
大家好,我是煜道。
今天我们一起来学习 正则表达式与JSON。
引言
正则表达式(Regular Expression)是一种强大的文本模式匹配工具,用于检索、替换或验证符合特定模式的字符串。JSON(JavaScript Object Notation)是一种轻量级的数据交换格式,因其简洁性和跨语言兼容性,已成为Web API数据传输的事实标准。
本文将系统介绍Python正则表达式的语法和使用方法,包括元字符、字符集、量词、边界匹配、分组以及常见操作函数。同时,本文也将详细讲解JSON数据格式的特点、Python中的JSON序列化和反序列化操作,以及它们在实际开发中的应用。
01 正则表达式基础
1.1 正则表达式简介
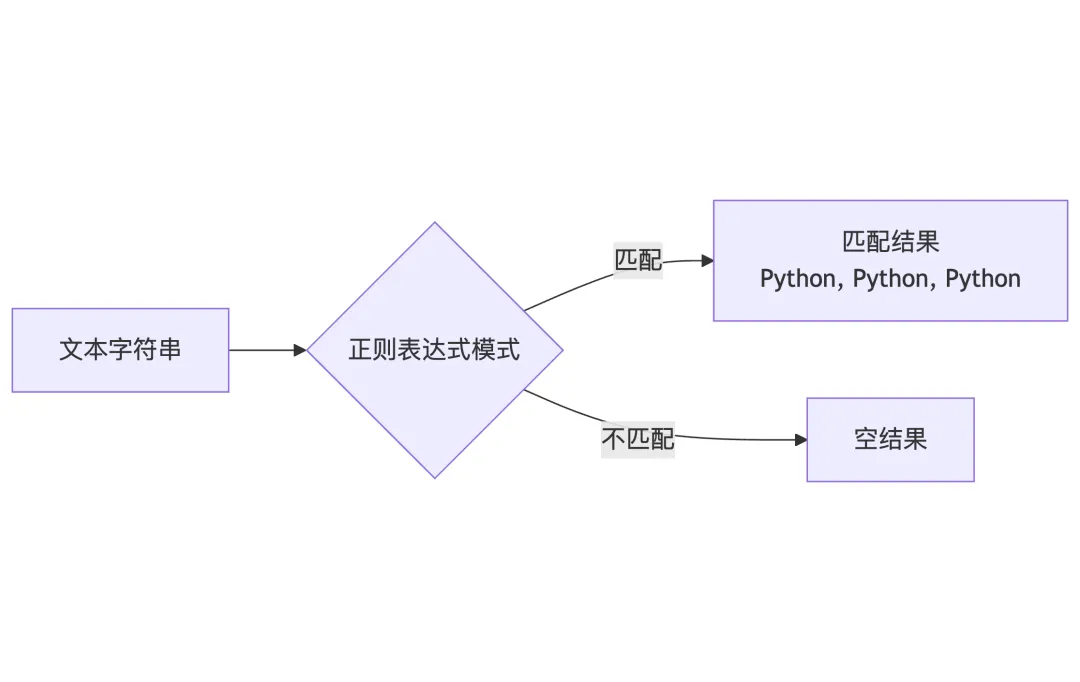
正则表达式是一个特殊的字符序列,用于描述字符串的匹配模式:
import retext = "Python is powerful. Python is popular. Python is fun."# 简单匹配pattern = "Python"result = re.findall(pattern, text)print(result) # ['Python', 'Python', 'Python']
1.2 元字符
元字符是正则表达式中具有特殊意义的字符:
import re# . 匹配任意字符print(re.findall("P.thon", "Python, Pithon, Pethon")) # ['Python', 'Pithon', 'Pethon']# ^ 匹配开头print(re.findall("^Python", "Python is great")) # ['Python']print(re.findall("^Python", "I love Python")) # []# $ 匹配结尾print(re.findall("Python$", "I love Python")) # ['Python']print(re.findall("Python$", "Python is great")) # []# * + ?print(re.findall("Py*hon", "Pyhon Pyyhon Pyyyhon")) # ['Pyhon', 'Pyyhon', 'Pyyyon']print(re.findall("Py+hon", "Pyhon Pyyhon")) # ['Pyhon', 'Pyyhon']print(re.findall("Py?hon", "Pyhon Pyyhon")) # ['Pyhon']
1.3 字符集
使用方括号[]定义字符集:
import re# [abc] 匹配任意一个a、b或cprint(re.findall("[abc]", "Pythona")) # ['a']# [^abc] 匹配非a、b、c的字符print(re.findall("[^abc]", "Python")) # ['P', 'y', 't', 'h', 'o', 'n']# [a-z] 范围匹配print(re.findall("[a-z]", "Python3")) # ['y', 't', 'h', 'o', 'n']# [0-9] 数字范围print(re.findall("[0-9]+", "abc123def456")) # ['123', '456']
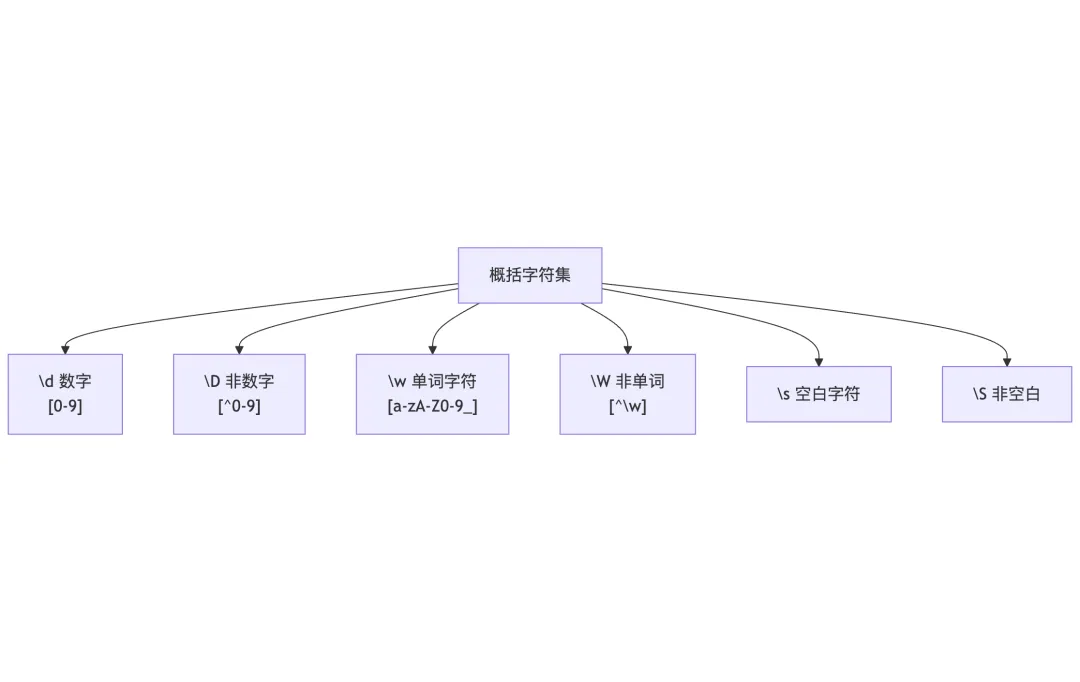
1.4 概括字符集
