 选型原则:先看锁持有时间,再看竞争率和 CPU 核心数,短 + 低 + 多核→自旋锁,否则→互斥锁。
