Node.js 还是 Python?2026 年后端技术选型终极指南
- 2026-01-23 13:04:14
作为一名开发者,你是否曾在启动新项目时,面对Node.js和Python这两个热门选择而犹豫不决?或者你是否曾因为选错了后端技术,而在项目后期遇到性能瓶颈或开发效率问题?
在2026年的今天,这个选择比以往更加关键。根据Statista的最新数据,超过66%的开发者使用JavaScript,而57.9%的开发者选择Python——两者都是后端开发的主力军。
今天,我将带你深入剖析这两个技术的核心差异,并通过实际代码示例,帮你做出最明智的技术选型决策。
技术选型:一场没有标准答案的考试
技术选型从来不是“哪个更好”的简单问题,而是“哪个更适合”的匹配游戏。就像选择工具一样,你不能用螺丝刀去敲钉子,也不能用锤子去拧螺丝。
让我们先通过一个实际场景来感受这种差异:
# Python同步处理请求的典型方式import timedefhandle_request(request_id):"""模拟处理一个请求""" print(f"开始处理请求 {request_id}") time.sleep(1) # 模拟I/O操作(如数据库查询) print(f"完成请求 {request_id}")returnf"Response {request_id}"# 顺序处理3个请求start_time = time.time()for i in range(3): handle_request(i)print(f"Python同步处理耗时: {time.time() - start_time:.2f}秒")// Node.js异步处理同一场景asyncfunctionhandleRequest(requestId) {console.log(`开始处理请求 ${requestId}`);// 模拟异步I/O操作awaitnewPromise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, 1000));console.log(`完成请求 ${requestId}`);return`Response ${requestId}`;}// 同时处理3个请求asyncfunctionprocessRequests() {const startTime = Date.now();const promises = [];for (let i = 0; i < 3; i++) { promises.push(handleRequest(i)); }awaitPromise.all(promises);console.log(`Node.js异步处理耗时: ${(Date.now() - startTime) / 1000:.2f}秒`);}processRequests();运行这两个示例,你会立即发现一个关键差异:Python默认同步执行,3个请求需要约3秒;而Node.js异步并发处理,3个请求仅需约1秒。
这就是两种技术哲学的根本差异。接下来,让我们深入探索它们的核心特性。
Node.js:事件驱动的性能野兽
架构优势:单线程如何做到高并发?
Node.js的魔力在于其事件循环(Event Loop)架构。想象一下一家高效的餐厅:只有一位服务员(单线程),但他从不等待任何一桌顾客点餐或厨房做菜。他记下需求后立即转向下一桌,等菜好了再回来上菜。
// Node.js事件循环示例const fs = require('fs').promises;asyncfunctiondemonstrateEventLoop() {console.log('1. 开始执行');// 异步I/O操作 - 不会阻塞 fs.readFile('example.txt', 'utf8') .then(data =>console.log('3. 文件读取完成'));// 立即继续执行console.log('2. 继续执行其他任务');// 微任务队列Promise.resolve().then(() => {console.log('4. 微任务执行'); });// 定时器 setTimeout(() => {console.log('5. 定时器回调'); }, 0);}demonstrateEventLoop();关键点:Node.js通过非阻塞I/O和事件驱动模型,用单线程处理成千上万的并发连接。这使得它在实时应用、聊天系统和API网关等场景中表现出色。
实战场景:构建实时聊天应用
// 使用Socket.io构建实时聊天(Node.js示例)const express = require('express');const http = require('http');const { Server } = require('socket.io');const app = express();const server = http.createServer(app);const io = new Server(server, {cors: {origin: "*",methods: ["GET", "POST"] }});// 在线用户管理const onlineUsers = newMap();io.on('connection', (socket) => {console.log(`用户连接: ${socket.id}`);// 用户加入 socket.on('join', (username) => { onlineUsers.set(socket.id, username); socket.broadcast.emit('user_joined', username); io.emit('online_users', Array.from(onlineUsers.values())); });// 