import retext = "Python3.12 is released on 2023-10-02.\nEmail: example@test.com"# 匹配所有数字print(re.findall(r"\d+", text)) # ['3', '12', '2023', '10', '02']# 匹配所有单词字符print(re.findall(r"\w+", text)) # ['Python3', '12', 'is', 'released', 'on', '2023', '10', '02', 'Email', 'example', 'test', 'com']# 匹配空白print(re.findall(r"\s", text)) # [' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', '\n', ' ']
1.5 数量词
数量词用于指定匹配的次数:
import re# {n} 恰好n次print(re.findall(r"\d{3}", "123 4567 89")) # ['123', '456']# {n,} 至少n次print(re.findall(r"\d{2,}", "1 12 123 1234")) # ['12', '123', '1234']# {n,m} n到m次print(re.findall(r"\d{2,4}", "1 12 123 12345 123456"))# ['12', '123', '1234', '1234', '56']
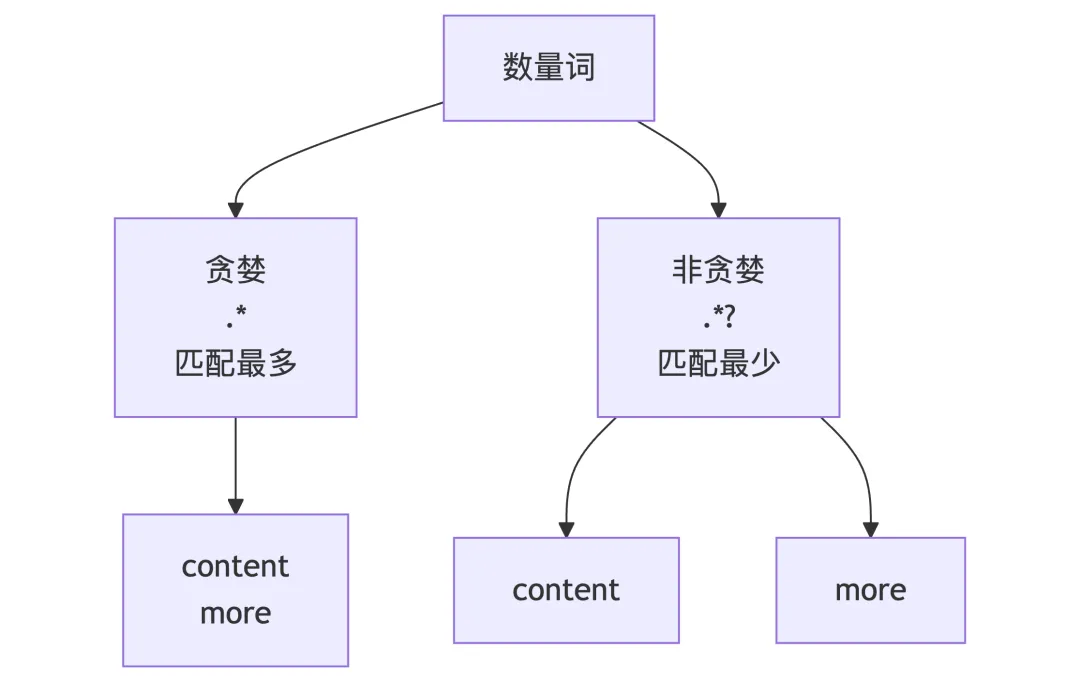
02 贪婪与非贪婪
2.1 贪婪匹配
正则表达式默认使用贪婪匹配,匹配尽可能多的字符:
import retext = "<div>content</div>"# 贪婪匹配print(re.findall(r"<div>.*</div>", text)) # ['<div>content</div>']
2.2 非贪婪匹配
使用?使量词变为非贪婪(最小匹配):
import retext = "<div>content</div><div>more</div>"# 贪婪匹配print(re.findall(r"<div>.*</div>", text))# ['<div>content</div><div>more</div>']# 非贪婪匹配print(re.findall(r"<div>.*?</div>", text))# ['<div>content</div>', '<div>more</div>']
03 边界匹配
3.1 单词边界
import retext = "The cat in the hat sat on the mat."# \b 单词边界print(re.findall(r"\b\w{3}\b", text))# ['The', 'cat', 'the', 'hat', 'sat', 'the', 'mat']# \B 非单词边界print(re.findall(r"\B\w{3}\B", text))# []
3.2 行边界
import retext = """Line 1Line 2Line 3"""# ^ 每行开头lines = re.findall(r"^Line \d+", text, re.MULTILINE)print(lines) # ['Line 1', 'Line 2', 'Line 3']# $ 每行结尾ends = re.findall(r"Line \d+$", text, re.MULTILINE)print(ends) # ['Line 1', 'Line 2', 'Line 3']
04 分组与捕获
4.1 分组
使用圆括号()创建分组:
import retext = "The price is $100, and the discount is $25."# 基本分组print(re.findall(r"\$\d+", text)) # ['$100', '$25']# 捕获分组matches = re.findall(r"(\$)(\d+)", text)print(matches) # [('$', '100'), ('$', '25')]# 命名分组pattern = r"(?P<currency>\$)(?P<amount>\d+)"matches = re.findall(pattern, text)print(matches) # [('$', '100'), ('$', '25')]
4.2 后向引用
import retext = "hello hello world world"# 引用前面的分组print(re.sub(r"(\w+) \1", r"\1", text)) # 'hello world'
05 re模块常用函数
5.1 match
从字符串开头匹配:
import repattern = r"\d+"text = "123abc456"match = re.match(pattern, text)print(match.group()) if match else print("No match") # '123'# match从开头开始no_match = re.match(r"[a-z]+", text)print(no_match) if no_match else print("No match") # No match
5.2 search
搜索整个字符串,找到第一个匹配:
import repattern = r"\d+"text = "abc123def456"match = re.search(pattern, text)print(match.group()) if match else print("No match") # '123'
5.3 findall
返回所有匹配的列表:
import repattern = r"\d+"text = "abc123def456ghi789"matches = re.findall(pattern, text)print(matches) # ['123', '456', '789']
5.4 finditer
返回所有匹配的迭代器:
import repattern = r"\d+"text = "abc123def456"for match in re.finditer(pattern, text): print(f"Match: {match.group()}, Position: {match.span()}")# Match: 123, Position: (3, 6)# Match: 456, Position: (9, 12)
5.5 sub/subn
替换匹配:
import retext = "The price is $100, and $200."# 替换print(re.sub(r"\$\d+", "XXX", text)) # 'The price is XXX, and XXX.'# 替换并统计次数result, count = re.subn(r"\$\d+", "XXX", text)print(result, count) # 'The price is XXX, and XXX.' 2# 使用函数替换defreplace_price(match): price_str = match.group() amount_str = price_str[1:] amount = int(amount_str)returnf"${amount * 2}"print(re.sub(r"\$\d+", replace_price, text))# 'The price is $200, and $400.'