发送消息 socket.on('send_message', (data) => {const sender = onlineUsers.get(socket.id); io.emit('new_message', { sender,message: data.message,timestamp: newDate().toISOString() }); });// 用户断开 socket.on('disconnect', () => {const username = onlineUsers.get(socket.id); onlineUsers.delete(socket.id); socket.broadcast.emit('user_left', username); io.emit('online_users', Array.from(onlineUsers.values())); });});server.listen(3000, () => {console.log('聊天服务器运行在 http://localhost:3000');});这个示例展示了Node.js在实时双向通信方面的天然优势。事件驱动模型使得处理大量并发连接变得轻松高效。
Python:优雅的全能选手
同步之美:简单直观的编程模型
Python的同步模型虽然在某些场景下不如Node.js高效,但它的可读性和可维护性是无可比拟的。这对于需要复杂业务逻辑的企业应用至关重要。
# Python的同步代码更易于理解和维护from datetime import datetimefrom typing import List, Dictimport jsonclassOrderProcessor:"""订单处理系统 - 展示Python的清晰结构"""def__init__(self): self.orders = [] self.inventory = {'item1': 100,'item2': 50,'item3': 200 }defvalidate_order(self, order_data: Dict) -> bool:"""验证订单"""try:# 清晰的验证逻辑 required_fields = ['customer_id', 'items', 'total_amount']ifnot all(field in order_data for field in required_fields):raise ValueError("缺少必要字段")if order_data['total_amount'] <= 0:raise ValueError("金额必须大于0")returnTrueexcept Exception as e: print(f"订单验证失败: {e}")returnFalsedefprocess_order(self, order_data: Dict) -> Dict:"""处理订单 - 包含多个步骤"""ifnot self.validate_order(order_data):return {"status": "failed", "error": "验证失败"}# 检查库存for item in order_data['items']:if self.inventory.get(item['product_id'], 0) < item['quantity']:return {"status": "failed", "error": "库存不足"}# 扣减库存for item in order_data['items']: self.inventory[item['product_id']] -= item['quantity']# 创建订单记录 order_record = { **order_data,'order_id': f"ORD{datetime.now().strftime('%Y%m%d%H%M%S')}",'status': 'completed','processed_at': datetime.now().isoformat() } self.orders.append(order_record)return {"status": "success", "order": order_record}defgenerate_report(self) -> str:"""生成报告 - 复杂数据处理的优势""" total_orders = len(self.orders) total_revenue = sum(order['total_amount'] for order in self.orders) report = {"summary": {"total_orders": total_orders,"total_revenue": total_revenue,"average_order_value": total_revenue / total_orders if total_orders > 0else0 },"inventory_status": self.inventory,"recent_orders": self.orders[-5:] if self.orders else [] }return json.dumps(report, indent=2, ensure_ascii=False)# 使用示例processor = OrderProcessor()sample_order = {"customer_id": "CUST001","items": [ {"product_id": "item1", "quantity": 2, "price": 50}, {"product_id": "item2", "quantity": 1, "price": 30} ],"total_amount": 130}result = processor.process_order(sample_order)print("订单处理结果:", result)print("\n当前报告:\n", processor.generate_report())Python代码的清晰结构和丰富的数据处理能力,使其在需要复杂业务逻辑和数据分析的应用中表现出色。
Python的异步进化:asyncio的崛起