5.6 split
使用正则表达式分割:
import retext = "apple, banana; orange. grape"# 多种分隔符parts = re.split(r"[,;.\s]+", text)print(parts) # ['apple', 'banana', 'orange', 'grape']
06 匹配模式
import retext = "Hello\nWorld"# re.I - 忽略大小写print(re.findall(r"hello", "Hello HELLO hello", re.I)) # ['Hello', 'HELLO', 'hello']# re.S - .匹配包括换行符print(re.findall(r".+", "Line1\nLine2", re.S))# ['Line1\nLine2']# re.M - ^和$匹配每行print(re.findall(r"^\w+", "Line1\nLine2", re.M))# ['Line1', 'Line2']# 组合使用text = """PythonjavascriptJAVA"""matches = re.findall(r"python", text, re.I | re.M)print(matches) # ['Python']
07 JSON数据格式
7.1 JSON简介
JSON(JavaScript Object Notation)是一种轻量级的数据交换格式:
{"name": "Python","version": 3.12,"is_popular": true,"features": ["easy", "powerful", "versatile"],"author": {"first_name": "Guido","last_name": "van Rossum" }}
JSON数据类型与Python对应:
7.2 JSON序列化( dumps )
import json# 基本类型data = {"name": "Python","version": 3.12,"is_popular": True,"creator": None}# 序列化json_str = json.dumps(data, indent=2, ensure_ascii=False)print(json_str)
7.3 JSON反序列化( loads )
import jsonjson_str = '{"name": "Python", "version": 3.12}'# 反序列化data = json.loads(json_str)print(data) # {'name': 'Python', 'version': 3.12}print(data["version"]) # 3.12
7.4 JSON与文件
import json# 写入JSON文件data = {"name": "Python", "version": 3.12}with open("config.json", "w", encoding="utf-8") as f: json.dump(data, f, indent=2, ensure_ascii=False)# 读取JSON文件with open("config.json", "r", encoding="utf-8") as f: data = json.load(f) print(data)
7.5 JSON序列化进阶
import jsonfrom datetime import datetime, date# 自定义日期序列化classDateEncoder(json.JSONEncoder):defdefault(self, obj):if isinstance(obj, (datetime, date)):return obj.isoformat()return super().default(obj)data = {"name": "event","date": datetime.now()}print(json.dumps(data, cls=DateEncoder))# {"name": "event", "date": "2024-01-15T10:30:00.000000"}# 自定义反序列化defdate_decoder(dct):if"date"in dct and isinstance(dct["date"], str): dct["date"] = datetime.fromisoformat(dct["date"])return dctjson_str = '{"name": "event", "date": "2024-01-15T10:30:00"}'data = json.loads(json_str, object_hook=date_decoder)
08 实战示例
8.1 邮箱验证
import redefvalidate_email(email): pattern = r"^[a-zA-Z0-9._%+-]+@[a-zA-Z0-9.-]+\.[a-zA-Z]{2,}$"return re.match(pattern, email) isnotNone# 测试emails = ["test@example.com", "invalid.email", "@example.com", "test@.com"]for email in emails: print(f"{email}: {validate_email(email)}")
8.2 日志解析
import refrom datetime import datetimeLOG_PATTERN = r"^(?P<timestamp>\d{4}-\d{2}-\d{2} \d{2}:\d{2}:\d{2}) (?P<level>\w+) (?P<message>.*)$"defparse_log_line(line): match = re.match(LOG_PATTERN, line)if match:return {"timestamp": datetime.strptime(match.group("timestamp"), "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S"),"level": match.group("level"),"message": match.group("message") }returnNone
8.3 配置文件读取
import jsonimport reclassConfig:def__init__(self, file_path): self.config = self._load_config(file_path)def_load_config(self, file_path):with open(file_path, 'r') as f: content = f.read()# 移除注释 content = re.sub(r'#.*$', '', content, flags=re.MULTILINE)return json.loads(content)defget(self, key, default=None):return self.config.get(key, default)# 使用config = Config("app.json")print(config.get("database.host"))
09 小结
本文介绍了Python中的正则表达式和JSON处理:
- re模块函数:match、search、findall、sub、split。
正则表达式和JSON是Python开发中最常用的工具之一。掌握正则表达式能够高效处理文本匹配和替换任务,而JSON则是Web开发和数据交换的标准格式。