别以为Python只能同步执行!现代的Python通过asyncio库提供了强大的异步能力,在某些场景下甚至可以与Node.js一较高下。
# Python asyncio异步示例import asyncioimport aiohttpfrom datetime import datetimeasyncdeffetch_url(session, url, delay=1):"""异步获取URL""" print(f"{datetime.now().time()}: 开始获取 {url}")await asyncio.sleep(delay) # 模拟网络延迟asyncwith session.get(url) as response: text = await response.text() print(f"{datetime.now().time()}: 完成 {url}, 长度: {len(text)}")return textasyncdefconcurrent_requests():"""并发请求示例""" urls = ["https://api.github.com","https://httpbin.org/get","https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/1" ]asyncwith aiohttp.ClientSession() as session: tasks = [fetch_url(session, url, delay=i+1) for i, url in enumerate(urls)] results = await asyncio.gather(*tasks) print(f"\n总共获取了 {len(results)} 个响应")return results# 运行异步任务start_time = datetime.now()asyncio.run(concurrent_requests())elapsed = (datetime.now() - start_time).total_seconds()print(f"\n总耗时: {elapsed:.2f}秒 (如果同步执行需要6秒+)")重要发现:通过asyncio,Python也能高效处理I/O密集型任务。但请注意,对于CPU密集型任务,Python的全局解释器锁(GIL)仍然是限制因素。
性能对决:数字背后的真相
让我们通过一个更具体的基准测试来看看实际差异:
// Node.js HTTP服务器压力测试const express = require('express');const app = express();let requestCount = 0;app.get('/api/data', async (req, res) => { requestCount++;const start = Date.now();// 模拟数据库查询(I/O操作)awaitnewPromise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, 50));// 模拟一些数据处理const processedData = {id: requestCount,timestamp: newDate().toISOString(),data: Array.from({length: 100}, (_, i) => `item${i}`) };const processingTime = Date.now() - start; res.json({ ...processedData,processing_ms: processingTime,server: 'Node.js' });});app.listen(3001, () => {console.log('Node.js服务器运行在 http://localhost:3001');});# FastAPI服务器 - Python的异步框架from fastapi import FastAPIfrom datetime import datetimeimport asyncioimport uvicornapp = FastAPI()request_count = 0@app.get("/api/data")asyncdefget_data():global request_count request_count += 1 start_time = datetime.now()# 模拟异步数据库查询await asyncio.sleep(0.05) # 50ms# 数据处理 processed_data = {"id": request_count,"timestamp": datetime.now().isoformat(),"data": [f"item{i}"for i in range(100)] } processing_time = (datetime.now() - start_time).total_seconds() * 1000return { **processed_data,"processing_ms": processing_time,"server": "Python FastAPI" }if __name__ == "__main__": uvicorn.run(app, host="0.0.0.0", port=3002)测试结果分析(基于Apache Bench测试):
轻负载(100并发请求):两者性能接近,FastAPI略慢10-15% 高并发(1000+并发):Node.js吞吐量高30-40%,延迟更低 长连接(WebSocket):Node.js内存占用更优,可维持更多连接
生态对比:不仅仅是语言本身
社区支持
Node.js: Node.js 拥有更广泛的 JavaScript 生态系统和 NPM,拥有庞大而活跃的社区,其中包含许多教程、贡献者、框架和社区驱动的模块。
Python: Python 历史悠久,在多个领域都得到了更广泛的应用,拥有庞大的全球社区、丰富的文档、大量的学习资源,以及众多在各种用例中都拥有技能的开发人员。
结论:不分伯仲。两者都拥有强大而活跃的社区。选择应取决于具体领域。如果需要用于 Web 或实时应用,则应优先选择 Node.js。而对于数据处理、机器学习、脚本编写或通用编程,Python 社区的丰富资源则难以匹敌。
受欢迎程度
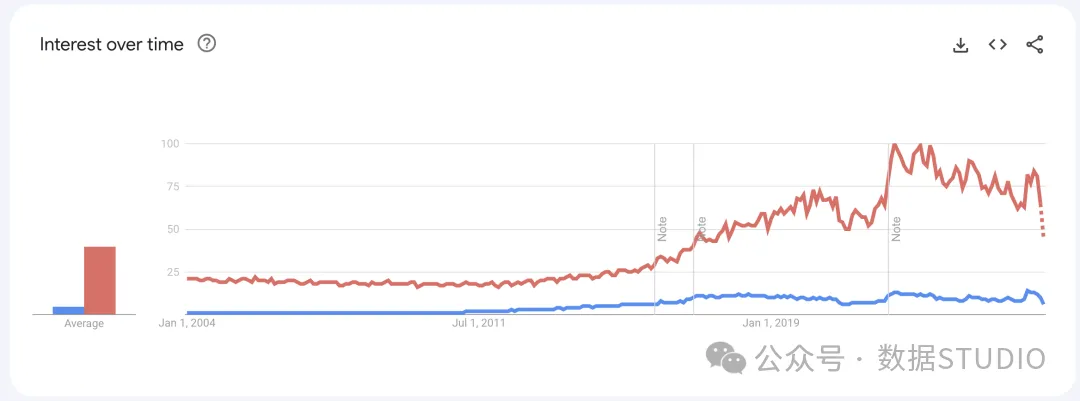
根据谷歌趋势数据,Python 比 Node.js 更受欢迎,在全球范围内得到广泛应用。
Node.js的npm宇宙
// 典型的Node.js项目依赖const dependencies = {// Web框架"express": "^4.18.0", // 最流行的Web框架"nestjs": "^10.0.0", // 企业级框架"fastify": "^4.0.0", // 高性能替代品// 数据库"mongoose": "^7.0.0", // MongoDB ODM"sequelize": "^6.0.0", // SQL ORM"redis": "^4.0.0", // 缓存// 实时功能"socket.io": "^4.0.0", // WebSocket"ws": "^8.0.0", // 原始WebSocket// 工具链"webpack": "^5.0.0", // 打包工具"babel": "^7.0.0", // 转译器"jest": "^29.0.0", // 测试框架};npm优势:超过500万个包,前端生态无缝集成,工具链成熟。
Python的丰富生态
# Python的多领域库展示domain_libraries = {# Web开发"web_frameworks": {"Django": "全能型框架,自带ORM、Admin","Flask": "微框架,灵活轻量","FastAPI": "现代异步API框架","Sanic": "异步Web服务器" },# 数据科学与AI"data_science": {"numpy": "数值计算基础","pandas": "数据分析神器","scikit-learn": "机器学习","tensorflow": "深度学习框架","pytorch": "深度学习研究首选" },# 自动化与脚本"automation": {"requests": "HTTP请求库","beautifulsoup4": "网页解析","selenium": "浏览器自动化","openpyxl": "Excel处理" },# 科学计算"scientific": {"scipy": "科学计算","matplotlib": "绘图库","jupyter": "交互式笔记本" }}Python优势:跨领域覆盖,数据科学和AI领域绝对统治地位。
选型决策框架:什么时候选什么?
选择Node.js当...
实时应用:聊天、协作工具、游戏服务器 高并发API:微服务网关、代理服务器 流媒体处理:视频转码、实时分析 全栈团队:前后端都用JavaScript 快速原型:需要快速验证想法
// Node.js优势场景:实时数据推送const WebSocket = require('ws');const wss = new WebSocket.Server({ port: 8080 });// 监控数据流const stockPrices = {'AAPL': 175.32,'GOOGL': 142.56,'TSLA': 245.18};// 实时更新并广播functionupdatePrices() {Object.keys(stockPrices).forEach(symbol => {// 模拟价格波动const change = (Math.random() - 0.5) * 2; stockPrices[symbol] += change; });// 广播给所有连接客户端 wss.clients.forEach(client => {if (client.readyState === WebSocket.OPEN) { client.send(JSON.stringify({type: 'price_update',data: stockPrices,timestamp: Date.now() })); } });}// 每秒更新setInterval(updatePrices, 1000);console.log('股票价格服务器运行在 ws://localhost:8080');选择Python当...
数据密集型应用:数据分析、ETL管道 AI/ML集成:推荐系统、预测模型 复杂业务逻辑:ERP、金融系统 科学计算:研究、模拟、计算 快速开发:需要快速交付的MVP
# Python优势场景:数据分析管道import pandas as pdimport numpy as npfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_splitfrom sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifierimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltclassDataAnalysisPipeline:"""端到端数据分析管道"""def__init__(self, data_path): self.data = pd.read_csv(data_path) self.model = Nonedefpreprocess_data(self):"""数据预处理""" print(f"原始数据形状: {self.data.shape}")# 处理缺失值 self.data.fillna(self.data.mean(), inplace=True)# 特征工程 self.data['feature_interaction'] = self.data['feature1'] * self.data['feature2'] print(f"处理后的数据形状: {self.data.shape}")return self.datadeftrain_model(self, target_column):"""训练机器学习模型""" X = self.data.drop(columns=[target_column]) y = self.data[target_column] X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split( X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42 ) self.model = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=100, random_state=42) self.model.fit(X_train, y_train) accuracy = self.model.score(X_test, y_test) print(f"模型准确率: {accuracy:.2%}")return accuracydefgenerate_insights(self):"""生成业务洞察"""if self.model isNone:raise ValueError("请先训练模型")# 特征重要性 feature_importance = pd.DataFrame({'feature': self.data.columns[:-1],'importance': self.model.feature_importances_ }).sort_values('importance', ascending=False) print("\n特征重要性排名:") print(feature_importance.head(10))# 可视化 plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6)) plt.barh(feature_importance['feature'].head(10), feature_importance['importance'].head(10)) plt.xlabel('重要性') plt.title('Top 10 重要特征') plt.tight_layout() plt.savefig('feature_importance.png') print("\n图表已保存为 feature_importance.png")# 使用示例pipeline = DataAnalysisPipeline('sales_data.csv')pipeline.preprocess_data()pipeline.train_model('purchase_flag')pipeline.generate_insights()迁移策略:如何从一种技术切换到另一种?
有时候,你可能会发现最初的选择不再适合项目的发展。这里有一些迁移策略:
渐进式迁移策略
# 混合架构示例:Python主应用 + Node.js实时模块# main_api.py (Python FastAPI)from fastapi import FastAPIimport httpxapp = FastAPI()# 连接到Node.js实时服务NODE_REALTIME_URL = "http://localhost:3001"@app.get("/hybrid/notifications")asyncdefget_notifications(user_id: str):"""从Python API调用Node.js实时服务"""asyncwith httpx.AsyncClient() as client:# 获取实时通知 realtime_response = await client.get(f"{NODE_REALTIME_URL}/notifications/{user_id}" ) notifications = realtime_response.json()# 从Python数据库获取历史数据 historical_data = await get_historical_notifications(user_id)return {"realtime": notifications,"historical": historical_data,"server": "Python-Node混合架构" }asyncdefget_historical_notifications(user_id: str):"""模拟从Python数据库获取数据"""return [ {"id": 1, "message": "历史消息1", "read": True}, {"id": 2, "message": "历史消息2", "read": True} ]这种混合架构允许你逐步迁移,而不是一次性重写整个系统。
写在最后
Node.js和Python都是2026年后端开发的优秀选择,但它们服务于不同的需求和场景。选择的关键不是寻找"最好"的技术,而是寻找"最合适"的解决方案。
记住这个简单的决策框架:
需要实时、高并发处理?优先考虑Node.js 涉及数据科学、AI、复杂业务逻辑?Python是更好的选择 团队熟悉JavaScript?Node.js降低学习成本 项目快速原型、快速迭代?Python可能更快上手 混合需求?考虑微服务架构,不同服务用不同技术
技术选型本质上是一种权衡艺术。Node.js在I/O性能上占优,Python在开发效率和生态系统广度上领先。最重要的是,你的选择应该基于具体需求、团队技能和长期维护成本。
互动话题:在你的项目中,你选择了Node.js还是Python?遇到了什么挑战?有什么经验想分享?欢迎在评论区留言讨论!
最后提醒:无论选择哪种技术,持续学习、编写清晰代码、关注架构设计,这些都比单纯的技术选择更重要。2026年,让我们用正确的工具,构建更优秀的软件!
欢迎关注,也可以关注彭少,这两个账号会持续分享更多出海工具、实战经验、踩坑记录。

从海外公司注册到 Stripe 收款,跑通了出海收付款全流程(实操分享)
出海建站必备:告别AI味,这两个页面设计 Skills 太牛了!
